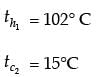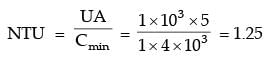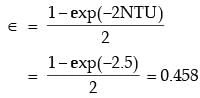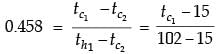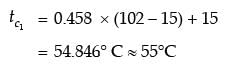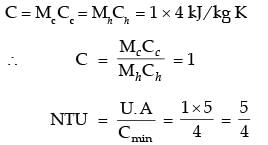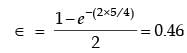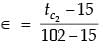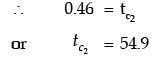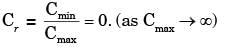Q1: A condenser is used as a heat exchanger in a large steam power plant in which steam is condensed to liquid water. The condenser is a shell and tube heat exchanger which consists of 1 shell and 20,000 tubes. Water flows through each of the tubes at a rate of 1 kg/s with an inlet temperature of 30° C. The steam in the condenser shell condenses at the rate of 430 kg /s at a temperature of 50 ° C. If the heat of vaporization is 2.326 MJ/k g and specific heat of water is 4 kJ/(kg. K), the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is ______ (rounded off to 3 decimal places).
Ans: (0.59 to 0.633)
no. of tube, n = 20, 000
 w = 1 kg/sec/ per tube
w = 1 kg/sec/ per tube
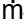 s = 430 kg/sec
s = 430 kg/sec
So,
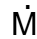 w = n x
w = n x 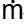 w
w
= 20000 x 1 = 20000 kg/sec
LHC = 2.236MJ/kg
C = 4 kJ/kgK
C min = Mw x C = 20000 x 4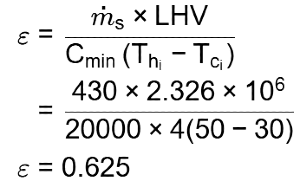
Q2: A plane, solid slab of thickness L , shown in the figure, has thermal conductivity k that varies with the spatial coordinate x as k = A + B x, where A and B are positive constants ( A > 0 , B > 0 ). The slab walls are maintained at fixed temperature of T ( x = 0 ) = 0 and T ( x = L ) = T0 > 0 . The slab has no internal heat sources. Considering one dimensional heat transfer, which one of the following plots qualitatively depicts the steady-state temperature distribution within the slab? [GATE ME 2024]
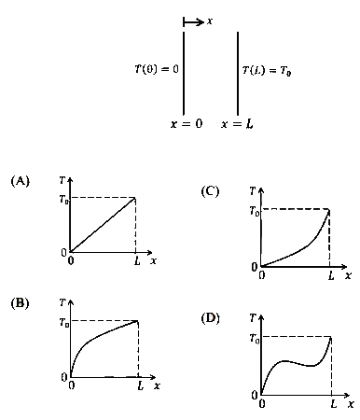 (a) A
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans: (b)
Give: k = A + Bx
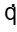 g → 0
g → 0
As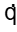 = - KA dT/dX
= - KA dT/dX
or, 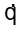 /A = C
/A = C
= - k (dT/dX) for steady state
So, -k (dT/dX) = constant
or, - (A + Bx) dT/dX = C
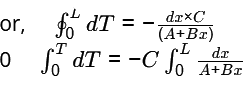
So, temperature distribution will follow logarithmic curve.
