Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Structure of Atom
Structure of Atom - Class 9 PDF Download
DEFINITION
Nucleus
Nucleus refers to the small dense region, in which positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons are present. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed orbits.
DEFINITION
Discovery of proton by Goldstein
In 1886, E. Goldstein carried out discharge tube experiments and discovered new radiations and called them canal rays. These rays were made up of positively charged particles and led to the discovery of proton.
DEFINITION
Thomson's model of an atom
J.J. Thomson was the first to put forward a model to explain the structure of an atom. Thomson's atomic model is also called water melon model or Christmas pudding model. He compared the electrons with the raisins in the spherical Christmas pudding and to seeds in a watermelon. In which he describe the resin as electrons and spherical body as central body in which electrons revolves.
DEFINITION
Postulates of Thomson's atomic model
- An atom consists of a positively charged sphere, with electrons set within the sphere.
- An atom is electrically neutral as the positive and negative charges within it are equal.
DEFINITION
Postulates of Rutherford's atomic model
Postulates of Rutherford's nuclear model:
Positive charge is concentrated in the center of the atom, called nucleus.
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths called orbits.
The nucleus is much smaller in size than the atom.
Positive charge is concentrated in the center of the atom, called nucleus.
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths called orbits.
The nucleus is much smaller in size than the atom.
DEFINITION
Drawbacks of Rutherford's atomic model
The orbital revolution of the electron is not expected to be stable. According to Rutherfords model, the electrons, while moving in their orbits, would give up energy. This would make them slow down, gradually and move towards the nucleus. The electrons will follow a spiral path and then fall into the nucleus. Ultimately, the atom would collapse. But in reality the atom is stable.
DEFINITION
Rutherford's model of an atom
To study the structure of atom, Rutherford performed a thin gold foil scattering experiment. For his experiments Rutherford used a gold foil. He made a narrow beam of alpha particles to fall on the gold foil. Observations made from the alpha ray scattering experiment: Most of the alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil without getting deflected, a small fraction of the alpha particles were deflected through small angles, a few alpha particles bounced back.
DEFINITION
Postulates of discovery of neutrons
The particle present in nucleus along with proton is neutral made from close combination of proton and electron.
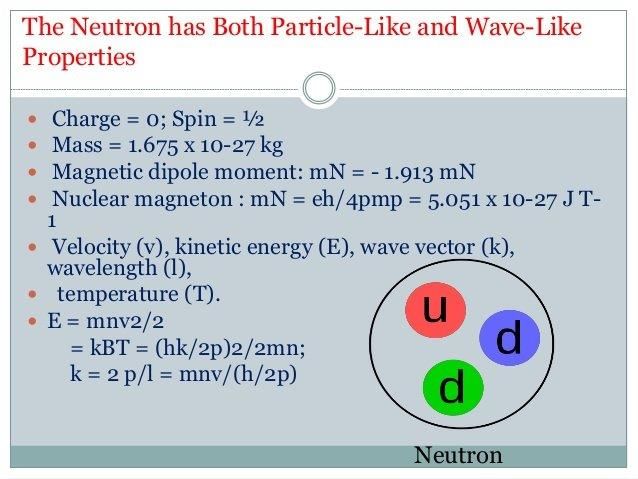
The particle has no charge and mass almost equal to the mass of proton.
The particle has no charge and mass almost equal to the mass of proton.
DEFINITION
Properties of neutrons
DEFINITION
Calculate valency of an atom
The valency of hydrogen and all metals is positive. The valency of non- metals is negative. The valency of a molecule is zero.
Valency is calculated by calculating number of electrons present in outermost orbitals of atom of element.
For example : Valency of Nitrogen is 3 because outermost orbital contain 3 electron.
Valency is calculated by calculating number of electrons present in outermost orbitals of atom of element.
For example : Valency of Nitrogen is 3 because outermost orbital contain 3 electron.
FORMULA
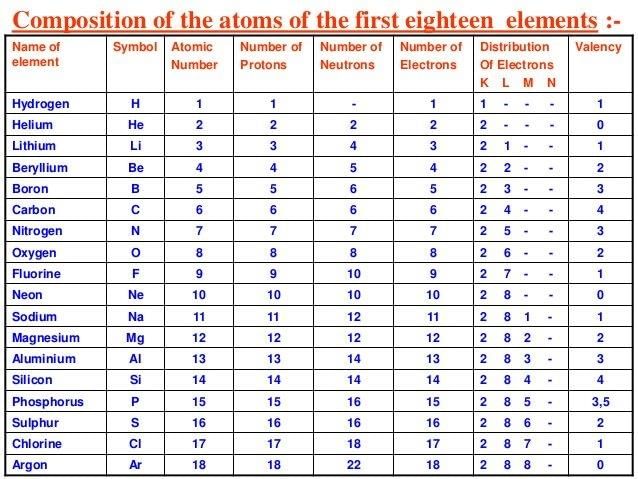
Number of electrons in different shells
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell is given by where n is a positive integer.
For K shell, n=1
For L shell, n=2
For M shell, n=3
For N shell, n=4 and so on.
For K shell, n=1
For L shell, n=2
For M shell, n=3
For N shell, n=4 and so on.
DIAGRAM
Table of configuration of first 18 elements
DEFINITION
Definition of Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element having the same atomic number (Z) but different mass numbers (A).
DEFINITION
Isobars
Atoms of different elements with different atomic numbers but the same mass numbers are called isobars.Isobars have different chemical properties because they have different atomic numbers.
Related Searches



















