Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:The no. of normal modes of vibration of naphthalene is
[2017]
Explanation
Naphthalene (C₁₀H₈) has 10 carbon atoms and 8 hydrogen atoms.
-
Calculate the total number of atoms:
- Naphthalene has a total of 10 (carbon) + 8 (hydrogen) = 18 atoms.
-
Degrees of freedom:
- Each atom in a molecule has 3 degrees of freedom (x, y, z directions).
- Therefore, naphthalene has 18×3=54 degrees of freedom.
-
Translation and rotation degrees of freedom:
- For a non-linear molecule, there are 3 translational and 3 rotational degrees of freedom.
- Thus, the total number of vibrational modes is obtained by subtracting the translational and rotational degrees of freedom from the total degrees of freedom.
Normal modes of vibration=Total degrees of freedom−Translational degrees of freedom−Rotational degrees of freedom
Normal modes of vibration=54−3−3=48.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:From the kinetic theory of gases, the ratio of most probable speed (Cmp) to root mean square speed (Crms) is
[2016]
Explanation
From the kinetic theory of gases, the mathematical expression of the most probable speed and the root mean square speed are : Cmp = √[2RT/M] and Crms = V[3RT/M]
where, R = Universal gas constant, T = Absolute temperature and M = Molar mass of gas
Cmp/Crms = √2/√3
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:The relationship between van der Waals 'b' co-efficient of N2 and O2 is
1. b(N2) = b(O2) = 0 ;
2. b(N2) = b(O2) ≠ 0 ;
3. b(N2) > b(O2) ;
4. b(N2) < b(O2)
[2016]
Explanation
In the van der Waals equation, b term stands for the volume correction term. Its value is given by : b = 4 NA (4/3) πr3 ; where r = radius of the gas molecule From the equation, it is evident that as the value of r increase, b value will also increase. As O atom is smaller than N atom, 0 2 has smaller r value than N2. Hence, b value will be smaller for O2 than N2.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:According to the equipartition principle, the predicted high temperature limiting value of the molar heat capacity at constant volume for C2H2 is
[2015]
Explanation
Acetylene (C2H2) is a tetra-atomic molecule. Hence, the total degree of freedom = 12. For linear tetra-atomic molecule, the translational, rotational and vibrational degree of freedoms are 3, 2 and 7 respectively. The translational, rotational and vibrational degree of freedom will contribute 1/2 kT, 1/2 kT and kT.
The translational kinetic energy, ∈ = 3/2 kT ; The rotational kinetic energy, ∈ = kT ; The vibrational kinetic energy, ∈ = 7 kT Hence, the total kinetic energy = 9.5 kT Hence, the molar kinetic energy, E = 9.5 NkT = 9.5 RT
Hence, the molar heat capacity at constant volume, Cv,m = d/dT[9.5 RT] = 9.5R
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:Among (l)Ar, (2)NH4CI, (3)HF and (4)HCl ,the strength of interatomic/intermolecular forces follows the order:
[2014]
Explanation
The major force present in Ar, NH4Cl, HF and HCl are London or, van der Walls force, ionic force, H-bonding as well as Debye force and Debye forces respectively. The order of strength of intermolecular force runs as : Ionic force > H-bond > Debye force > London force.
Hence, the strength interatomic/intermolecular forces follows the order : 2 > 3 > 4 > 1.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:According to the equipartition principle of energy, the molar heat capacity at constant volume for CO2(g), SO2(g) and H2O (g) follows the trend :
1. CO2 = SO2 = H2O ;
2. CO2 > SO2 = H2O ;
3. H2P > SP2 = CP2 ;
4. CO2 = SO2 > H2O
[2014]
Explanation
CO2 is a linear tri-atomic molecule while SO2 and H2O are non-linear tri-atomic molecules.
In case of CO2: It is a linear tri-atomic molecule. The total degrees of freedom = 3N = 9. The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees o f freedom for C 0 2 molecule are 3, 2 and 4 respectively. Hence, the total molar energy of the system, Emolar = 3/2 RT + 2/2 RT + 4 R T 13/2 RT.
Hence, the molar heat capacity at constant volume, Cv = (dE/dT)v =13/2 R = 6.5 R.
In case of SO2 and H2O : These are non-linear tri- atomic molecules. The total degrees of freedom = 3N = 9. The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedom for these molecule are 3, 3 and 3 respectively. Hence, the total molar energy of the system, Emolar =3/2 RT + 3/2 RT + 3RT = 6 RT.
Hence, the molar heat capacity at constant volume, Cv - (dE/dT)v = 6 R.