Q1: Consider a counter-flow heat exchanger with the inlet temperatures of two fluids (1 and 2) being T1 , in = 300 K and T2 , in = 350 K The heat capacity rates of the two fluids are C1 = 1000 W/ KC1 =1000W/K and C2 = 400 W/K C, and the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is 0.5. The actual heat transfer rate is _____ kW. (Answer in integer) [GATE ME 2023]
Ans: (9.999 to 10.001)
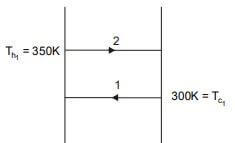 Data given
Data given
C1 = 1000 W/K
C2 = 400 W/K
ϵ = qactual/qmax
for qmax, C should be minimum
So, Cmin = C2
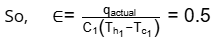
qactual = 0.5 x 400 (350 - 300)
= 10kW
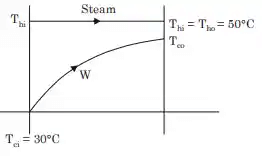
Q1: Saturated vapor at 200 ° C condenses to saturated liquid at the rate of 150 kg/s on the shell side of a heat exchanger (enthalpy of condensation h fg = 2400 kJ/ kg ). A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ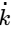 g − 1
g − 1 − 1 enters at 100 ° C on the tube side. If the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is 0.9, then the mass flow rate of the fluid in the tube side is ____ kg/s (in integer). [GATE ME 2022,SET-2]
− 1 enters at 100 ° C on the tube side. If the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is 0.9, then the mass flow rate of the fluid in the tube side is ____ kg/s (in integer). [GATE ME 2022,SET-2]
Ans: (1000 to 1000)
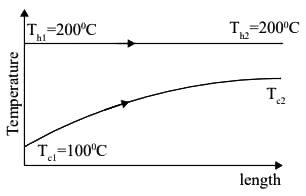 Hot fluid
Hot fluid
Th1 = Th2 = 200° C
ṁ h = 150kg/s
= hfg = 2400kj/kg
Cold fluid
Tc1 = 100° C
ϵ = 0.9
ṁc = ? kg/ sec
If fluid is under phase change then that fluid have in finite heat capacity rate.
In this case hot fluid is under phase change so C max = ∞
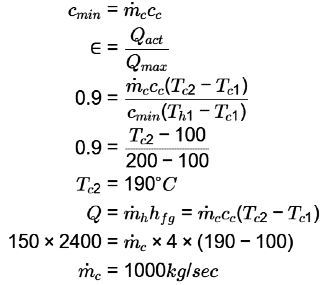
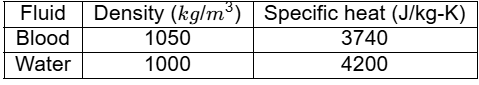
Q2: During open-heart surgery, a patient ?s blood is cooled down to 25°C from 37°C using a concentric tube counter-flow heat exchanger. Water enters the heat exchanger at 4°C and leaves at 18°C. Blood flow rate during the surgery is 5 L/minute. Use the following fluid properties:
Effectiveness of the heat exchanger is _________ (round off to 2 decimal places). [GATE ME 2022, SET-1]
Ans: (0.4 to 0.44)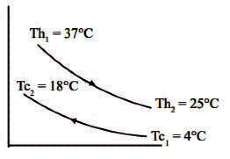 For preferred heat exchange between load and water.
For preferred heat exchange between load and water.
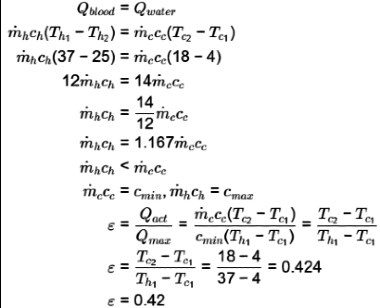
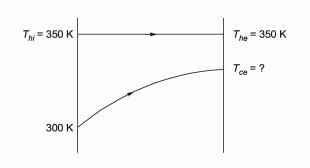
Q1: A shell and tube heat exchanger is used as a steam condenser. Coolant water enters the tube at 300 K at a rate of 100 kg/s. The overall heat transfer coefficient is 1500 W/m 2. K, and total heat transfer area is 400 m2 . Steam condenses at a saturation temperature of 350 K. Assume that the specific heat of coolant water is 4000 J/kg.K. The temperature of the coolant water coming out of the condenser is _______K (round off to the nearest integer). [GATE ME 2021, SET-2]
Ans: (337 to 341)
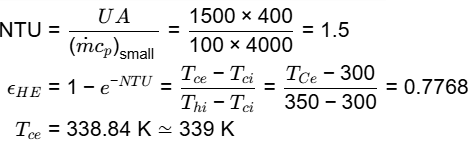
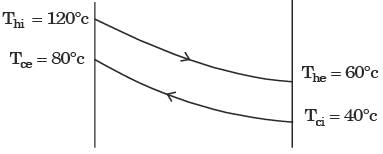
Q1: In a concentric tube counter-flow heat exchanger, hot oil enters at 102 °C and leaves at 65°C. Cold water enters at 25 °C and leaves at 42°C. The log mean temperature difference (LMTD) is ______°C (round off to one decimal place) [GATE ME 2020, SET-1]
Ans: (48.8 to 49.8)
Thi = 102°C, The = 65°C,
Tc, i = 25°C, Tce = 42°C
LMTD = (ΔT1 - ΔT2) / ln(ΔT1 / ΔT2)
ΔT1 = 102°C - 42°C = 60°C
ΔT2 = 65°C - 25°C = 40°C7
LMTD = (60 - 40) / ln(60 / 40) = 20 / 0.4054 = 49.3°C
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In shell and tube heat exchanger, baffles are mainly used to
