Important Electrochemistry Formulas for JEE and NEET
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry cells consist of two half-cells where oxidation and reduction reactions take place. It consists of two electrodes made of metals with different reactivity and due to the difference in electrode potential chemical reactions take place resulting in electrical energy.
Measurement of Electrode Potential
Standard electrode potential is measured using the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) as a reference.
Cell Potential ( E cell ) = Cathode Potential (E cathode ) - Anode Potential (E anode )
- For any electrode → oxidation potential (O.P) = - Reduction potential (R.P)
- Ecell = R.P of cathode - R.P of anode
- Ecell = R.P. of cathode + O.P of anode
- Ecell is always a positive quantity & Anode will be electrode of low R.P
- E°Cell = SRP of cathode - SRP of anode.
Greater the SRP value greater will be oxidising power.
Gibbs Free Energy Change
ΔG = - nFEcellΔG° = - nFE°cell
Nernst Equation
(Effect of concentration and temp of an emf of cell)
⇒ ΔG = ΔG° + RT lnQ (where Q is raection quotient)
ΔG° = - RT ln Keq
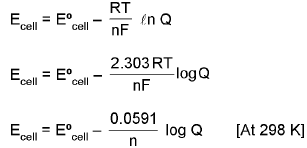
At chemical equilibrium
ΔG = 0 ; ECell = 0.
-
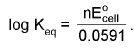
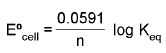
For an electrode M(s)/Mn+.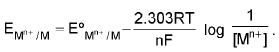
Concentration Cell
A cell in which both the electrods are made up of same material.
For all concentration cell E°cell = 0.
(a) Electrolyte Concentration Cell :
eg. Zn(s) / Zn2+ (c1) || Zn2+(c2) / Zn(s) 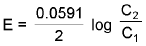
(b) Electrode Concentration Cell:
eg. Pt, H2(P1 atm) / H+ (1M) / H2(P2atm) / Pt 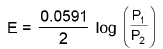
Different Types Of Electrodes:
1. Metal-Metal ion Electrode: M(s)/Mn+. Mn+ + ne- → M(s)
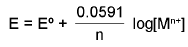
2. Gas-ion Electrode: Pt/H2(Patm)/H+(XM) as a reduction electrode 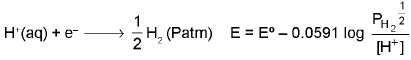
3. Oxidation-reduction Electrode: Pt / Fe2+, Fe3+ as a reduction electrode Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ 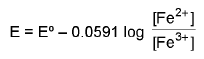
4. Metal-Metal insoluble salt Electrode: eg. Ag/AgCI, Cl- as a reduction electrode AgCI(s) + e- → Ag(s) + Cl-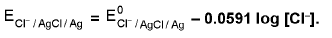
Calculation Of Different Thermodynamics Function Of Cell Reaction
- ΔG = -n FEcell
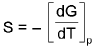 (At costant pressure).
(At costant pressure).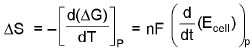
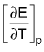 = Temperature cofficient of e.m.f of the cell.E = a + bT + CT2 + ....
= Temperature cofficient of e.m.f of the cell.E = a + bT + CT2 + ....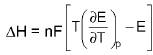
- ΔCp of cell reaction
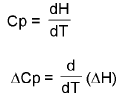
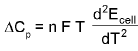
Electrolysis:
Electrolysis is the phenomenon where an electrolyte undergoes decomposition when electricity is passed through its aqueous solution or molten state.In the electrolysis of various electrolytes, two types of electrodes are employed: inert electrodes and active electrodes.
(a) 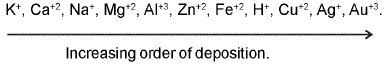
(b) Similarly the an ion which is strogner reducing agent(low value of SRP) is liberated first at the anode.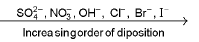
Faraday First Law of Electrolysis

Faraday Second Law of Electrolysis
W α E
W/E = constant
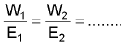
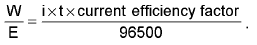
Current Efficiency = 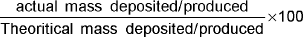
Condition For Simultaneous Deposition Of Cu & Fe At Cathode: 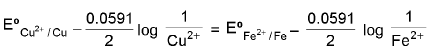 Condition for the simultaneous deposition of Cu & Fe on cathode.
Condition for the simultaneous deposition of Cu & Fe on cathode.
Conductance:
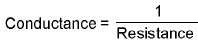
- Specific conductance or conductivity :
(Reciprocal of specific resistance) k = 1/ρ K = specific conductance - Equivalent conductance:
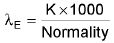 unit: -ohm-1 cm2 eq-1
unit: -ohm-1 cm2 eq-1 - Molar conductance:
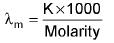 unit: -ohm-1 cm2 mole-1
unit: -ohm-1 cm2 mole-1
specific conductance = conductance x l/a
Kohlrausch’s Law:
Variation of λeq /λM of a solution with concentration :
(i) Strong electrolyte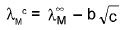
(ii) Weak electrolytes :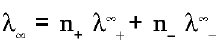 where λ is the molar conductivity
where λ is the molar conductivity
n+ = No of cations obtained after dissociation per formula unit
n_ = No of anions obtained after dissociation per formula unit
Application Of Kohlrausch Law:
1. Calculation of λ0M of weak electrolytes :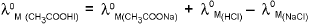
2. To calculate degree of diossociation of a week electrolyte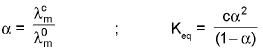
3. Solubility (S) of sparingly soluble salt & their Ksp
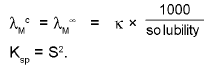
Ionic Mobility:
It is the distance travelled by the ion per second under the potential gradient of 1 volts per cm. It’s unit is cm2s-1v-1.
Absolute ionic mobility:
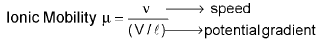
Transport Number:
Where tc = Transport Number of cation & ta = Transport Number of anion
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Important Electrochemistry Formulas for JEE and NEET
| 1. What is the relationship between Gibbs Free Energy and electrode potential in electrochemistry? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the electrode potential using the Nernst equation? |  |
| 3. What is electrolysis and what are its main applications? |  |
| 4. What are some important formulas used in electrochemistry? |  |
| 5. How does temperature affect electrode potential in electrochemical cells? |  |

















