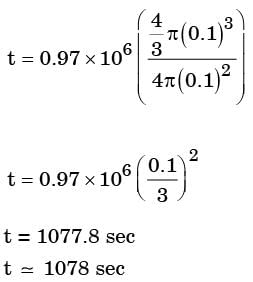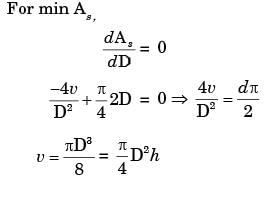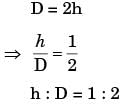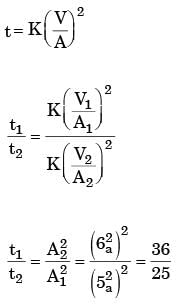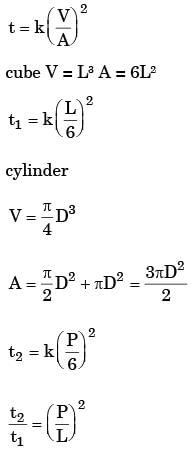Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:The contraction allowance provided on the pattern and core boxes compensates for the following type of contraction
[ME 1988]
Explanation
Third stage of contraction solidification contraction compensated by pattern allowances.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:Chills are used in moulds to
[ME 1989]
Explanation
Chills are used to promote uni-directional solidification.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:Two cubical castings of the same metal and size of 2 cm side and 4 cm side are moulded in green sand. If the smaller casting solidifies in 2 mins, the expected time of solidifications of large casting will be
[ME 1989]
Explanation
T2 = 2 × 4 = 8 min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:When there is no room temperature change, the total shrinkage allowance on a pattern is independent of
[ME 1991]
Explanation
Pattern allowances only taking care of solid shrinkage.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:With a solidification factor of 0.97 × 106 s/m2, the solidification time (in seconds) for a spherical casting of 200 mm diameter is
[ME 2003]
Explanation
D = 200 m m
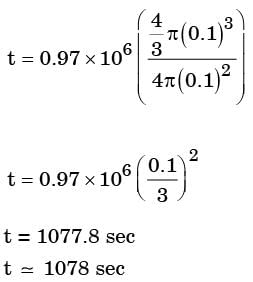
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
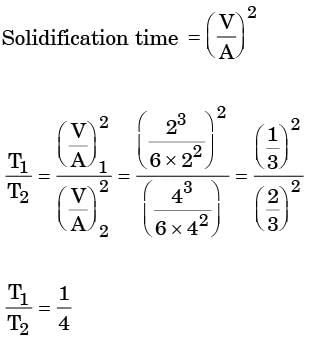
Try yourself:Volume of a cube of side l and volume of a sphere of radius r are equal. Both the cube and the sphere are solid and of same material. They are being east. The ratio of the solidification time of the cube to the same of sphere is
[ME 2007]
Explanation
Vcube = Vsphere
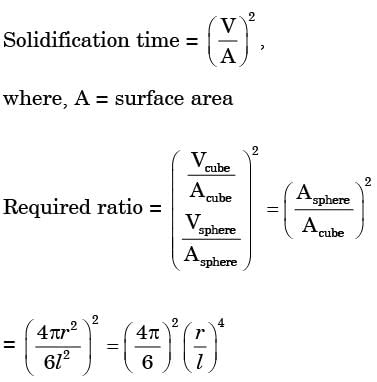
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:A cubic casting of 50 mm side under goes volumetric solidification shrinkage and volumetric solid contraction of 4% and 6% respectively. No riser is used. Assume uniform cooling in all directions. The side of the cube after solidification and contraction is
[ME 2011]
Explanation
Side of cube after solidification
(0.96×(50)3)1/3 = 49.32mm
Side of cube after contraction
(0.94×(49.32)3)1/3 = 48.32mm
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:A cube shaped casting solidifies in 5 min. The solidification time in min for a cube of the same material, which is 8 times heavier than the original casting, will be
[ME 2013]
Explanation
Solidification time,
t=k(V/A)2
For cube:
(V/A)=a/6
t1/t2=(a1/a2)2
t1=5(a2/a1)2.....(i)
m1=V1×ρ1
m1=V2×ρ2
V2=8V1
a32=8a31
⇒a2=2a1
a2/a1=2......(ii)
From the Equations (i) and (ii)
t2=5(2)2=5×4=20min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
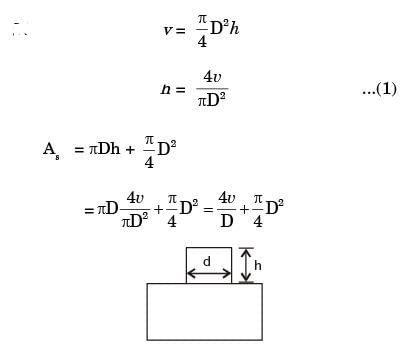
Try yourself:A cylindrical blind riser with diameter d and height h, is placed on the top of the mold cavity of a closed type sand mould as shown in the figure. If the riser is of constant volume, then the rate of solidification in the riser is the least when the ratio h : d is
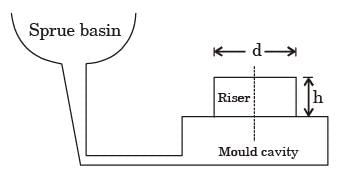
