GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics | Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: A liquid fills a horizontal capillary tube whose one end is dipped in a large pool of the liquid. Experiments show that the distance L travelled by the liquid meniscus inside the capillary in time t is given by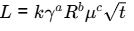
where γ is the surface tension, R is the inner radius of the capillary, and μ μ is the dynamic viscosity of the liquid. If k is a dimensionless constant, then the exponent a a is _____ (rounded off to 1 decimal place). [GATE ME 2024]
Ans: (0.5 to 0.5)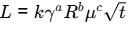
Dimensions - length, L = [ L ]
Surface Tension, γ = [ M T− 2]
Radius, R = [L]
Dynamic viscosity, μ = [M L− 1 T− 1 ]
Time, t = [T]
K is dimensionless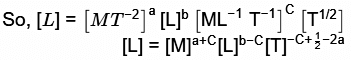
So, a + c = 0 ⇒ c =−a
-2a - c + 1/2 = 0
-a + 1/2 = 0
⇒ a = 1/2
⇒ a = 0.5
Q1: A tube of uniform diameter D is immersed in a steady flowing inviscid liquid stream of velocity V, as shown in the figure. Gravitational acceleration is represented by g. The volume flow rate through the tube is ______. [GATE ME 2022, SET-2]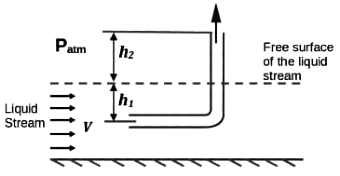 (a) π/4 D2V
(a) π/4 D2V
(b) π/4 D2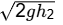
(c) π/4 D2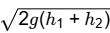
(d) π/4 D2 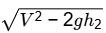
Ans: (d) 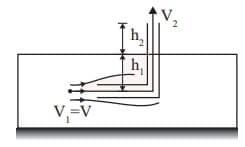
By applying Bernoulli's equation between (1) and (2)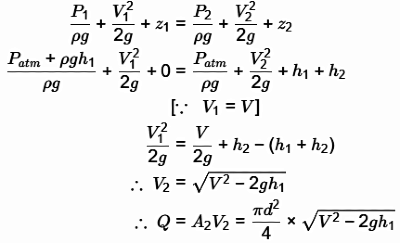
Q2: Consider steady, one-dimensional compressible flow of a gas in a pipe of diameter 1 m. At one location in the pipe, the density and velocity are 1 kg/m3 and 100 m/s, respectively. At a downstream location in the pipe, the velocity is 170 m/s. If the pressure drop between these two locations is 10 kPa, the force exerted by the gas on the pipe between these two locations is ____________ N. [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
(a) 350π2
(b)750π
(c) 1000π
(d) 3000
Ans: (b)
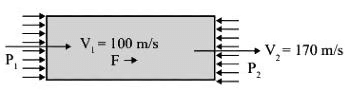
Applying momentum equation to the pipe flow,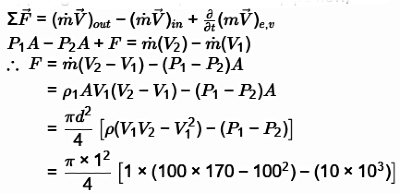
= - 750π N
Negative sign shows that assumed direction of force is opposite of actual direction.
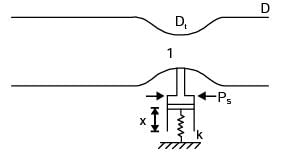
Q1: A cylindrical jet of water (density = 1000 kg/m3) impinges at the center of a flat, circular plate and spreads radially outwards, as shown in the figure. The plate is resting on a linear spring with a spring constant k = 1 k N/m k. The incoming jet diameter is D=1cm.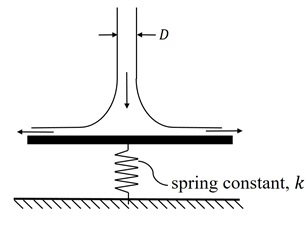
