NCERT Exemplar - Hydrocarbons - 2 | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Matching Type Questions |

|
| Assertion and Reason Type |

|
| Long Answer Type |

|
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.20. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain.
Ans. Due to the presence of a π -electron cloud above and below the plane of alkenes and arenes, these are electron-rich molecules and, therefore, provide sites for the attack of electrophiles. Hence, they undergo electrophilic reactions. Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions because they are unsaturated molecules. For example,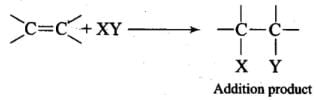 Arenes, on the other hand, cannot undergo electrophilic addition reactions. This is because benzene has a large resonance energy of 150.4 kJ mol-1. During electrophilic addition reactions, two new σ-bonds are formed but the aromatic character of benzene gets destroyed and, therefore, resonance energy of benzene ring is lost. Hence, electrophilic addition reactions of arenes are not energetically favourable.
Arenes, on the other hand, cannot undergo electrophilic addition reactions. This is because benzene has a large resonance energy of 150.4 kJ mol-1. During electrophilic addition reactions, two new σ-bonds are formed but the aromatic character of benzene gets destroyed and, therefore, resonance energy of benzene ring is lost. Hence, electrophilic addition reactions of arenes are not energetically favourable.
Arenes, in contrast, undergo electrophilic substitution reactions in which σ C – H bond is broken and new σ C – X bond is formed: The aromatic character of benzene ring is not destroyed and benzene retains its resonance energy. Hence, arenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
Q.21. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia form trans alkenes. Will the butene thus formed on reduction of 2-butyne show the geometrical isomerism?
Ans.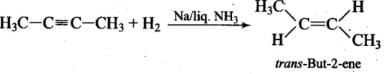 Thus, but-2-ene is capable of showing geometrical isomerism.
Thus, but-2-ene is capable of showing geometrical isomerism.
Q.22. Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
Ans. Ethane contains carbon-carbon sigma (σ) bond. Electron distribution of the sigma molecular orbital is symmetrical around the internuclear axis of the C – C bond which is not disturbed due to rotation about its axis. This permits free rotation around a C-C single bond. However, rotation around a C – C single bond is not completely free. It is hindered by a small energy barrier due to weak repulsive interaction between the adjacent bonds. Such a type of repulsive interaction is called torsional strain.
Of all the conformations of ethane, the staggered form has the least torsional strain and the eclipsed form has the maximum torsional strain. The energy difference between the two extreme forms is of the order of 12.5 kJ mol-1, which is very small. It has not been possible to separate and isolate different conformational isomers of ethane.
Q.23. Draw Newman and Sawhorse projections for the eclipsed and staggered conformations of ethane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?
Ans. 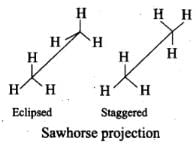
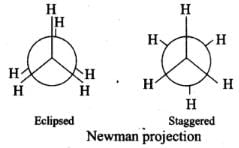 In staggered form of ethane, the electron clouds of carbon-hydrogen bonds are as far apart as possible. Thus, there are minimum repulsive forces, minimum energy and maximum stability of the molecule.
In staggered form of ethane, the electron clouds of carbon-hydrogen bonds are as far apart as possible. Thus, there are minimum repulsive forces, minimum energy and maximum stability of the molecule.
On the other hand, when the staggered form changes into the eclipsed form, the electron clouds of the carbon-hydrogen bonds come closer to each other resulting in increase in electron cloud repulsions. To check the increased repulsive forces, molecule will have to possess more energy and thus has lesser stability.
Q.24. The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI, HBr and HCl with propene is the same and the bond energy of HCl, HBr and HI is 430.5 kJ mol-1, 363.7 kJ mol–1 and 296.8 kJ mol–1 respectively. What will be the order of reactivity of these halogen acids?
Ans. The bond dissociation enthalpy decreases in the order HCl > HBr > HI, therefore, the order of reactivity is in the reverse order i.e., HI > HBr > HCl.
Q.25. What will be the product obtained as a result of the following reaction and why?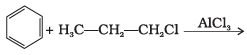 Ans.
