Points to Remember: Electrochemistry & Solutions | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
Points to be Remembered
1. Some Useful Concentration Terms:
I. Molarity: If a solution contains molecular weight amount of a substance in one litre then the solution is known as 1(M) solution.
The molecular weight of KMnO4 is 158 gm/mol. Hence, to prepare 1(M) KMnO4 solution we need to dissolve 158 gm of solid KMnO4 and the volume is made upto the mark of 1 litre.
II. Normality: If a solution contains equivalent weight amount of a substance in one litre then the solution is known as 1(N) solution.
Determination of Equivalent Weight:
A. For Acids: Equivalent weight = Mol. weight/No. of replaceable acidic proton of the acid.
The molecular weight of H2SO4 is 98. But, it contains two acidic hydrogens. Hence, its equivalent weight will be 98/2 = 49.
Hence, to prepare 1(N) H2SO4 solution we need to dissolve 49 gm of H2SO4 in 1 litre.
B. For Bases: Equivalent weight = Mol. weight/No. of replaceable hydroxyl group of the base.
The molecular weight of Al(OH)3 is 78. But, it contains three hydroxyl groups. Hence, its equivalent weight will be 78/3 = 26.
Hence, to prepare 1(N) Al(OH)3 solution we need to dissolve 26 gm of Al(OH)3 in 1 litre solution.
C. For Oxidants: Equivalent weight = Mol. weight/No. of electrons transfer involved in the process.
Let us consider the reactions of KMnO4 (mol. weight = 158 gm/mol) in three different mediums:
- Acidic Medium: In acidic medium, KMnO4 will convert to Mn2+ state. Hence, the no. of electrons transfer involved in the reaction = 5.
Hence, equivalent weight = 158/5 = 31.6 gm/mol
Hence, to prepare 1(N) KMnO4 solution under acidic condition, we need to dissolve 31.6 gm of KMnO-4 in 1 litre solution. - Basic Medium: In basic medium, KMnO4 will convert to MnO-4 state. Hence, the no. o f electrons transfer involved in the reaction = 1.
Hence, equivalent weight = 158/1 = 158 gm/mol Hence, to prepare 1(N) KMnO4 solution under basic condition, we need to dissolve 158 gm of KMnO4 in 1 litre solution. - Neutral Medium: In neutral medium, KMnO4 will convert to MnO2 state. Hence, the no. of electrons transfer involved in the reaction = 3.
Hence, equivalent weight = 158/3 = 52.6 gm/mol
Hence, to prepare 1(N) KMnO4 solution under neutral condition, we need to dissolve 52.6 gm of KMnO4 in 1 litre solution.
III. Formality: If a solution contains formula weight amount of a substance in 1 litre solution then the solution is known as 1(F) solution. The ionic compounds such as NaCl have no definite composition. Hence, instead of their mol. weight formula weight are taken. The formula weight of NaCl is 58.5 gm/mol. Hence, to prepare 1(F) NaCl solution we need to dissolve 58.5 gm of NaCl in 1 litre solution.
IV. Molality: If a solution contains mol. weight amount of a substance in 1 kg solvent then the solution is known as 1(m) solution.
Only this concentration term is independent on temperature.
2. Vapour Pressure: The pressure given by vapour on the surface of a solution is called vapour pressure.
Factors Affecting Vapour Pressure:
- Nature of the Solvent: If the solvent has greater intermolecular force, lesser no. of solvent molecules will go into vapour state. Hence, lower will be the vapour pressure.
- Nature of Solute: If the added solute is nonvolatile in nature, these will also be present on the solution surface. But, as these are non-volatile in nature, lesser no. of solvent molecules will goes into the vapour state. Hence, lower will be the vapour pressure.
- Temperature: Higher is the temperature, greater no. of solvent molecules will go in vapour state. Hence, greater will be the vapour pressure.
3. Ideal Solution:
I. Definition: A solution which follows Raoult's law under all temperature and concentration is known as ideal solution.
II. Characteristic of Ideal Solution:
- It follows Raoult's law under all temperature and concentration.
- The change in volume during mixing of two pure solvents to prepare ideal solution will be zero i.e. ΔVmixing = 0.
- The change in enthalpy during mixing of two pure solvents to prepare ideal solution will be zero i.e. ΔHmixing = 0.
III. Example: Almost no solution is ideal. But, there are some pairs which can nearly behave as ideal solution. A solution of n-hexane and n-heptane.
