Discovery of Subatomic Particles: Electron, Proton & Neutron | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Atomic Structure? |

|
| Subatomic Particles |

|
| Millikan's Oil Drop Method |

|
| Discovery of Proton |

|
| Discovery of Neutrons |

|
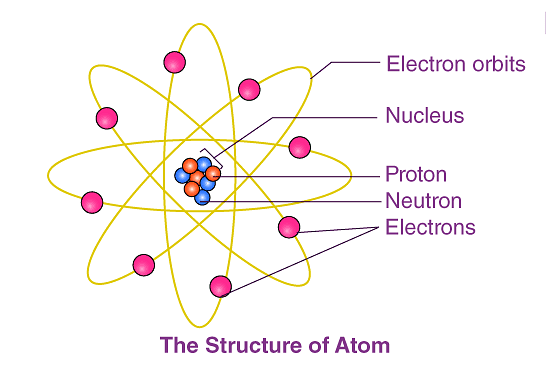
What is Atomic Structure?
- The atomic structure of an element refers to the constitution of its nucleus and the arrangement of the electrons around it. Primarily, the atomic structure of matter is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons.
- The protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of the atom, which is surrounded by the electrons belonging to the atom.

- Atoms of different elements have different atomic structures because they contain different numbers of protons and electrons. This is the reason for the unique characteristics of different elements.
Subatomic Particles
Electron
- The charge of an electron is -1e, which approximates to -1.602 × 10-19 C
- The mass of an electron is approximately 9.1 × 10-31 Kg.
- Due to the relatively negligible mass of electrons, they are ignored when calculating the mass of an atom.
Discovery of Electron
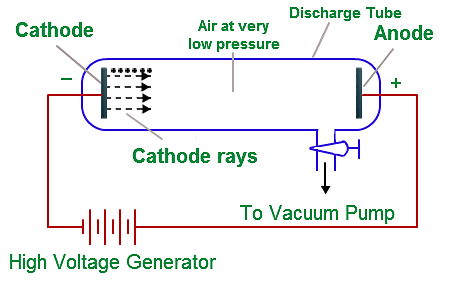
The electron was the first fundamental particle. It was discovered by J.J. Thomson in 1897 by utilising Faraday's study of electrical discharge in partially evacuated tubes, known as cathode ray tubes.
Cathode ray tube: It is a cylindrical hard glass tube fitted with two metallic electrodes connected to the oppositely charged poles of a battery.
Observation: When the gas taken in the tube was subjected to very low pressure maintained by a vacuum pump and high voltage (10.000 volts), then current flown through the stream of particles moving in the tube from cathode (negative electrode) to anode (positive electrode). Therefore, these stream of particles were known as cathode rays.
 Cathode Ray Tube
Cathode Ray Tube
Why Gases Under Low Pressure are Used?
At low pressure, there is enough space between the gaseous atoms so that the ions can accelerate to such a high speed that when they strike another atom can eject electrons of it. creating more positive ions and free electrons.
Confirmation of Rays: Presence of cathode rays were confirmed by making a hole in the anode which resulted in cathode rays striking the phosphorescent. zinc sulphide coating on the tube behind the anode. So, the bright spot produced confirmed cathode rays.
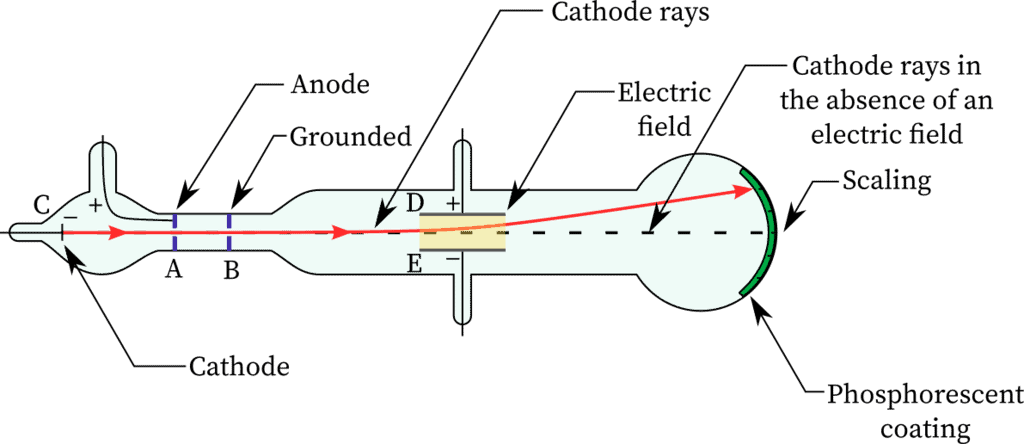
Characteristics of Cathode Rays
(1) The cathode rays move from cathode to anode.
(2) These rays are observed with the help of fluorescent or phosphorescent material as these are not visible.
(3) These rays travel in a straight line in the absence of electric and magnetic field. It is confirmed by the formation of a shadow on the opposite side of the cathode when a small object is placed between the cathode and anode
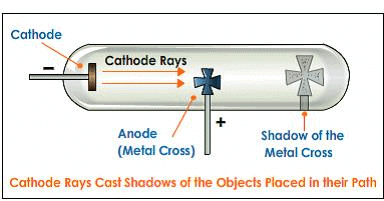