Ans. 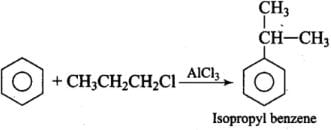
Propyl chloride forms CH3 – CH2 – CH+2 with anhydrous A1C13 which is less stable. This rearranges to a more stable carbocation as: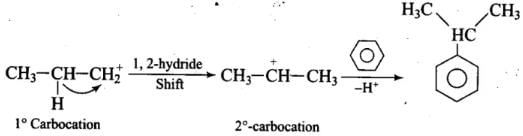
Q.26. How will you convert benzene into
(1) p-nitrobromobenzene
(2) m-nitrobromobenzene
Ans.
(1) Benzene into p-nitro bromobenzene:
C6H6 + Br2 (In presence of anhyd. FeBr3) → C6H5Br + HBr
C6H5Br + Conc. HNO3 + Conc. H2SO4 → p-nitrobromobenzene
(2) Benzene into m-nitrobromobenzene:
C6H6 + Conc. HNO3 +Conc. H2SO4 → C6H5NO2
C6H5NO2 + Br2 (In presence of anhyd.FeBr3) → m-nitrobromobenzene.
Q.27. Arrange the following set of compounds in the order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile. Give reason.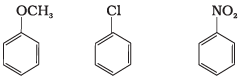 Ans. The methoxy group (-OCH3) is electron releasing group and increases electron density of benzene ring due to +R effect. Hence it makes anisole more reactive than benzene.
Ans. The methoxy group (-OCH3) is electron releasing group and increases electron density of benzene ring due to +R effect. Hence it makes anisole more reactive than benzene.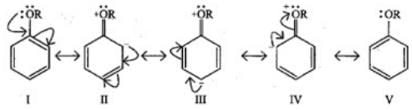
In case of Cl group it gives -I effect and +R effect. Its reactivity is less than methoxybenzene. —NO2 group gives -I effect and -R effect so it is less reactive than chlorobenzene.
Q.28. Despite their - I effect, halogens are o- and p-directing in haloarenes. Explain.
Ans. Halogens present on benzene ring have -I and +R effect, -I effect deactivates the ring but +R effect increases the electron density on ortho and para positions. Hence, halogens are ortho and para directing.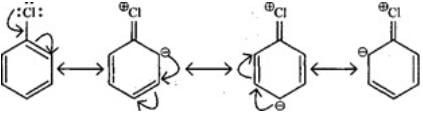
Q.29. Why does presence of a nitro group make the benzene ring less reactive in comparison to the unsubstituted benzene ring. Explain.
Ans. Nitro group has -I and -R effect due to that benzene ring deactivates and electron density decreases on ortho and para positions as compared to meta positions.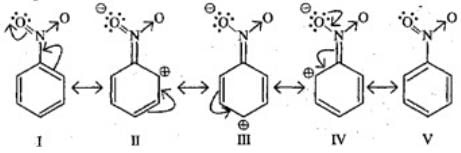
Q.30. Suggest a route for the preparation of nitrobenzene starting from acetylene?
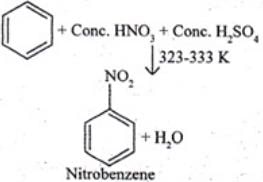
Ans. Ethyne, when passed through red hot iron tube at 873 K, undergoes cyclic polymerization to give benzene which upon subsequent nitration gives nitrobenzene.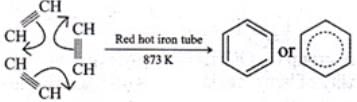
Q.31. Predict the major product (s) of the following reactions and explain their formation.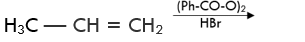
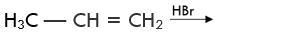
Ans. Addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markonikov rule. It states that negative part of the addendum (adding molecule) gets attached to that carbon atom which possesses lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
Mechanism: Hydrogen bromide provides an electrophile, H+, which attacks the double bond to form carbocation as shown below: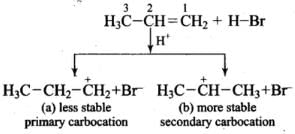
The carbocation (b) is attacked by Br- ion to form the product as follows: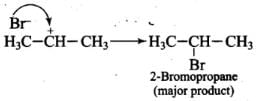
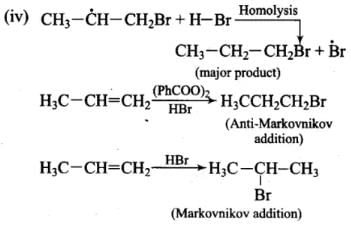
Addition reaction of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes in the presence of peroxide follows the anti-Markovnikov rule.
