Thrust and Pressure - Class 9 PDF Download
Thrust
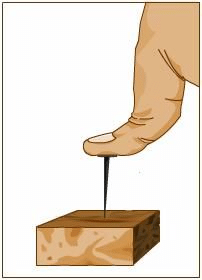
Definition:
Thrust is a vector quantity.
Note:
- A body when placed on a surface, exerts a thrust on the surface which is equal to its weight.
- The thrust is the same in whatsoever way the body is placed on the surface.
Unit of thrust
- It is measured in the units of force.
- The S.I. unit of thrust is newton (N) and C.G.S. unit is dyne.
1 N = 105 dyne - The gravitational unit of thrust in M.K.S. system is kgf and in C.G.S. is gf.
1 kgf = 9.8 N and 1 gf = 980 dyne
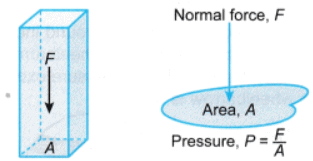 Thrust and Pressure
Thrust and Pressure
Pressure
The S.I. unit of pressure is Pascal (Pa) or newton per metre2 (N/m2). - One pascal is the pressure exerted on a surface of area 1 m2 by a force of 1 N acting normally on it.
- The C.G.S. unit is dyne cm-2.
1 N/m2 = 10 dyne/cm2 - Other units of pressure are bar and millibar, where
1 bar = 105 N m-2 and 1 millibar = 10-3 bar = 102 N m-2 - The atmospheric pressure is generally expressed in terms of the height of the mercury column. At normal temperature and pressure, the barometric height is 0.76 m of Hg (or 76 cm of Hg or 760 mm of Hg) at sea level, which is taken as 1 atmosphere. Thus the atmospheric pressure is also expressed in a unit atmosphere (atm) where,
1 atmosphere (atm) = 0.76 m of Hg = 1.013 x 105 Pa - Sometimes we use torr as the unit of atmospheric pressure after the name of the scientist Torricelli where,
1 torr = 1 mm of Hg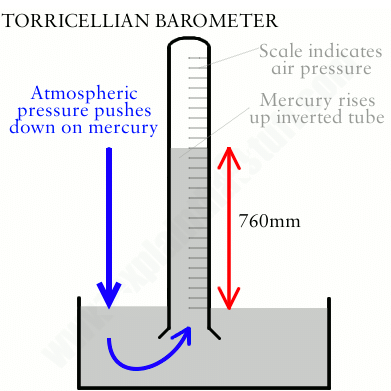
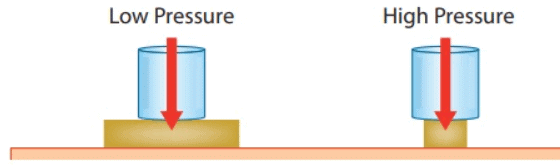
Factors affecting the pressure: The pressure exerted on the surface depends on:
(1) the thrust
(2) the area on which the thrust is applied
Note:
The pressure on a surface is increased by making the area of surface small on which the thrust acts.
Example:
- The ends of nails or pins are made pointed so that large pressure is exerted at the pointed ends and they can be driven into with a less effort.
- The cutting tools also have either sharp or pointed edges, so that a smaller thrust may cause a greater pressure at the edges and cutting can be done with less effort.
Similarly, the pressure on a surface is reduced by making the area of surface large on which the thrust acts.
Example:
- Wide wooden sleepers are placed below the railway tracks so that the pressure exerted by the rails on the ground becomes less.
- The foundations of buildings are made wider than the walls, so that the pressure exerted by the building on the ground becomes less.
FAQs on Thrust and Pressure - Class 9
| 1. What is thrust? |  |
| 2. How is thrust generated in jet engines? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the amount of thrust produced by a jet engine? |  |
| 4. How does pressure relate to thrust? |  |
| 5. Can thrust be increased by increasing the pressure? |  |