(4) They rotate the little paddle wheel placed In their path. This shows that cathode rays contain material particles having both mass and velocity.
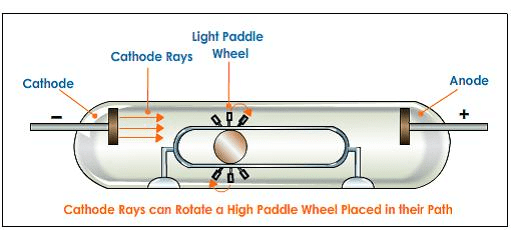
(5) These rays consist of electrons produced by the ionization of the gaseous atoms by the discharge and they were responsible for the flow of current.
(6) The application of electric and magnetic fields deflected cathode rays as expected from negatively charged particles
(7) They produce X-rays when they strike against the surface of hard metals like tungsten, molybdenum, etc.
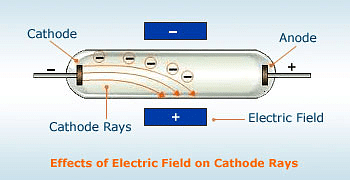
In fact all the above observations led to the conclusion that the cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles Those charged particles constituting the cathode rays wore named electrons.
Millikan's Oil Drop Method
In this method, oil droplets in the form of mist, produced by the atomiser, were allowed to enter through a tiny hole in the upper plate of electrical condenser.
- The downward motion of these droplets was viewed through the telescope, equipped with a micrometer eye piece.
- By measuring the rate of fall of these droplets, Millikan was able to measure the mass of oil droplets.
- The air inside the chamber was ionized by passing a beam of X-rays through it.
- The electrical charge on these oil droplets was acquired by collisions with gaseous ions.
- The fall of these charged oil droplets can be retarded, accelerated or made stationary depending upon the charge on the droplets and the polarity and strength of the voltage applied to the plate.
- By carefully measuring the effects of electrical field strength on the motion of oil droplets, Millikan concluded that the magnitude of electrical charge, q, on the droplets is always an integral multiple of the electrical charge, e, that is, q = ne, where n = 1, 2, 3...
- The highest common factor (HCF) of charges on oil droplet was taken as charge on electron.
- Charged plate (–) Oil droplet under observation
Proton
- Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. The charge of a proton is 1e, which corresponds to approximately 1.602 × 10-19 C
- The mass of a proton is approximately 1.672 × 10-27 Kg
- Protons are over 1800 times heavier than electrons.
- The total number of protons in the atoms of an element is always equal to the atomic number of the element.
Discovery of Proton
The atom as whole is electrically neutral. During electric discharge in the cathode ray tube the gaseous atoms present, get ionise to form ions (positively charged particles) and electron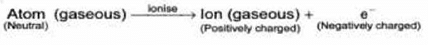
When electrons were discovered, then Goldstein brought the idea that there must be some positively charged particles that neutralise the negative charge of the electrons to maintain electrical neutrality of an atom.
This idea led to the discovery of proton. The discovery of proton by Goldstein was done on the basis of the cathode ray experiment conducted by using a perforated cathode.