4. Non-ideal Solution:
I. Definition: A solution which does not follow Raoult's law is known as non-ideal solution.
II. Characteristic of Ideal Solution:
- It does not follow Raoult's law
- The change in volume during mixing of two pure solvents to prepare non-ideal solution will be nonzero i.e. ΔVmixing ≠ 0.
- The change in enthalpy during mixing of two pure solvents to prepare non-ideal solution will be nonzero i.e. ΔHmixing ≠ 0.
III. Example: Almost all solutions are non-ideal. A solution of water and nitric acid.
5. Deviation from Ideal Behaviour:
A. Positive Deviation: Let us consider two pure solvents. They have their own vapour pressure. Let A is more volatile than B. Hence, vapour pressure of A is more than that of B After mixing vapour pressure of the mixture increases. This is called positive deviation.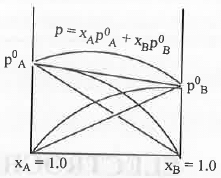 Cause of Positive Deviation: Let us consider the example of solution of ethanol with cyclohexane. Ethanol has high intermolecular force due to the formation of inter-molecular H-bonding. After mixing non-polar cyclohexane molecule will enter in between ethanol molecules and inhibit H-bond formation. Hence, the inter-molecular force of solution will decrease. Hence, the vapour of the solution will increase.
Cause of Positive Deviation: Let us consider the example of solution of ethanol with cyclohexane. Ethanol has high intermolecular force due to the formation of inter-molecular H-bonding. After mixing non-polar cyclohexane molecule will enter in between ethanol molecules and inhibit H-bond formation. Hence, the inter-molecular force of solution will decrease. Hence, the vapour of the solution will increase.
B. Negative Deviation: Let us consider two pure solvents. They have their own vapour pressure. Let A is more volatile than B. Hence, vapour pressure of A is more than that of B After mixing vapour pressure of the mixture decrease. This is called negative deviation.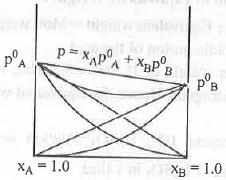 Cause of Negative Deviation: Let us consider the example of solution of acetone with chloroform. After mixing chloroform will form inter-molecular H-bond with acetone. Hence, the inter-molecular force of solution will increase. Hence, the vapour of the solution will decrease.
Cause of Negative Deviation: Let us consider the example of solution of acetone with chloroform. After mixing chloroform will form inter-molecular H-bond with acetone. Hence, the inter-molecular force of solution will increase. Hence, the vapour of the solution will decrease.
6. Relation Among Different Colligative Properties:
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure : x2 = (p° - P)/P°
- Elevation of Boiling Point: x2 = (Lv.ΔTb)/(RTb2)
- Depression of Freezing Point: x2 = (Lf.ΔTf)/(RTf2)
- Osmotic Pressure : x2 = πVm/RT
where, x2 = mole fraction of solute in solution, (p° - p)/p° = Relative lowering of vapour pressure, Lv = Latent heat of vaporization of pure solvent, Tb = Boiling point of pure solvent, ,ΔTb = Elevation of boiling point of solution, Lf = Latent heat o f freezing of pure solvent, Tf = Freezing point of pure solvent,.ΔTf = Depression of freezing point of solution, π = Osmotic pressure of solution.
7. Abnormal Behaviour of Solution: Raoult's law and Van't Hoff law are applicable for the determination of Colligative properties (Relative lowering of vapour pressure, Elevation of boiling point, Depression of freezing point, Osmotic pressure) for dilute solutions. In case of non-electrolyte like glucose, sucrose, urea etc. the calculated values of such properties are nearly matched with the experimental values. But, in case of strong electrolytes such as NaCl, KCl, MgCl2 etc. the calculated values of those properties has significant difference from the experimental values. Hence, it can be concluded that such electrolyte behaves differently in solution. This is known as abnormal behaviour of solution. This can occur due to the following two reasons:
1. Association of solute in solution and 2. Dissociation of solute in solution.
The extent of association, x = [i-1]/[(1/n)-1] and the extent of dissociation, α = [i-1]/[n-1] where, i = Van't Hoff factor, n = No. of molecules undergo association to produce one associated molecules for association and No. of ions produced after dissociation of one molecule for dissociation.
|
84 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Electrochemistry & Solutions - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is electrochemistry? |  |
| 2. How does an electrochemical cell work? |  |
| 3. What is a solution in chemistry? |  |
| 4. How is concentration measured in a solution? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between conductivity and concentration in a solution? |  |
