Mechanism: Peroxide effect proceeds via free radical chain mechanism as given below: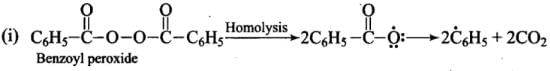
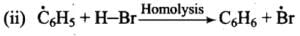
(iii)
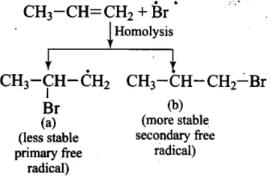
Q.32. Nucleophiles and electrophiles are reaction intermediates having electron rich and electron deficient centres respectively. Hence, they tend to attack electron deficient and electron rich centres respectively. Classify the following species as electrophiles and nucleophiles.
(i) H3CO–
(ii)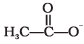
(iii) Cl
(iv) Cl2C:
(v) (H3C)3C+
(vi) Br-
(vii) H3COH
(viii) R-NH-R
Ans. Electrophiles are electron seeking species or electron-deficient species. These species may be neutral or positively charged.
(iii) Cl
(iv) Cl2C:
(v) (H3C)3C+ are electrophiles.
Nucleophiles are electron rich species and may be neutral or negatively charged.
(i) H3CO-
(ii) CH3COO-
(iv) Br-
(vi) CH3OH
(viii) R—NH—R are nucleophiles.
Q.33. The relative reactivity of 1°, 2°, 3° hydrogen’s towards chlorination is 1 : 3.8 : 5. Calculate the percentages of all monochlorinated products obtained from 2-methylbutane.
Ans.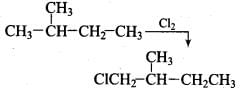
(A) Primary (9 positions for Cl group possible)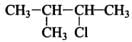
(B) Secondary (2 positions for Cl group possible at CH)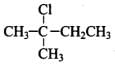
(c) Tertiary (1 position for Cl group possible) Relative amounts of A, B and C compounds = Number of hydrogen x Relative reactivity.
So, relative amounts = 9 + 7.6 +5 = 21.6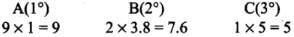
Total amount = 9 + 7.6 + 5 = 21.6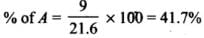
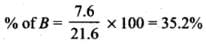
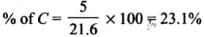
Q.34. Write the structures and names of products obtained in the reactions of sodium with a mixture of 1-iodo-2-methylpropane and 2-iodopropane.
Ans. Products obtained are based on Wurtz reaction, n-alkyl halide on treatment with Name talin presence of ether gives alkane having double carbon atoms.
RX + 2Na + XR→ R-R + 2NaX
CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2l + 2Na + ICH2-CH(CH3)-CH3 Dry either→
2NaI + CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH3 (2,5-dimethyUiexane)
CH3 - CH(CH3)I + 2Na + I(CH3)CH-CH3→
2NaI + CH3-CH(CH3)-CH(CH3)-CH3
(2, 4-dimethylbutane)
CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2l + 2Na + I CH(CH3)-CH3→
2NaICH3-CH(CH3)-CH-CH3-CH3
(2, 4-dimethylpentane)
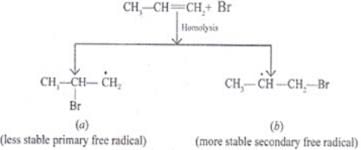
Q.35. Write hydrocarbon radicals that can be formed as intermediates during monochlorination of 2-methylpropane? Which of them is more stable? Give reasons.
Ans. 2-methylpropane gives two types of radicals:
Tertiary 3° free radical is more stable because it has 9 α Hydrogen and Due to hyperconjugation structure sit stabilized.
Primary 1° free radical is less stable because of only 1 α hydrogen and one hyper conjugative structure.
Q.36. An alkane C8H18 is obtained as the only product on subjecting a primary alkyl halide to Wurtz reaction. On monobromination, this alkane yields a single isomer of a tertiary bromide. Write the structure of alkane and the tertiary bromide.
Ans. 2C4H9X + 2 Na→C8H16 + 2NaI
C8H16 + Br2→Single isomer of tertiary bromide.
C4H9X can be n-Butyl halide = CH3—(CH2)2-CH2X (It is primary halide) And CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2X
2CH3-CH(CH3) -CH2X + 2Na 2NaX +CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH3.
This compound gives only one isomer of tertiary bromide. Therefore, the name of C8H16 is 2, 5-dimethylhexane.
CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH(CH3-CH3+ Br2^ HBr + CH3—CBr(CH3-CH2-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH3
2-Bromo 2, 5-dimethylhexane.
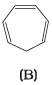
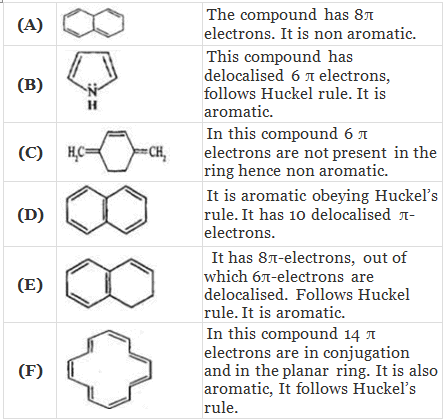
Q.37. The ring systems having following characteristics are aromatic.
(i) Planar ring containing conjugated π bonds.
(ii) Complete delocalisation of the π−electrons in ring system i.e. each atom in the ring has unhybridised p-orbital, and
(iii) Presence of (4n + 2) π−electrons in the ring where n is an integer (n = 0, 1, 2,...........) [Huckel rule].
Using this information classify the following compounds as aromatic/nonaromatic.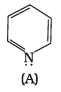


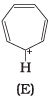

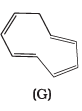
Ans.
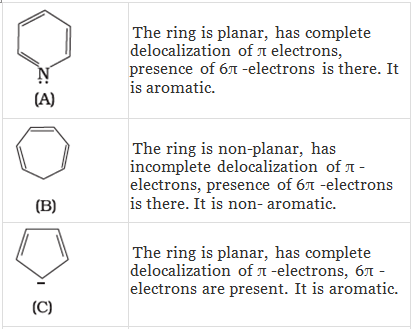
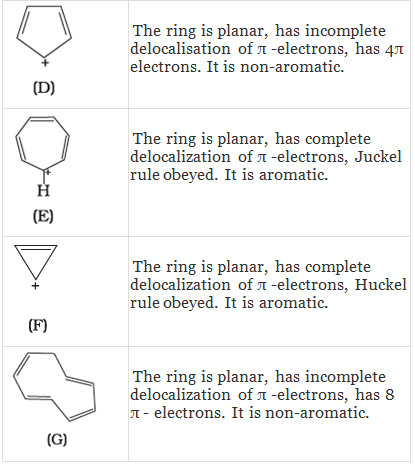
Q.38. Which of the following compounds are aromatic according to Huckel’s rule?
(A)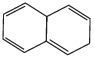
(B)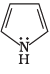
(C)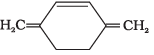
(D)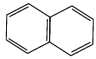
(E)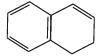
(F)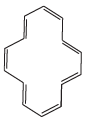
Ans.
Q.39. Suggest a route to prepare ethyl hydrogen sulphate (CH3–CH2–OSO2—OH) starting from ethanol (C2H5OH).
Ans. Preparation of ethyl hydrogen sulphate [CH3CH2-OSO2-OH] starting from ethanol.
Step-1: Protonation of alcohol and formation of carbocation
H2SO4 → H+ + - OSO2OH
CH3 - CH2 - O -H + H+ → CH3 - CH2 - + OH2
CH3 - CH2 - + OH2 → CH3 - + CH2 + H2O
Step-2: Attack of nucleophile
HO - SO2 - O- + + CH2 - CH3 → CH3 - CH2 - O - SO2 - OH
Ans. Peroxide effect proceeds via free radical chain mechanism as given below:
(i)

(ii)
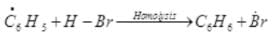
(iii)
(iv)

Peroxide effect is observed only in the case of HBr and not seen in case of HI and HCI. This is due to the fact that the H-Cl bond is stronger than B-Br bond. Also, bond energy of H-Cl bond is higher than H-Br. H-Cl bond is not cleaved by the free radical whereas the HI bond is weaker and iodine free radicals combine to form iodine molecules.
Matching Type Questions
Q.41. Match the hydrocarbons in Column I with the boiling points given in Column II.
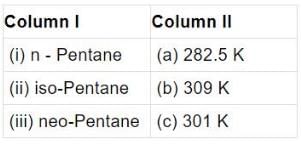
Ans. (i)→(b);(ii) →(c);(iii) →(a)
Explanation:
Q.42. Match the following reactants in Column I with the corresponding reaction products in Column II.