Some rays were formed by ionization of gas and move towards cathode known as anode rays or canal rays.
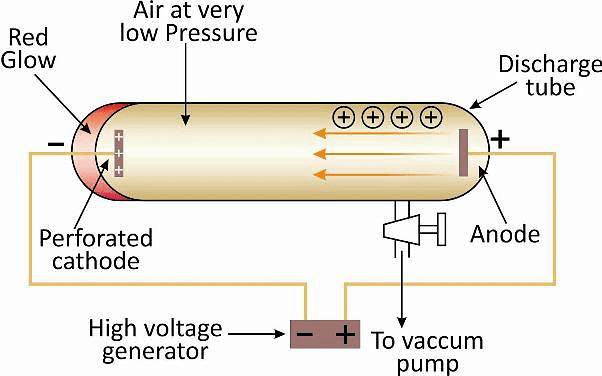 Anode Rays
Anode Rays
Anode rays were found as a stream of positively charged particles in contrast to cathode rays. When hydrogen gas is taken in a discharge tube, then these positively charged particles were found to be protons. A proton is produced when one electron is removed from hydrogen atom (H).
Properties of the Anode Rays
(1) Anode rays travel in straight lines.
(2) Anode rays possess positive charge therefore they move towards the negatively charged electrodes.
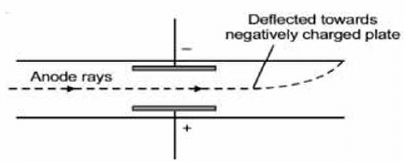
(3) The properties of anode rays, unlike cathode rays depend upon the nature of the gas taken in the discharge tube as the e/m ratio of the positive rays is different for different gases.
(4) The mass of the positive particles Is same as the atomic mass of the gas inside the discharge tube
(5) The charged ions which move towards cathode carries magnitude of positive charge depending upon the number of electrons lost by the corresponding gaseous atoms or molecules.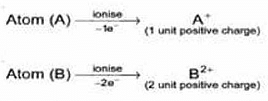
Origin of anode rays: These rays are believed to be produced as a result of knock out of the electrons from the gaseous atoms by the bombardment of high speed stream of electrons from cathode.
Neutron
- The mass of a neutron is almost the same as that of a proton i.e. 1.674×10-27 Kg
- Neutrons are electrically neutral particles and carry no charge.
- Different isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but vary in the number of neutrons present in their respective nuclei.
Discovery of Neutrons
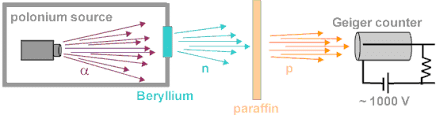
Neutron was discovered by Chadwick (1932). when he bombarded a thin sheet of beryllium 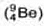 by α - particles
by α - particles 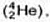 then electrically neutral particles having a mass slightly greater than that of the protons were emitted He named these particles as neutrons.
then electrically neutral particles having a mass slightly greater than that of the protons were emitted He named these particles as neutrons.Mass of Neutrons: Slightly greater than the mass of protons /.e., 1.674 x 10-24 g
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
FAQs on Discovery of Subatomic Particles: Electron, Proton & Neutron - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the subatomic particles that make up an atom? |  |
| 2. How was Millikan's Oil Drop Method used to determine the charge of an electron? |  |
| 3. Who is credited with the discovery of the proton? |  |
| 4. When were neutrons discovered and by whom? |  |
| 5. What are the properties and roles of electrons, protons, and neutrons in atomic structure? |  |
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|