[1991]
Explanation
Baffles are used to deflect the flow.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:The practice to use steam on the shell side and water on the tube side in condensers of steam power plant is because
[1994]
Explanation
Air leaked into the condensor can be easily extracted.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:Hot oil is cooled from 80 to 50°C in an oil cooler which uses air as the coolant. The air temperature rises from 30 to 40°C. The designer uses a LMTD value of 26°C. The type of heat exchanger is
[2005]
Explanation
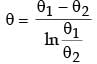
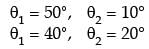
As given value is between these two, so cross flow is the best option.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In a heat exchanger, it is observed that ΔT1 = ΔT2 where ΔT1 is the temperature difference between the two single phase fluid streams at one end and ΔT2 is the temperature difference at the other end. This heat exchanger is
[2014]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In certain heat exchanger, both the fluids have identical mass flow rate specific heat product. The hot fluid enters at 76°C and leaves at 47°C, and the cold fluid entering at 28°C leave at 55°C, the effectiveness of the HE is
[1997]
Explanation
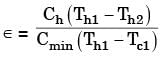
Here, Ch = Cc.
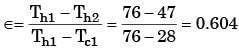
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In a counter flow heat exchanger, for the hot fluid the heat capacity = 2 kJ/kgK, mass flow rate = 5 kg/s, inlet temperature = 150°C, outlet temperature = 100°C. For the cold fluid, heat capacity = 4 kJ/kg K, mass flow rate = 10 kg/s, inlet temperature = 20°C. Neglecting heat transfer to the surroundings, the outlet temperature of the cold fluid in °C is
[1994]
Explanation
Heat lost by fluid = Heat gained by cold fluid
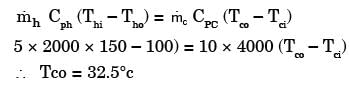
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
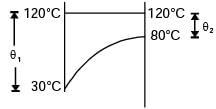
Try yourself:In a condenser, water enters at 30°C and flows at the rate 1500 kg/hr. The condensing steam is at a temperature of 120°C and cooling water leaves the condenser at 80°C. Specific heat of water is 4.187 kJ/kgK. If the overall heat transfer coefficient is 2000 W/m2K, the heat transfer area is
[2005]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:An industrial gas (c = 1 kJ/kgK) enters a parallel flow heat exchanger at 250°C with a flow rate of 2 kg/s to heat a water stream. The water stream (c = 4 kJ/kgK) enters the heat exchanger at 50°C with a flow rate of 1 kg/s.The heat exchanger has an effectiveness of 0.75. The gas stream exit temperature will be
[2010]
Explanation
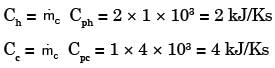
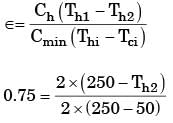
Th2 = 100°C
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:Cold water flowing at 0.1 kg/s is heated from 20°C to 70°C in a counter flow type heat exchanger by a hot water stream flowing at 0.1 kg/s and entering at 90°C. The specific heat of water is 4200 J/(kgK) and density is 1000 kg/m3. If the overall heat transfer coefficient U for the heat exchanger is 2000 W/(m2K), the required heat exchange area (in m2) is
[2011]
Explanation
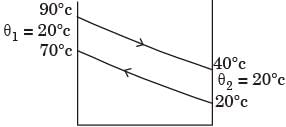
Ch = Cc = 0.1 × 4200 = 420 J/s
Cc (Tc1 – Tc2) = Ch (Th1 – Th2)
(70 – 20) = 90° Th2
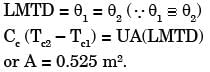