[ME 2014,Set-3]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:The solidification time of a casting is proportional to 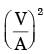 where V is the volume of the casting and A is the total casting surface area losing heat. Two cubes of same material and size are cast using sand casting process. The top face of one of the cubes is completely insulated. The ratio of the solidification time for the cube with top face insulated to that of the other cube is
where V is the volume of the casting and A is the total casting surface area losing heat. Two cubes of same material and size are cast using sand casting process. The top face of one of the cubes is completely insulated. The ratio of the solidification time for the cube with top face insulated to that of the other cube is
[ME 2015,Set-1]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:Equal amounts of a liquid metal at the same temperature are poured into three moulds made of steel, copper and aluminum. The shape of the cavity is a cylinder with 15 mm diameter. The size of the moulds are such that the outside temperature of the moulds do not increase appreciably beyond the atmospheric temperature during solidification. The sequence of solidification in the mould from the fastest to slowest is (Thermal conductivities of steel, copper and aluminum are 60.5, 401 and 237 W/mK, respectively. Specific heats of steel, copper and aluminum are 434, 385 and 903 J/ kgK, respectively. Densities of steel, copper and aluminum are 7854, 8933 and 2700 kg/m3, respectively.)
[ME 2016,Set-3]
Explanation
Solidification time is inversely proportional to diffusivity and based on the values diffusivity is highest for copper, next is aluminium and then steel. Hence the solidification time is lowest for copper, next aluminium and then steel.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:A cast Steel slab of dimension 30 × 20 × 5 cm is poured horizontally using a side riser. The riser is cylindrical in shape with diameter and height, both equal to D. The freezing ratio of the mould is
[PI 2005]
Explanation
Case steel slab = 30 × 20 × 5 cm3
Modulus of Casting
Mc=V/A=30×20×5/((2×30×20)+(2×30×5)+(2×20×5))
=30/17
Mc=1.76
Modulus of Riser
Mr=V/A= (π/4)D3/(2×(π/4)D2+πD2)
= (D/4)/(6/4) = D/6
Freezing ratio =Mr/Mc
F.R=D/6×17/30=17D/180
=0.094D≈8D/75
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Solidification & Cooling
Try yourself:A solid cylinder of diameter D and height equal to D, and a solid cube of side L are being sand cast by using the same material. Assuming there is no superheat in both the cases, the ratio of solidification times of the cylinder to the solidification time of the cube is
[PI 2009]
Explanation
Report a problem

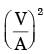 where V is the volume of the casting and A is the total casting surface area losing heat. Two cubes of same material and size are cast using sand casting process. The top face of one of the cubes is completely insulated. The ratio of the solidification time for the cube with top face insulated to that of the other cube is
where V is the volume of the casting and A is the total casting surface area losing heat. Two cubes of same material and size are cast using sand casting process. The top face of one of the cubes is completely insulated. The ratio of the solidification time for the cube with top face insulated to that of the other cube is