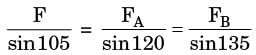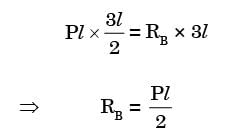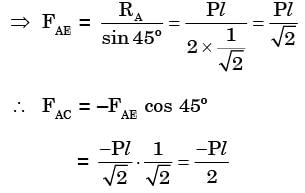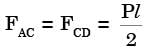Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
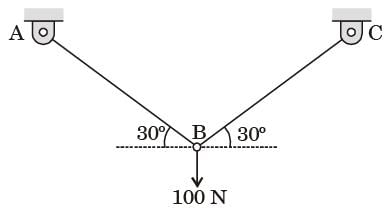
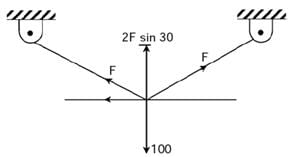
Try yourself:Two identical trusses support a load of 100 N as shown in the figure. The length of each truss is 1.0 m, cross-sectional area is 200 mm2; Young's modulus E = 200 GPa. The force in the truss AB (in N) is
[2015]
Explanation
⇒ 2F sin 30 = 100
⇒ F = 100 N
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
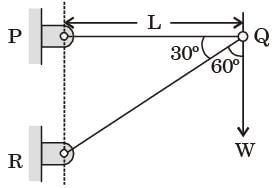
Try yourself:A two member truss PQR is supporting a load W. The axial forces in members PQ and QR are respectively
[2016]
Explanation
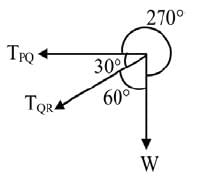
Lami’s theorem is used to find the F
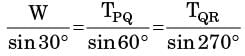
⇒ TPQ = √3W(T)
⇒ TQR = – 2W = 2W(C)
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
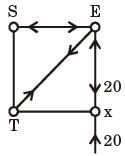
Try yourself:For the truss shown in the figure, the magnitude of the force (in kN) in the member SR is
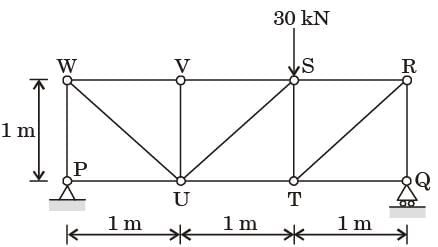
[2015]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
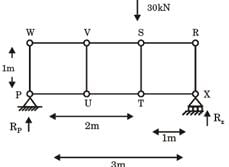
Try yourself:For the truss shown in figure, the magnitude of the force in member PR and the support reaction at R are respectively
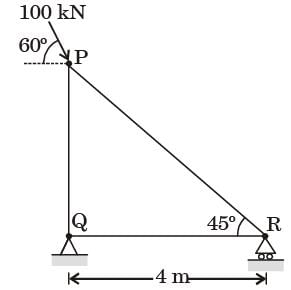
[2015]
Explanation
∑MQ = 0
100 × cos 60 × 4 = Ra × 4
⇒ Ra = 50 kN
FPR × cos 45 = 100 cos 60
⇒ FPR = 70.71 kN
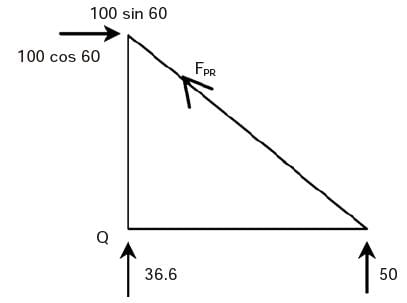
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
Try yourself:For the truss shown in the figure, the forces F1 and F2 are 9 kN and 3 kN, respectively. The force (in kN) in the member QS is (All dimensions are in m)
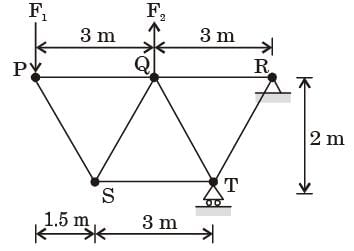
[2014]
Explanation
By method of sections
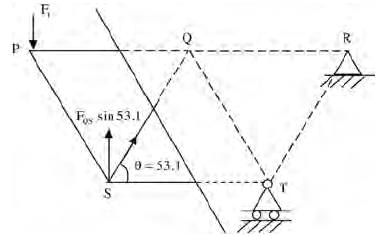
∑V = 0
F1 = FQS si n 53.1
⇒ FQS = 11.25(T)
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
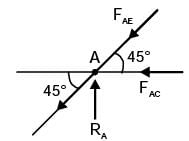
Try yourself:Two steel truss members, AC md BC, each having cross sectional are of 100 mm2, are subjected to a horizontal force F as shown in figure. All the joints are hinged.
