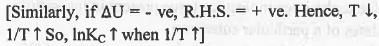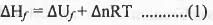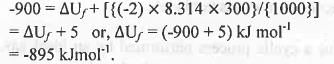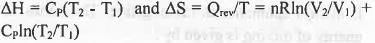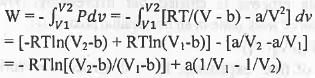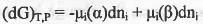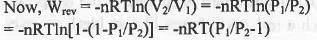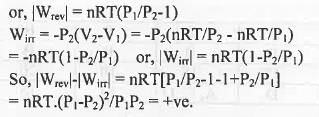*Multiple options can be correct
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:Intensive variable(s) is/are
[2017]
Explanation
The properties which are independent on the mass of a system are known as intensive properties while the properties which are dependent on the mass of the system are known as extensive properties.
The ratio of any two extensive properties is an example of an intensive property.
Temperature and pressure are independent on the mass of the system. That's why these are examples of intensive properties. Density is the ratio of mass and volume. Both mass and volume are dependent on the mass of the system. That's why these are extensive properties. Hence, their ratio i.e. density is an intensive property.
Hence, the correct answers are : (A, C, D).
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:A straight line having a slope -ΔU°/R is obtained in a plot between
[2017]
Explanation
We know that : dlnKP/dT = ΔH/RT2 (Van't Hoff equation) But, when we consider KP, it signifies that that at constant pressure equilibrium constant which corresponds to the energy term also at constant pressure which is ΔH.
Similarly, we can consider : dlnKC/dT = ΔU/RT2 at constant volume
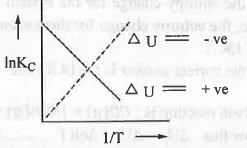
Hence, ln(KC2/KC1) = - (ΔU°/R)[(1/T2) - (1/T1)] or, InKC ∝ - ΔU°/RT
If ΔU° = +ve, then T will decrease while 1/T will increase. Hence, R.H.S. of the equation become -ve.
So, InKC will decrease when 1/T will increase. Hence, a plot of lnKC vs. 1/T will be a straight line with slope = -ΔU°/R.
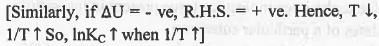
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:The correct order of entropy for various states of CO2 is
1. CO2 (s) > CO2 (I) > CO2 (g) ;
2. CO2 (1) > CO2 (s) > CO2 (g) ;
3. CO2 (g) > CO2 (I) > CO2 (s) ;
4. CO2 (g) > CO2 (s) > CO2 (1).
[2016]
Explanation
Entropy depends on the disorder!iness. Greater is the disorderliness, higher will be the entropy. The order of disorderliness of the various states of a particular substance is : gas > liquid > solid. This is due to the inter-molecular force present in the various states of a particular substance.
Hence, the order o f entropy for various states of CO2 is : CO2 (g) > CO2 (1 )> CO2 (s)
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:Which of the following thermodynamic relation(s) is/are correct?
1. (dT/dV)s = (dP/dS)v ;
2. (dT/dP)s = (dV/dS)p ;
3. (dS/dV)T = (dP/dT)v ;
4. (dS/dP)T = (dV/dT)P
[2015]
Explanation
The four fundamental equation of states of thermodynamics are :
dG = -SdT + VdP .. .(l), dA = -SdT-PdV . ..(2) dH = TdS + VdP ....(3), dU = TdS - PdV ......(4)
Differentiating equation (1) with respect to T at constant P, we have (dG/dT)P = - S .....(5)
Differentiating equation (5) with respect to P at constant T, (d2G/dPdT)T = - (dS/dP)T
Differentiating equation (1) with respect to P at constant T, we have (dG/dP)-T = V ..... (6)
Differentiating equation (6) with respect to T at constant P, (d2G/dTdP)P = (dV/dT)P
Hence, we obtain the following equation : (dV/dT)P = - (dS/dP)T
Differentiating equation (2) with respect to T at constant V, we have (dA/dT)V = - S ..... (7)
Differentiating equation (7) with respect to V at constant T, (d2A/dVdT)T = - (dS/dV)T
Differentiating equation (2) with respect to V at constant T, we have (dA/dV)T = - P ..... (8)
Differentiating equation (8) with respect to T at constant V, (d2A/dTdV)v = - (dP/dT)v
Hence, we obtain the following equation : (dS/dV)T= (dP/dT)v
Differentiating equation (3) with respect to S at constant P, we have (dH/dS)P = T ..... (9)
Differentiating equation (9) with respect to P at constant S, (d2H/dPdS)s = (dT/dP)s
Differentiating equation (3) with respect to P at constant S, we have (dH/dP)s = V ..... (10)
Differentiating equation (10) with respect to S at constant P, (d2H/dSdP)P = (dV/dS)P
Hence, we obtain the following equation : (dT/dP)s = (dV/dS)P
Differentiating equation (4) with respect to S at constant V, we have (dU/dS)P = T ..... (11)
Differentiating equation (11) with respect to V at constant S, (d2U/dVdS)s = (dT/dV)s
Differentiating equation (4) with respect to V at constant S, we have (dU/dV)s = - P ..... (12)
Differentiating equation (12) with respect to S at constant V, (d2U/dSdV)v = - (dP/dS)v
Hence, we obtain the following equation : (dT/dV)s = - (dP/dS)v
Hence, the correct answers are : (B, C).