Hence, the molar heat capacity of CO2 at constant volume is greater than the molar heat capacity of H2O and SO2 at constant volume.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:The average speed of H2, N2 and O2 gas molecules is in the order
1. H2 > N2 > O2 ;
2. O2 > N2 > H2 ;
3. H2 > O2 > N2 ;
4. N2 > O2 > H2.
[2012]
Explanation
The mathematical expression for the average speed is as follows :
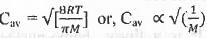
Hence, from the expression of Cav, it is evident that higher is the molecular weight of the gas molecule, lower will be the value of Cav.
The molecular weight of the following gas molecules is as follows : O2 > N2 > H2.
Hence, the average speed of the given gas molecules is as follow's : H2 > N2 > O2.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:Based on the principle of equipartition of energy, the molar heat capacity of CO2 at constant volume Cv,m is
[2011]
Explanation
The total energy of a molecule is the sum of its translational, rotational and vibrational energy. Carbon dioxide is a linear tri-atomic molecule. The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedom of CO2 are 3, 2 and (9 - 5) = 4 respectively. Hence, the translational, rotational and vibrational energies of CO2 molecule are .3/2RT, RT and 4RT. Hence, applying the principle of equipartition of energy, the molar heat capacity of CO2 at constant volume Cv.m = d/dT(3/2RT + RT + 4 RT) = d/dT(6.5RT) = 6.5R.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:The molar internal energy of a gas at temperature T is Um(T). The molar internal energy at T = 0 is Um(0). The correct expression that relates these two with appropriate contributions is
1. Um(T) = Um(0) + 3RT | Linear molecule ; translation only]
2. Um(T) = Um(0) + 5/2RT | Linear molecule ; translation and rotation only|
3. Um(T) = Um(0) + 3/2RT | Non-linear molecule ; translation and rotation only|
4. Um(T) = Um(0) + RT | Non-linear molecule ; translation only|.
[2010]
Explanation
In case o f linear and non-linear molecules, there are three translational degrees of freedom, each of which will contribute 1/2 RT. Hence, the total contribution towards internal energy is 3/2 RT.
In case of linear' molecule, there are two rotational degrees of freedom, each of which will contribute 1/2 RT. Hence, the total contribution towards internal energy is RT.
In case of non-linear molecule, there are three rotational degrees of freedom, each of which will contribute 1/2 RT. Hence, the total contribution towards internal energy is 3/2 RT.
Hence, in case of linear molecule, the total contribution towards internal energy by translational and rotational degrees of freedom : (3/2 + 1)RT = 5/2 RT.
Hence, in case of linear molecule the molar internal energies of the gas at temperature T, Um(T) and at T = 0., Um(0) are related as : Um(T) = Um(0) + 5/2RT (Considering translation and rotation only).
Hence, Ihe correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:Consider two identical containers, one with 1 mole of H2 and the other with 1 mole of He. If the root-mean-square ( RMS ) velocities of two gases are the same , then the ratio of the temperature T(H2)/T(He) is
[2009]
Explanation
The expression o f root-meati-square velocity is Vrms = (3 RT/M)(1/2)
According to the question,
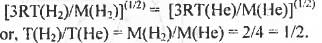
Hence, the ratio T(H2)/T(He) has the value 1/2. Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:For an ideal gas, the plot that is NONLINEAR is
1. PV vs. T ;
2. PV vs. P, at constant T ;
3. P vs. V, at constant T ;
4. In P vs. In V, at constant T.
[2009]
Explanation
The equation of state for an ideal gas is as follows : PV = nRT
Where, P = pressure of the gas ; V = volume of the gas ; n = no. of moles of the gas
T = absolute temperature of the gas ; R = Universal gas constant.
From this relation one can easily written PV = K = Constant
Hence, a plot of P vs. V will be a rectangular parabola which is non-iinear in nature.
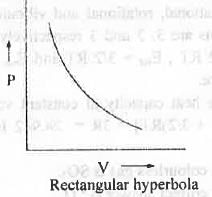
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:Given that the most probable speed of oxygen gas is 1000 ms-1, the average speed under the same conditions is
[2008]
Explanation
We know that the most probable speed is given by :
Cmp = (2RT/M)(1/2) =1000
or, 2RT/M= 1000000
or, T = 500000M/R
The average speed is given by
Cav = (8RT/πM)(1/2) = {(8R X 500000M)/(RMπ)}(1/2)
=1128 ms-1
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:The Maxwell-Boitzmann distribution for molecule speeds is shown in the following figure.