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:A balanced counter flow heat exchanger has a surface area of 20 m2 and overall heat transfer coefficient of 20 W/m2K. Air (cp = 1000 J/kgK) entering at 0.4 kg/s and 280 K is to be preheated by the air leaving the system at 0.4 kg/s and 300 K. The temperature (in K) of the preheated air is
[2015]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In a counter-flow heat exchanger, water is heated at the rate of 1.5 kg/s from 40°C to 80°C by an oil entering at 120°C and leaving at 60°C. The specific heats of water and oil are 4.2 kJ/ kgK and 2 kJ/kgK, respectively. The overall heat transfer coefficient is 400 W/m2K.The required heat transfer surface area (in m2) is
[2007]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:Air enters a counter flow HE at 70°C and leaves at 40°C. Water enters at 30°C and leaves at 50°C, the LMTD in degree C is
[2000]
Explanation
∴ ΔT1 = 70 - 50 = 20°C, ΔT2 = 40 - 30 = 10°C
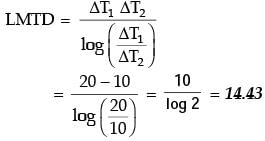
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:For the same inlet and exit temperatures of the hot and cold fluids, the log mean temperature difference (LMTD) is
[2002]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In a counterflow heat exchanger, hot fluid enters at 60°C and cold fluid leaves at 30°C. Mass flow rate of the hot fluid is 1 kg/s and that the cold fluid is 2 kg/s. Specific heat of the hot fluid is 10 kJ/kgK and that of the cold fluid is 5 kJ/kgK. The Log Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) for the heat exchanger in °C is
[2007]
Explanation
Heat capacity of hot fluid
= 1 × 10 = 10 kJ / k – s
Heat capacity of cold fluid
= 2 × 5 = 10 kJ / k – s
Since heat capacity is same, so LMTD is difference of temperature at either end
i.e. LMTD = 60º – 30º = 30º C
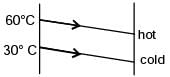
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:The logarithmic mean temperature difference (LMTD) of a counter flow heat exchanger is 20°C. The cold fluid enters at 20°C and the hot fluid enters at 100°C. Mass flow rate of the cold fluid is twice that of the hot fluid. Specific heat at constant pressure of the hot fluid is twice that of the cold fluid. The exit temperature of the cold fluid
[2008]
Explanation
θ1 = θ2
∴ θm = 20°C
Th1 – Tc2 = 20°C
100 – Tc2 = 20°C
Tc2 = 80°C
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In a condenser of a power plant, the steam condenses at a temperature of 60°C. The cooling water enters at 30°C and leaves at 45°C. The Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) of the condenser is
[2011]
Explanation
Flow configuration in condenser as shown below.
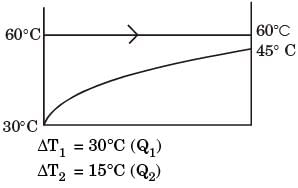
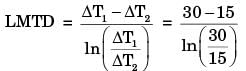
= 21.6° C
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:Water (c = 4.18 kJ/kgK) at 80°C enters a counter flow heat exchanger with a mass flow rate of 0.5 kg/s. Air (c = 1 kJ/kgK) enter at 30°C with a mass flow rate 2.09 kg/s. If the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is 0.8, the LMTD (in °C) is
[2012]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:For a heat exchanger, ΔTmax is the maximum temperature difference and ΔTmin is the minimum temperature difference between the two fluids. LMTD is the log mean temperature difference. Cmin and Cmax are the minimum and the maximum heat capacity rates. The maximum possible heat transfer (Qmax) between the two fluids is
[2014]
Explanation
The temperature difference is not for a given fluid but across the fluids and maximum heat transfer occurs for Cmin and the temperature difference is equal to 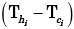 .
