UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Environment for UPSC CSE > Agriculture
Agriculture | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
What Is Agriculture?
- Agriculture is the science and art of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago.
- Silviculture is the art of cultivating forest trees.
- Sericulture is the rearing of silkworms for the production of raw silk.
- Apiculture is the maintenance of honey bee colonies, commonly in hives, by humans
- Olericulture is the science of vegetable growing, dealing with the culture of non-woody (herbaceous) plants for food.
- Viticulture is the science, production and study of grapes
- Floriculture is a discipline of horticulture concerned with the cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants for gardens
- Arboriculture is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants
- Pomology is a horticulture branch that focuses on the cultivation, production, harvest, and storage of fruit, etc.
- Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in an air or mist environment without the use of soil or an aggregate medium
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants using mineral nutrient solutions, in water, without soil.
- Terrestrial plants may also be grown with their roots in the mineral nutrient solution only or in an inert medium, such as perlite, gravel, mineral wool, expanded clay or coconut husk.
- Geoponic in farming practice, refers to growing plants in normal soil
Scope and Importance of Agriculture
- With a 17.2 percent contribution to the gross domestic product (GDP), agriculture provides livelihood support to about two-thirds of the country's population.
- The sector employs 56.7 per cent of the country's workforce and is the single largest private sector occupation.
- Agriculture accounts for about 14.7 per cent of the total export earnings and provides raw material to many industries (textiles, silk, sugar, rice, flour mills, milk products).
- The agriculture sector acts as a bulwark in maintaining food security and, in the process, national security as well.
- The allied sectors like horticulture, animal husbandry, dairy and fisheries have an important role in improving the rural masses' overall economic conditions and health and nutrition.
Problems of Indian Agriculture
- Fragmentation of land holding.
- Existence of small and marginal farmers.
- Regional variation.
- Dependence of seasonal rainfall.
- Low productivity of land.
- Increasing disguised unemployment.
- Disorder in marketing of Agricultural products.
- Weak land reformation.
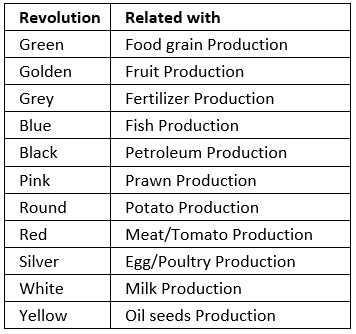
Revolutions in Agriculture
➤ Crop And Its Classifications
- Agronomy is a Greek word derived from agros meaning ‘field’ and nomos meaning management. It is a specialized branch in agriculture dealing with crop production and soil management. Crops refer to grown plants on a large scale for food, clothing, and other human uses.
➤ Classification based on climate
- Tropical: Crops grow well in warm & hot climate. E.g. Rice, sugarcane, Jowar etc
- Temperate: Crops grow well in cool climates. E.g. Wheat, Oats, Gram, Potato etc.
➤ Classification Based on growing season
- Kharif/Rainy/Monsoon crops: The crops grown in monsoon months from June to Oct-Nov, Require warm, wet weather at major periods of crop growth, also required short day length for flowering. E.g. Cotton, Rice, Jowar, bajara.
- Rabi/winter/cold seasons crops: The crops grown in the winter season from Oct to March month. Crops grow well in cold and dry weather. Require longer day length for flowering. E.g. Wheat, gram, sunflower etc.
- Summer/Zaid crops: crops grown in summer month from March to June. Require warm dry weather for major growth period and longer day length for flowering. E.g. Groundnuts, Watermelon, Pumpkins, Gourds.
➤ Agronomic Classification of Crops
- Cereals
- Cereals a recultivated grasses grown for their edible starchy grains. Larger grains used as staple food are cereals. Rice, wheat, maize, barley and oats. The most important cereal of world is rice.
(i) Bread wheat
(ii) Macaroni wheat
(iii) Emmer wheat
(iv) Dwarf wheat - Millets
(i) They are also annual grasses of the group cereals. But they are grown in less or less important area whose productivity and economics are also less.
(ii) These are staple food of poor people. In India pearl millet is a staple food in Rajasthan
(iii) a) Major millets and b) Minor millets
(iv) It is based on area production and productivity and grain size. - Major millets
(i) Sorghum /Jowar
(ii) Pearl Millet /Bajra/cumbu
(iii) Finger millet or ragi - Minor millets
(i) Fox tail millet
(ii) Little millet
(iii) Common millet
(iv) Barnyard millet
(v) Kodomillet - Pulses or Grain Legumes
- Pulses are major sources of protein in Indian diet and provide most essential amino acids to a certain degree. Economically, pulses are the cheapest source of protein.
- It is cultivated to enrich the soil, utilize the residual moisture, and give revenue in a shorter period.
(i) Red gram
(ii) Black gram
(iii) Green gram
(iv) Cowpea
(v) Bengalgram
(vi) Horsegram
(vii) Dewgram
(viii) Soyabean
(ix) Peas or gardenpea
(x) Garden bean
➤ Oil Seed Crops
- These crops are cultivated for the production of oil. Either for edible on industrial or medicinal purpose. They contain more fat.
(i) Groundnut or peanut
(ii) Sesamum or gingelly
(iii) Sunflower
(iv) Castor
(v) Linseed or flax
(vi) Niger
(vii) Safflower
(viii) Rapeseed & Mustard - 45 – 50% oil content is present in these seeds.
➤ Sugar Crops
- Juice extracted from
- Sugar stem used for jaggery or sugar
(i) Number of by products like Molasses, bagasse, pressmud
(ii) Molasses used for alcohol and yeast formation
(iii) Bagasse for paper making and fuel
(iv) Pressmud used for soil amendment
(v) Trash (green leaf + dry foliage) – the waste is used for cattle feed - Sugar beet – Tuber for extraction of sugar
- Tubers and tops are used as a fodder for cattle feed.
The document Agriculture | Environment for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Environment for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
97 videos|187 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Agriculture - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is agriculture? |  |
Ans. Agriculture refers to the practice of cultivating crops, raising animals, and producing food, fiber, medicinal plants, and other products used to sustain and enhance human life.
| 2. What are the main types of agriculture? |  |
Ans. The main types of agriculture include subsistence agriculture, commercial agriculture, intensive agriculture, extensive agriculture, organic agriculture, and sustainable agriculture.
| 3. How does agriculture impact the environment? |  |
Ans. Agriculture can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment. Positive impacts include carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and soil conservation. Negative impacts can include deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions from livestock.
| 4. What are the challenges faced by the agriculture industry? |  |
Ans. The agriculture industry faces various challenges, such as climate change, limited access to resources, pests and diseases, market volatility, and the need for sustainable farming practices.
| 5. How can technology improve agriculture? |  |
Ans. Technology plays a crucial role in improving agriculture by increasing productivity, reducing resource use, improving crop and livestock management, enhancing data collection and analysis, and promoting precision farming techniques. Examples of agricultural technologies include drones, GPS systems, and automated machinery.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