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:For an isothermal free expansion of an ideal gas into vacuum, which one of the following set of values is correct
(1) ΔU = 0, q > 0, w < 0 ;
(2) ΔU > 0, q > 0, w = 0 ;
(3) ΔU = 0, q = 0, w = 0 ;
(4) ΔU < 0, q = 0, w < 0.
[2015]
Explanation
For isothermal process temperature remains constant. Hence, the change of internal energy, ΔU = [Cv(T2 - T1)] will be zero.
For free expansion work done will also become zero as expansion occurs against zero external pressure.. Mathematically, Wirr = - Pex(V2 - V1) = 0.
From the 1 st law of thermodynamics, q + W = ΔU
As both W and ΔU are zero, q will also become zero. Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:The standard enthalpy of formation 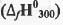 at 1 bar and 300 K for the formation of CICF2CF2CI (g) from its constituent elements in the standard state is - 900 kJ mol-1 . Given that R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1, the standard internal energy of formation
at 1 bar and 300 K for the formation of CICF2CF2CI (g) from its constituent elements in the standard state is - 900 kJ mol-1 . Given that R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1, the standard internal energy of formation 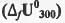 at the same pressure and temperature is
at the same pressure and temperature is
[2012]
Explanation
We know that 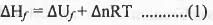
The equation for the formation of CICF2CF2CI (g) from its constituent elements in the standard state is :
2 C(s) + Cl2(g) + 2 F2(g) = ClCF2CF2Cl (g)
Hence, here Δn = 1-3 = -2 ; R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1
T = 300 K.
Putting these values in the equation (1), we have
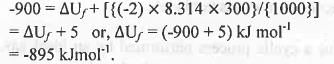
Hence, the standard internal energy of formation is : -895 kJmol-1.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:The enthalpy of vaporization(ΔHvap) is zero at
1. Boyle temperature ;
2. Critical temperature ;
3. Inversion temperature ;
4. Boiling temperature.
[2012]
Explanation
Boyle temperature is defined as the temperature at which a real gas behaves like an ideal gas over a certain range of pressure.
Critical temperature is defined as the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by applying pressure only.
Inversion temperature is the temperature at which no Joule-Thomson effect is observed.
Boiling temperature is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of a liquid become equal to the external pressure of atmosphere.
Enthalpy of vaporization is the enthalpy change when one mole of liquid is converted into vapour at its boiling temperature.
Hence, above critical temperature no liquid state will exist. Hence, at critical temperature the enthalpy of vaporization is zero.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
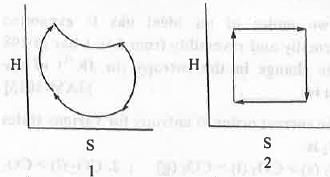
Try yourself:For an ideal gas undergoing reversible Carnot Cycle, the plot of enthalpy (H) vs. entropy (S) is
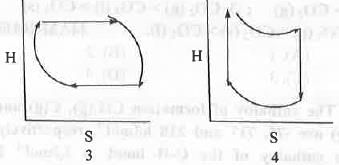
[2011]
Explanation
For reversible process the expression of enthalpy and entropy are as follows :
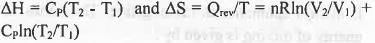
The four processes involved in the Carnot Cycle are : 1. Isothermal reversible expansion ; 2. Adiabatic reversible expansion ; C. Isothermal reversible compression ; D. Adiabatic reversible compression. In case of 1st step : Here, T is kept constant but volume increase. Hence, the change in enthalpy will be zero but the change in entropy will be positive.
In case of 2nd step : Here, Q is kept constant but T decrease. Hence, the change in entropy will be zero but the change in enthalpy will be negative.
In case of 3rd step : Here, T is kept constant but volume decrease. Hence, the change in enthalpy will be zero but the change in entropy will be negative.
In case of 4th step : Here, Q is kept constant but T increase. Hence, the change in entropy will be zero but the change in enthalpy will be positive.
Hence, all these four steps are properly explained by the graph 2.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:One mole of a van der Waals gas undergoes reversible isothermal transformation from an initial volume V1 to a final volume V2. The expression for the work done is
1. RTIn(V2/V1 )+ a(V2-V1) ;
2. -RTln[(V2-b)/(V1 - b)] + a(1/V1 - 1/V2) ;
3. RTIn(P2/P1) ;
4. RTln[(V2-b)/(V1 - b)] - a ( 1/V1 - 1/V2).
[2011]
Explanation
For one mole, the van der Waals equation of state is : (p + a/V2)(V - b) = RT or, P = RT/(V - b) - a/V2. The expression for the work done is :
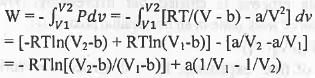
Hence, the correct answer i s : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:Choose the incorrect statement among the following:
1. When ideal gases are mixed, the entropy of mixing is positive ;
2. At equilibrium, the chemical potential of a species is the same in all of the phases of the system ;
3. The total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the each gas in the mixture ;
4. When a gas is allowed to expand, the maximum work is obtained when the process is carried out irreversibly.
[2010]
Explanation
For ideal gases, the Gibbs free energy of mixing is always spontaneous i.e. negative. The Gibbs free energy of mixing is given by :
ΔG mixing — ΔH mixing - TΔS mixing
For ideal solution, ΔHmixing is zero. H ence, ΔG mixing = - TΔS mixing. This in dicated that the entropy of mixing will be positive.
