Best Study Material for NEET Exam
NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Mind Map: Laws of Motion
Mind Map: Laws of Motion - NEET PDF Download
FAQs on Mind Map: Laws of Motion - NEET
| 1. What are the three laws of motion? |  |
| 2. How do the laws of motion explain the behavior of objects? |  |
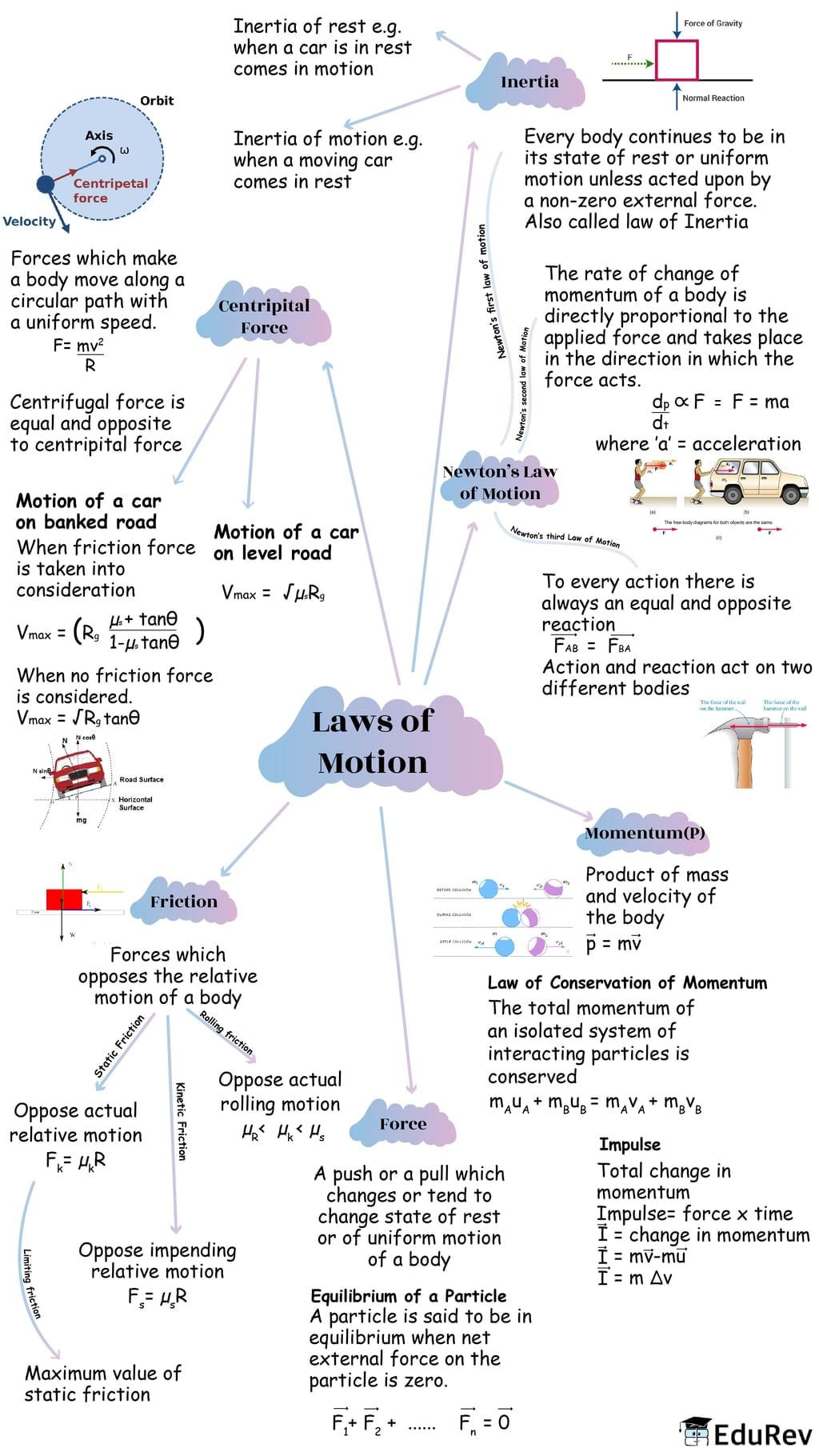
Ans. The laws of motion provide a framework for understanding how objects move and interact with each other.
Newton's First Law of Motion explains that objects tend to maintain their state of motion unless acted upon by an external force. This means that if no forces are acting on an object, it will continue to move at a constant velocity or remain at rest.
Newton's Second Law of Motion explains how the motion of an object changes when a net force is applied. It states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to its mass. This law allows us to calculate the resulting acceleration of an object when a force is applied to it.
Newton's Third Law of Motion explains the interaction between two objects. It states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude in the opposite direction on the first object. This law helps explain phenomena such as the recoil of a gun when fired.
| 3. How are the laws of motion relevant in everyday life? |  |
Ans. The laws of motion have numerous applications in our daily lives. Some examples include:
1. Driving a car: Newton's laws of motion explain how a car accelerates, decelerates, and turns. The first law explains why objects inside the car move forward when the car suddenly stops. The second law helps us understand how various forces, such as friction and air resistance, affect the car's motion. The third law explains the reaction forces between the car's tires and the road surface.
2. Sports: The laws of motion are fundamental in various sports activities. For example, the laws explain how a ball moves when it is thrown, kicked, or hit. They also help athletes understand the principles of balance, force application, and motion control.
3. Construction and engineering: Engineers and architects rely on the laws of motion to design structures, bridges, and machines. Understanding these laws helps ensure the stability and safety of structures and the efficient functioning of machinery.
4. Space exploration: The laws of motion are crucial in space exploration and satellite navigation. They govern the motion of spacecraft, the trajectory of rockets, and the movement of planets and celestial bodies.
| 4. How did Isaac Newton contribute to the laws of motion? |  |
Ans. Sir Isaac Newton, a renowned physicist and mathematician, made significant contributions to the laws of motion. He formulated the three laws of motion and laid the foundation for classical mechanics.
Newton's First Law of Motion, also known as the law of inertia, was proposed by Newton in his work "Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica" published in 1687. This law states that objects at rest remain at rest, and objects in motion continue to move with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
Newton's Second Law of Motion, which relates force, mass, and acceleration, was also introduced in the "Principia." It states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
Newton's Third Law of Motion, stating that every action has an equal and opposite reaction, was also presented in the "Principia." This law describes the interaction between two objects and the forces they exert on each other.
Newton's laws of motion revolutionized the understanding of motion and laid the groundwork for the development of classical physics.
| 5. How do the laws of motion apply to objects in equilibrium? |  |
Ans. Objects in equilibrium are those that are either at rest or moving with a constant velocity. The laws of motion still apply to such objects, although the net force acting on them is zero.
Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. In the case of objects in equilibrium, the absence of a net force means that the object will continue to remain at rest or move with a constant velocity.
Newton's Second Law of Motion, which relates force, mass, and acceleration, can also be applied to objects in equilibrium. If the net force acting on the object is zero, then the acceleration of the object will also be zero according to the formula F = ma.
Newton's Third Law of Motion, stating that every action has an equal and opposite reaction, still applies to objects in equilibrium. Although there may be forces acting on the object, the equal and opposite reaction forces cancel each other out, resulting in a net force of zero.
In summary, the laws of motion provide a framework for understanding the behavior of objects in equilibrium, even though the net force acting on them is zero.
Download as PDF
Related Searches