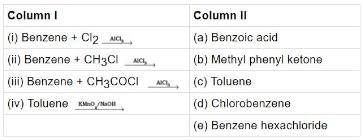
Ans. (i)→(d);(ii)→(c);(iii)→(b);(iv)→(a)
Solution.
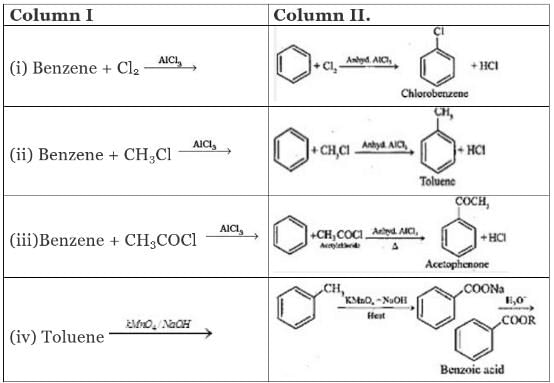
Q.43. Match the reactions given in Column I with the reaction types in Column II.
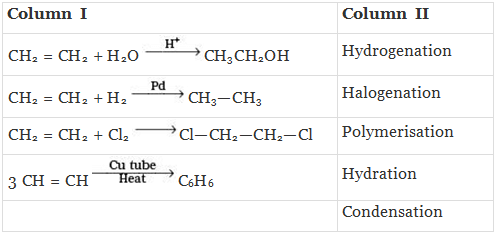
Ans. (i)→(d);(ii)→(a);(iii)→(b);(iv)→(c)
Solution.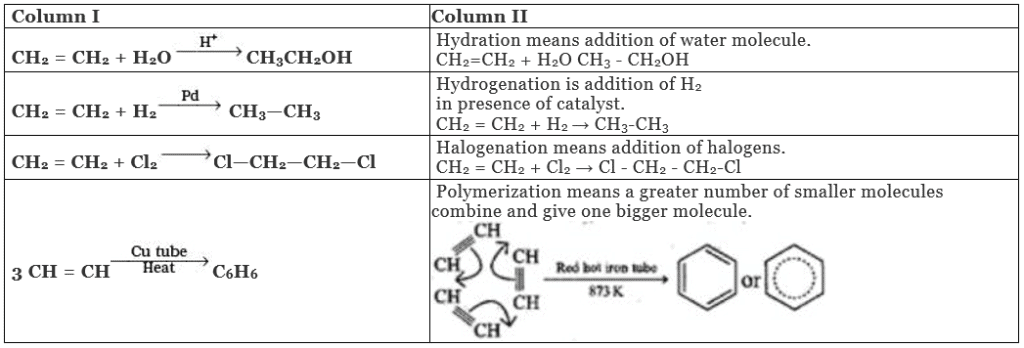
Assertion and Reason Type
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Q.44. Assertion (A): The compound cyclooctane has the following structural formula :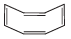 It is cyclic and has conjugated 8π-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
It is cyclic and has conjugated 8π-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
Reason (R) : (4n + 2) π electrons rule does not hold good and ring is not planar.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Ans. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Solution. Both A and R are Correct, and R is correct explanation of A.
Aromaticity is shown by compounds possessing following characteristics:
- Planarity
- Complete delocalization of the π electrons in the ring.
- Presence of (4n + 2) π electrons in the ring where n is an integer (4 = 0, 1, 2,...). This is often referred to as Huckel Rule.
Q.45. Assertion (A): Toluene on Friedel Crafts methylation gives o– and p–xylene.
Reason (R) : CH3-group bonded to benzene ring increases electron density at o– and p– position.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Ans. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Solution.
Toluene has -CH3 group attached to benzene ring. CH3 group is electron withdrawing group which activates benzene ring due to hyperconjugation effect and increases electron density on ortho and para positions for the attack of electrophiles.
Q.46. Assertion (A): Nitration of benzene with nitric acid requires the use of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Reason (R): The mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid produces the electrophile, NO+2.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Ans. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Solution.