Let a species i is present in two phases α and β at constant T and P. If infinitesimal amount dnj of species i is transferred from phase α to the phase β, the Gibbs free energy change for this two-phase system will be : 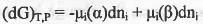
At equilibrium, 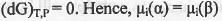
Hence, it can be concluded that at equilibrium, the chemical potential of a species is the same in all of the phases of the system .
The total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases will be the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. This is known as Daltons law of partial pressure.
Let an ideal gas expands reversibly and irreversibly from the initial pressure and volume P1 and V1 to the final pressure and volume P2 and V2 isothermally.
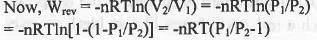
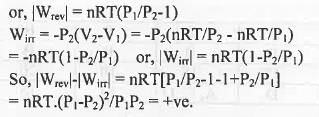
Hence, when a gas is allowed to expand, the maximum work is obtained when the process is carried out reversibly.
Hence, the incorrect statement is : When a gas is allowed to expand, the maximum work is obtained when the process is carried out irreversibly.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:The work done during the free expansion of one mole of an ideal gas at 27°C to twice its original volume is (Given : RT = 2494 J.mol-1, In 2 = 0.7, log 2 = 0.3).
[2010]
Explanation
This process is carried out irreversibly. The expression of work done in an irreversible process is :
Wirr = -Pex(V2-V1)
In case of free expansion, Pex = 0. Hence, the work done will also be zero.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:When 100 gm. of water is reversible heated from 50° C to 75° C at 1 atm, the change in entropy (JK-1) of the universe is
[2008]
Explanation
We know that the change in entropy of the universe is the sum of the change in entropy of the system and the change in entropy of the surrounding.
ΔSUniverse = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurrounding
In case of a reversible process, the change in entropy of the system is the same in magnitude but opposite in sign with the change in entropy of the surrounding. Hence, the net change in entropy of the universe will be zero.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:When one mole of ice is converted to water at 0°C and 1 atm, the work done (L atm) is
[2008]
Explanation
When one mole of ice is converted at 0°C and 1 atm, the work done : W = PΔV
Here, P = 1 atm and ΔV = 18 mL = 18 x 10-3 ≌ 20 x 10-3 = 2 L
Hence, the work done = 2 L.atm = 2 x 10-3 L.atm per kg.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:For a cyclic process performed by an ideal gas, changes in some thermodynamic functions are zero. Indicate the set in which all the functions are zero.
1. w, ΔE, AH, ΔG ;
2. q, ΔS, AH, ΔA ;
3. q, ΔE, AS, ΔG ;
4. ΔE, ΔS, ΔH, ΔA.
[2007]
Explanation
For a cyclic process performed by an ideal gas, changes in those thermodynamic functions are zero which are State functions i.e. which are independent of the path in which the change takes place. The following are the State functions : E, S, H, A. Hence, for the cyclic process performed by an ideal gas these thermodynamic functions are zero.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Thermodynamics
Try yourself:A system undergoes two cyclic processes 1 and 2 . Process 1 is reversible and process 2 is irreversible. The correct statement relating to the two process is
1. ΔS (for process 1 ) = 0, while ΔS (for process 2) ≠ 0 ;
2. qcyclic = 0 for process 1 and qcyc|ic ≠ 0 for process 2 ;
3. More heat can be converted to work in process 1 than in process 2 ;
4. More work can be converted to heat in process 1 than in process 2.
[2006]
Explanation
In case of a cyclic process if the process is reversible in nature then the ΔS (combining both the system and surrounding ) will be zero. But, if the process is irreversible in nature then the entropy change due to the system may be zero but the combination of the system and surrounding must be greater than zero.
Hence, in case of cyclic reversible process ΔSUniverse= ΔSsystem + ΔSsurrounding = 0 but in case of a cyclic irreversible process ΔSunivense = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurrounding > 0. So, ΔS (for process 1 ) = 0, while ΔS (for process 2) ≠ 0.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
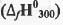 at 1 bar and 300 K for the formation of CICF2CF2CI (g) from its constituent elements in the standard state is - 900 kJ mol-1 . Given that R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1, the standard internal energy of formation
at 1 bar and 300 K for the formation of CICF2CF2CI (g) from its constituent elements in the standard state is - 900 kJ mol-1 . Given that R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1, the standard internal energy of formation 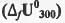 at the same pressure and temperature is
at the same pressure and temperature is