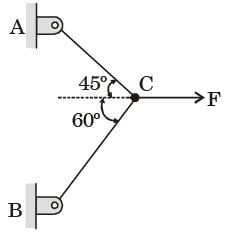
The maximum force F in kN that can be applied at C such that the axial stress in any of the truss members DOES NOT exceed 100 MPa is
[2012]
Explanation
From Lami’s theorem,
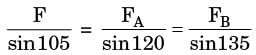
⇒ FA = 0.8965 F; FB = 0.732 F
Hence maximum force is FA
and stress = FA/Area = 100 MPa
∴ 0.8965 F/100 = 100 MPa
⇒ F = 11154.48 N or 11.15 k N
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
Try yourself:Two steel truss members, AC md BC, each having cross sectional are of 100 mm2, are subjected to a horizontal force F as shown in figure. All the joints are hinged.
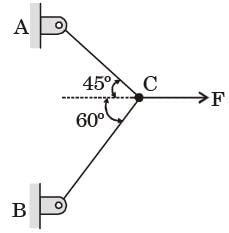
If F = 1 kN, the magnitude of the vertical reaction force developed at the point B in kN is
[2012]
Explanation
Vertical reaction at point B,
RB = FB cos 30 = 0.633 F
F = 1k N
∴ RB = 0.633 kN
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
Try yourself:Consider a truss PQR loaded at P with aforce Fas shown in the figure.
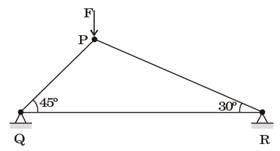
The tension in the number QR is
[2008]
Explanation
TPQ cos 40° + TPR cos 60° + F = 0
and TPQ sin 40° = TPR sin 60°
From these equations
TPQ and TPR can be found in terms of F
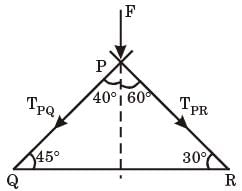
Now at Q, T TQR = TPQ cos 45°
Solving these equations, we get
TQR = 0.63 F
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
Try yourself:The figure shows a pin-jointed plane truss Ioaded at the point M by hanging a mass of 100 kg. The member LN of the truss is subjected to a load of
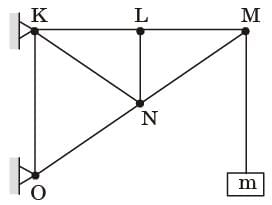
[2004]
Explanation
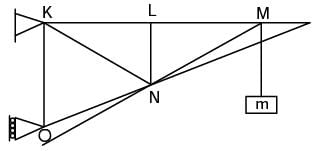
Consider all forces at point L
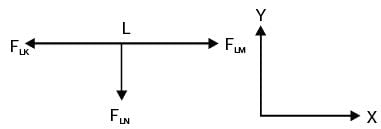
Summation of all forces along x-direction,
FLK = FLM
Summation of all forces along y-direction,
FLN = 0
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Structural Analysis
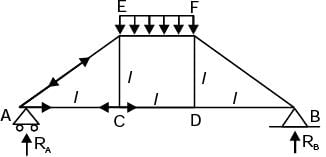
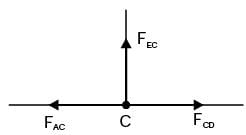
Try yourself:A truss consists of horizontal members (AC, CD, DB and EF) and vertical members (CE and DF) having length l each. The-members AE, DE and BF are inclined at 45° to the horizontal For the uniformly distributed load p per unit length on the members EF of the truss shown in figure given below, the force in the member CD is
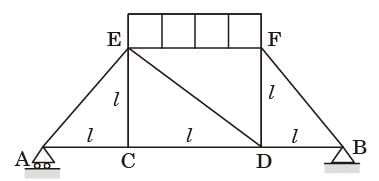
[2003]
Explanation
Report a problem


















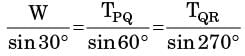
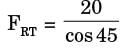 (i)
(i)