If the spring shows a steady deflection of 1 cm upon impingement of jet, then the velocity of the incoming jet is _______m/s (round off to one decimal place). [GATE ME 2021, SET-1]
Ans: (11.2 to 11.4)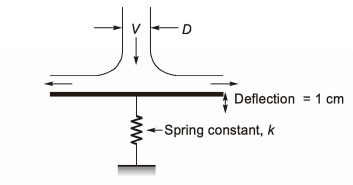 δ = 1cm
δ = 1cm
D = 1cm
p = 1000 kg/m3
K = 1kN - m
Force due to jet = Spring force
pAV2 = kx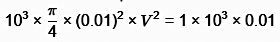
V = 11.28 m/s ≃ 11.3 m/s
4 [2005]
[2005]
[2003]
[1999]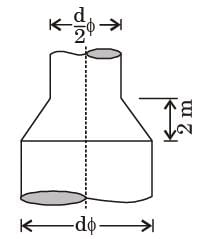
[1990]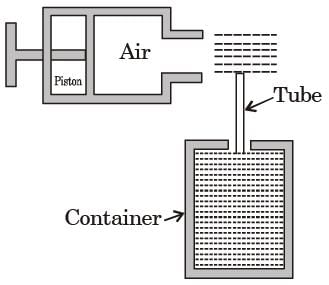
[2018, Set-2]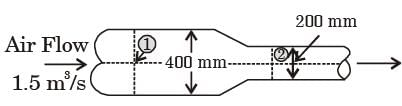
[2015,Set-2]
[2009]
The cross-sectional'area of all three pipelines are constant. The following data is given
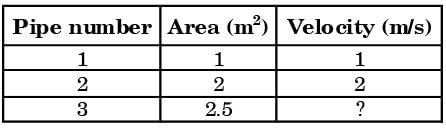
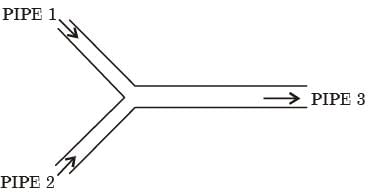
Assuming the water properties and the velocities to be uniform across the cross-section of the inlets and the outlet, the exit velocity (in m/s) in pipe 3 is
[2009]
[2004]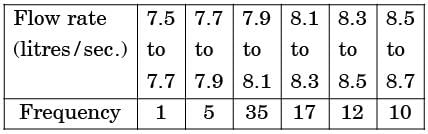
Mean flow rate of the liquid is
[2000]
|
56 videos|146 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics - Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is fluid dynamics? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of fluid dynamics? |  |
| 3. What are the fundamental principles of fluid dynamics? |  |
| 4. How is fluid dynamics related to Bernoulli's principle? |  |
| 5. What are some common challenges in studying fluid dynamics? |  |

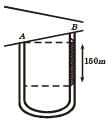
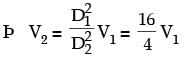
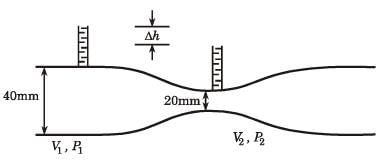
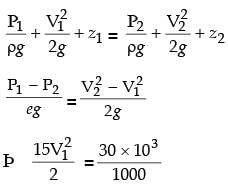
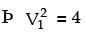
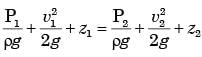
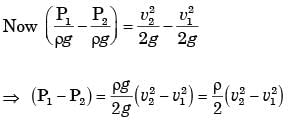
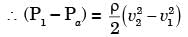
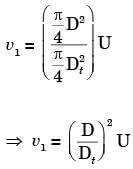
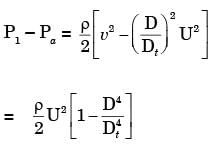
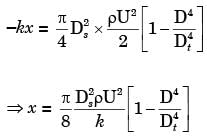
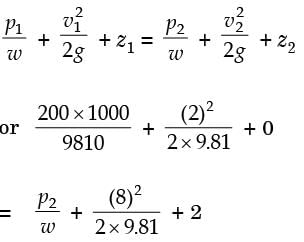
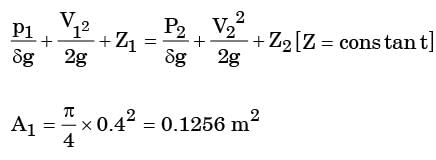
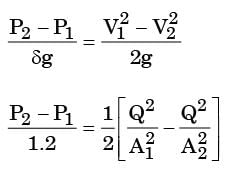
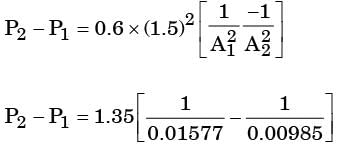
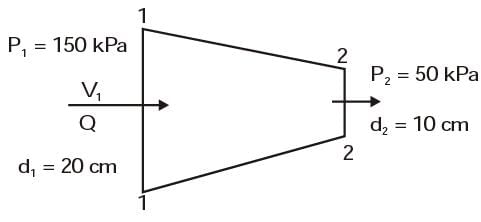
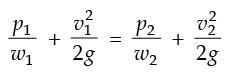
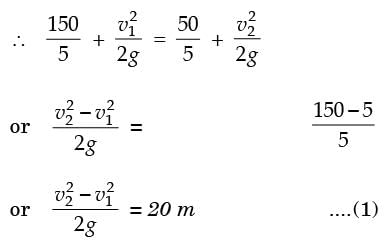
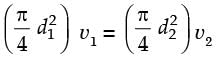
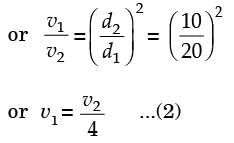
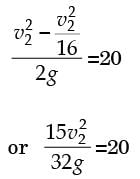
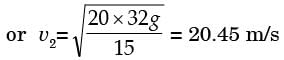
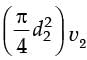
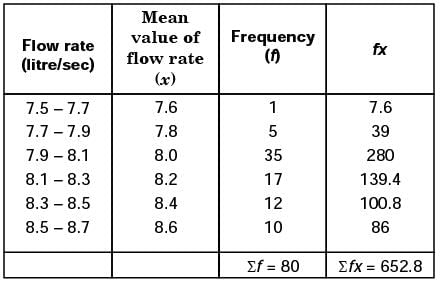
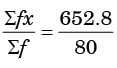 = 8.16.
= 8.16.



