In nitration, benzene is treating with nitrating mixture, i,e. conc. HNO3 and H2SO4 and H2SO4 helps in furishing NO2+ (ElectrophiIe).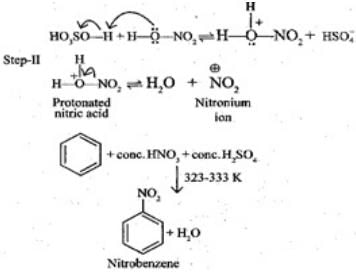
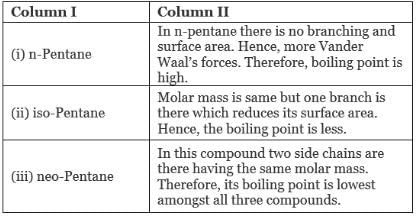
Q.47. Assertion (A): Among isomeric pentanes, 2, 2-dimethylpentane has highest boiling point.
Reason (R): Branching does not affect the boiling point.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Ans. (iii) Both A and R are not correct.
Solution.
Among isomeric pentanes 2, 2-dimethylpentane has lowest boiling point and on branching boiling point decreases.
Long Answer Type
Q.48. An alkyl halide C5H11Br (A) reacts with ethanolic KOH to give an alkene ‘B’, which reacts with Br2 to give a compound ‘C’, which on dehydrobromination gives an alkyne ‘D’. On treatment with sodium metal in liquid ammonia one mole of ‘D’ gives one mole of the sodium salt of ‘D’ and half a mole of hydrogen gas. Complete hydrogenation of ‘D’ yields a straight chain alkane. Identify A,B, C and D. Give the reactions invovled.
Ans. The reactions involved in identification of A, B, C and D are as follows:
C5H11Br(A) + alc. KOH→C5H10(B)
C5H10(B) + Br2/CS2→C5H10Br2(C)
C5H10 Br2(C) + alc. KOH→C5H8(D) Alkyne.
2C5H8 + 2Na→2C5H7Na + H2
Hydrogenation of alkyne (D) gives straight-chain alkane hence all the compounds A, B, C and D must be straight-chain compounds. Alkyne gives sodium alkenyl which proves D is terminal alkyne.
Q.49. 896 mL vapour of a hydrocarbon ‘A’ having carbon 87.80% and hydrogen 12.19% weighs 3.28g at STP. Hydrogenation of ‘A’ gives 2-methyl pentane. Also ‘A’ on hydration in the presence of H2SO4 and HgSO4 gives a ketone ‘B’ having molecular formula C6H12O. The ketone ‘B’ gives a positive iodoform test. Find the structure of ‘A’ and give the reactions involved.
Ans. To calculate molar mass of hydrocarbon A it is given that 896 ml of Hydrocarbon ‘A’CxHy Weighs 3.28 g at STP.
22400 ml of has ACxHy mass = 3.28 x 22400 ml/896 ml = 831 g /mol.
Hence, the molar mass of A= 831 g mol.
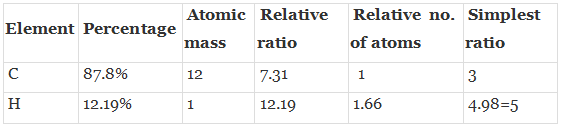
Thus, empirical formula = C3H5
Empirical formula weight = 3 x 12 =36 + 5 = 41.
Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
n = Mol. Mass/empirical mass = 831 /41 = 2.02.
Molecular formula = [C3H5]2 = C6H10
To determine the structure of (A) and (B):
C6H10 on hydrogenation with 2 moles 0f H2 gives C6H12 and structure is 2-methyl pentane.(A) on hydration in presence of dil. H=H2SO4 and HgSO4 gives C6H12O which gives Iodoform test positive. Hence, structure of A= (CH3)2CH—CH—C=CH(4-methyl pent-yne) and (B) is 4-methyl pentanone-2.
Q.50. An unsaturated hydrocarbon ‘A’ adds two molecules of H2 and on reductive ozonolysis gives butane-1,4-dial, ethanal and propanone. Give the structure of ‘A’, write its IUPAC name and explain the reactions involved.
Ans. Compound A on ozonolysis gives:
CH3CHO + O = CH-CH2 - CH2 - CHO + O = C(CH3)2
The structure of A is:
CH3-CH = CH2-CH2-CH2-CH =C(CH3)2
IUPAC name: 2-methyl octa 2, 6 diene.
|
22 videos|163 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar - Hydrocarbons - 2 - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What are hydrocarbons? |  |
| 2. How are hydrocarbons classified? |  |
| 3. What are the uses of hydrocarbons? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of hydrocarbons in the petroleum industry? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of hydrocarbons? |  |




