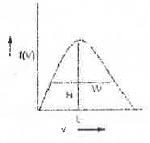
In the figure, H is the height of the peak, L is the location of the maximum and W is the width at half height. As the temperature is decreased
1. H increases, L decreases and W increases ;
2. M Increases, L decreases and W decreases ;
3. H decreases, L Increases and W increases ;
4. H decreases, L decreases and W decreases.
[2006]
Explanation
- The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes how the speeds of molecules in a gas vary with temperature.
- As temperature decreases:
- H (Height): Increases. Lower temperature means more molecules have speeds close to the average, increasing peak height.
- L (Location of Maximum): Decreases. Lower temperature means the most probable speed decreases.
- W (Width at Half Height): Decreases. Lower temperature leads to a narrower distribution of speeds.
- Therefore, option C is correct: H decreases, L decreases, and W decreases.
From the above diagram, it is evident that as the temperature is increased, broadening of the curve occurs. Hence, the curve maximum shift towards right and it become flatten. Hence, the height of the peak decreases while the location of the peak increases and also width at the half height increases.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:The molar heat capacity at constant volume of a colourless gas is found to be 25 J/mol/K. at room temperature. The gas must be
[2006]
Explanation
In case of N2 : It is a linear, homo-nuclear diatomic molecule. Hence, the total degrees of freedom = 3.2 = 6.
The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedoms are 3, 2 and 1 respectively. Hence, the Etrans = 3/2 RT ; Erot = RT and Evib = 0 at room temperature.
Hence, the heat capacity at constant volume, Cv = d/dT [(3/2 + 1 )RT] = 5/2R = 20.785 J/mol/K In case of O2 : It is a linear, homo-nuclear diatomic molecule. Hence, the total degrees of freedom = 3.2 = 6.
The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedoms are 3, 2 and 1 respectively. Hence, the Etrans = 3/2 RT ; Erot = RT and EVib = 0 at room temperature.
Hence, the heat capacity at constant volume, Cv = d/dT [(3/2 + 1)RT] = 5/2R = 20.785 J/mol/K
In case of CO2 : It is a linear, hetero-nuclear triatomic molecule. Hence, the total degrees of freedom = 3.3=9.
The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedoms are 3, 2 and 4 respectively. Hence, the Etrans = 3/2 RT ; Erot = RT and EVib = 0 at room temperature.
Hence, the heat capacity at constant volume, Cv = d/dT [(3/2 + 1)RT] = 5/2R = 20.785 J/mol/K
In case of SO2 : It is a non-linear, hetero-nuclear triatomic molecule. Hence, the total degrees of freedom = 3.3 = 9.
The translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedoms are 3, 3 and 3 respectively. Hence, the Etrans = 3/2 RT ; Erot = 3/2 RT and Evib = 0 at room temperature.
Hence, the heat capacity at constant volume, Cv = d/dT [(3/2 + 3/2)RT] = 3R = 24.942 J/mol/K = 25 J/mol/K.
Hence, the colourless gas is SO2.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Questions: Theory of Gases
Try yourself:For the distribution of molecular velocities of gases, identify the correct order from the following (where vmp, , vav and vrms are the most probable velocity , average velocity and root mean square velocity respectively):
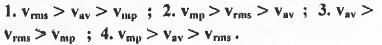
[2005]
Explanation
The most probable velocity (vmp), average velocity (vav) and root mean square velocity (vrms) are defined as :
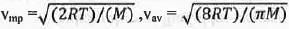
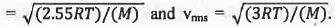 From these equations it is clear that the value of root the mean square velocity is highest while the value of the most probable velocity is lowest. Hence, the decreasing order of various types of velocities : vrms > Vav > Vmp.
From these equations it is clear that the value of root the mean square velocity is highest while the value of the most probable velocity is lowest. Hence, the decreasing order of various types of velocities : vrms > Vav > Vmp.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem

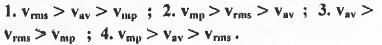






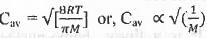
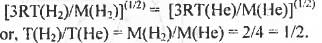

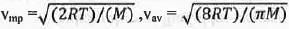
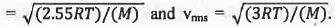 From these equations it is clear that the value of root the mean square velocity is highest while the value of the most probable velocity is lowest. Hence, the decreasing order of various types of velocities : vrms > Vav > Vmp.
From these equations it is clear that the value of root the mean square velocity is highest while the value of the most probable velocity is lowest. Hence, the decreasing order of various types of velocities : vrms > Vav > Vmp. 