.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:In a parallel flow heat exchanger operating under steady state, the heat capacity rates (product of specific heat at constant pressure and mass flow rate) of the hot and cold fluid are equal. The hot fluid, flowing at 1 kg/s with cp = 4 kJ/kgK, enters the heat exchanger at 102°C while the cold fluid has an inlet temperature of 15°C. The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger is estimated to be 1 kW/m2K and the corresponding heat transfer surface area is 5 m2. Neglect heat transfer between the heat exchanger and the ambient. The heat exchanger is characterized by the following relation:
2ε = 1 - expt(-2NTU). The exit temperature (in °C) for the cold fluid is
[2009]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Exchangers
Try yourself:Saturated vapor is condensed to saturated liquid in a condenser. The heat capacity ratio is 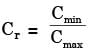 The effectiveness (e) of the condenser is
The effectiveness (e) of the condenser is
[2015]
Explanation
ε of condenser is given by 1-exp(-NTU)
Because 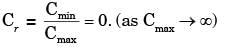
Report a problem

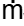 w = 1 kg/sec/ per tube
w = 1 kg/sec/ per tube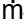 s = 430 kg/sec
s = 430 kg/sec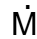 w = n x
w = n x 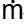 w
w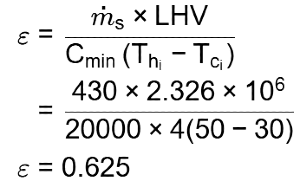
 (a) A
(a) A g → 0
g → 0 = - KA dT/dX
= - KA dT/dX /A = C
/A = C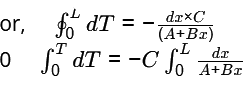
 Data given
Data given
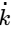 g − 1
g − 1 − 1 enters at 100 ° C on the tube side. If the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is 0.9, then the mass flow rate of the fluid in the tube side is ____ kg/s (in integer). [GATE ME 2022,SET-2]
− 1 enters at 100 ° C on the tube side. If the effectiveness of the heat exchanger is 0.9, then the mass flow rate of the fluid in the tube side is ____ kg/s (in integer). [GATE ME 2022,SET-2] Hot fluid
Hot fluid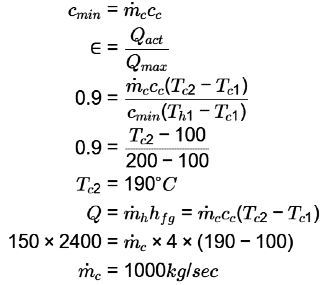

 For preferred heat exchange between load and water.
For preferred heat exchange between load and water.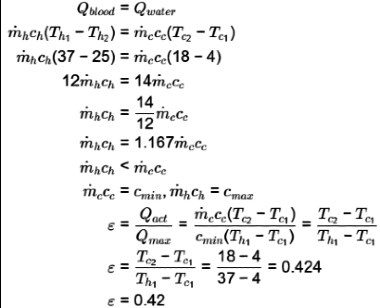

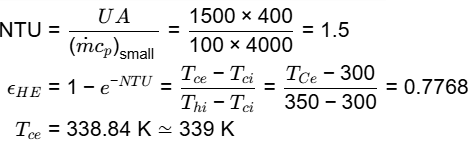
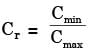 The effectiveness (e) of the condenser is
The effectiveness (e) of the condenser is






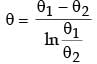
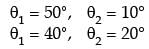
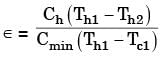
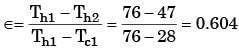
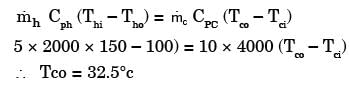
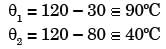
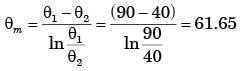
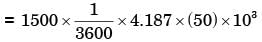
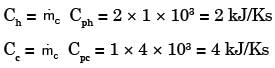
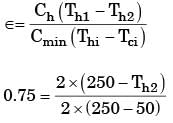

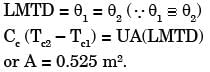
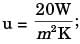 Temperature Tci = 280K
Temperature Tci = 280K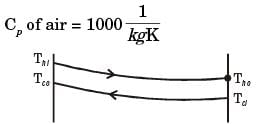
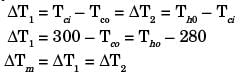
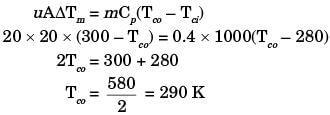
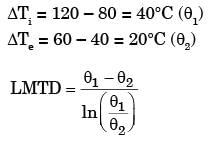
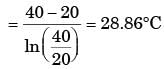
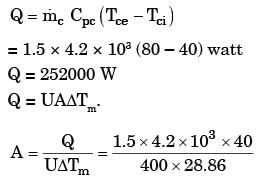
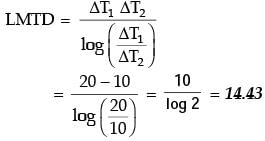


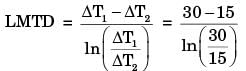
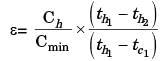
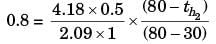
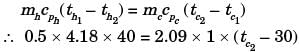
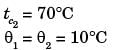
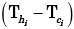 .
.