Notes of "The Living World" Class 11th. PDF Download
When we look around us, we can observe endless species of living living organisms. These organisms have great adoptability to survive in diversified habitats. All living organisms differ from non living from a number of characters.
What is living?
The state of being alive (OR) A living may be defined as a conscious self regulating, interacting, biomolecules and cells.
We find living organisms in all kinds of habitats such as aquatic, terrestrial and aerial.
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING ORGANISMS
1) All living organisms exhibit growth and development.
[•]Living organisms grow by increase in the mass or by number of cells. Unlike plants, in animals growth stops at certain age, thereafter only the lost cells of certain tissues are replaced by cell division.
[•]In living organisms, growth is internal and is called
intussusception..
[•]Non living things like rocks do exhibit growth by the deposition of materials, this growth is external and is called accretion.
2) All living organisms reproduce.
Reproduction is the process of production of young ones by an organism of its own kind. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually. Asexual reproduction takes place as follows:-
✓ Fungi reproduce by the formation of spores.
✓ Yeast, Hydra reproduce by budding.
✓ Planaria reproduce by regeneration of the lost form.
✓ Filamentous algae
reproduces by fragmentation.
✓ Bacteria, Amoeba and other unicellular forms reproduce and also grows by cell division.
3) All living organisms exhibit metabolism.
All living organisms are made up of various chemicals. A number of chemicals are
constantly made and are changed to enable the survival of the cell.
"The sum of all the chemical reactions taking place in an organism is called Metabolism". [Anabolism - constructive chemical activity,
Catabolism - destructive chemical activity]
4) All living organisms have consciousness.
All living organisms respond to external stimulus may be physical or chemical or biological.
Ex:- Many plants produce flowers at specific photo period.
5) All living organisms have cellular organization.
All living organisms are made up of structural and functional units called cells. The co-ordinate function of the cell and its components enables smooth function.
Diversity in the living world
When we look around, we can observe endless variety of living organisms. It is impossible to remember the names and characters of all the organisms. The common names (vernacular names) are given to organisms, differ from one region to another, which leads to confusions.
"The scientific method of naming a living organism by using two components, a generic name and a species name is called Bionomial nomenclature". This was proposed by Corollas Linnaeus.
International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) and International Code for Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) laid certain rules and procedures while naming a living organism.
Rules for Binomial Nomenclature:-
✓ The names of all living organism should be binomial that is, it should contain two
components that is generic name and a species name.
✓ The generic should be a noun and should start with capital letter. The species name should start with a small letter.
✓ The scientific name should be derived from Latin or should be suitably Latinized.
✓ The scientific should often be descriptive that is, it should highlight certain important
characters of particular organism.
✓ The scientific name should be printed in Italics and when handwritten, it should be
underlined separately.
Ex:- Mangifera indica. If it is printed in Italics, it should be written like Mangifera indica , If it is handwritten, it should be underlined separately like Mangifera indica.
✓ The name of the author should be abbreviated suitably next to the species name.
Ex:- Mangifera indica Linn.
✓ If an organism is re-described by another author, the original authors name should be kept in bracket followed by the abbreviation
of second author name.
Advantages of Binomial Nomenclature:-
1) It avoids confusion of local names.
2) The scientific names are universally accepted so that each organism is called a
single specific name accepted throughout the world.
3) As the scientific names are derived from Greek or Latin, which are considered as dead
languages, therefore there is no scope for change.
Systematics:-
The study of diversities of all the living organisms based on comparative and evolutionary relationships is called Systematics. The term 'Systematic' is derived from Latin word 'Systema'
(systematic arrangement of living organisms), this word was first used by the scientist Corollas Linnaeus in his book systema naturae.
Taxonomic categories:-
Each classificatory group is called as rank or taxon or category.
The arrangement of taxon in ascending or in descending order is called Taxonomic hierarchy or Linnaean hierarchy.
Kingdom → Phylum/Division → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species.
Species:- It is the basic unit of classification. A species is the group of individuals with fundamental similarities.
Ex:- Mangifera indica, Homo sapiens. Here, indica, sapiens represent the species name, whereas Mangifera and Homo represents the genera a higher taxon.
Genus:- It is an aggregate of closely related species.
Ex:- lion (panthera-Leo),
leopard (p.pardus), tiger (p.tigress), with several common features are all species of the genus Panthera.
Family:- It is a taxonomic category which includes a group of related genera. Families are characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features.
Ex:- the genus Panthera, comprising lion, tiger, and leopard are put along P.felis (cat) in the family felidae.
Order:- It is a high taxonomic category which includes an assemblage of related
families.
Ex:- Felidae, Canidae are kept in an order carnivore as both exhibit few similar characters.
Class:- It is a taxonomic category which includes related order.
Ex:- class mammalian, contains orders like primata comprising gorilla, monkey, order carnivore comprising cats, dogs etc..,
Phylum:- It includes a group of class where few features are common. The term division is used in place of phylum for plants.
Ex:- the classes amphibians, reptiles, mammalian contains the notochord and dorsal hollow nerve chord commonly hence are included is single phylum chordata.
Kingdom:- It is the highest category or taxon it includes closely related phylums or divisions.
Ex:- All animals belonging to different phyla are assigned in the kingdom animalia. All plants belonging to different division are kept under one kingdom plantae.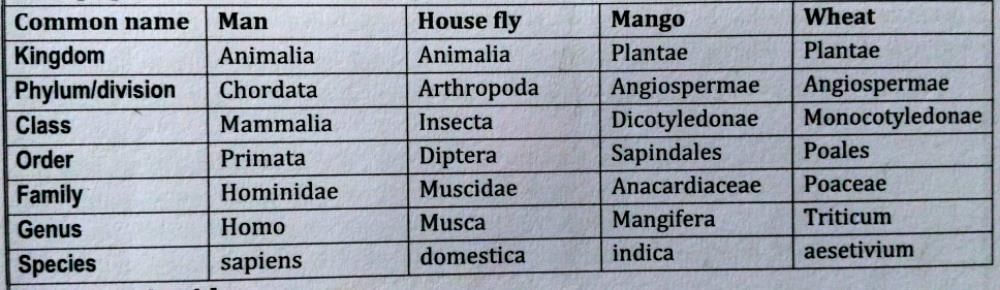
Taxonomic aids
"These are certain procedure and techniques developed by biologist to preserve and to store information of different organisms".
Taxonomical studies involve intensive laboratory and field studies. These taxonomic studies are useful to understand the bio-reserves and their diversity. These studies are useful in different fields of biology.
1) Herbarium:- It is a store house of collected plant specimens that are dried, pressed and preserved on the sheet for future use. The pressed sheet contains the description of the plant classification, common name, date, and time and collectors name. The herbarium sheets are stored in the herbarium according to the accepted system of classification, the herbarium sheets provides us the ready reference to identify, understand various species of plants.
2) Botanical garden:- These are the specialized gardens which have the collection of live plants grown for reference and identification purposes. Each plant in the garden are labeled indicating the common name and the scientific name and family.
Ex:- KEW botanical garden in England and Indian botanical garden in Howrah (India).
3) Museums:- Are the store house of the preserved plants and animals for study and reference? Various specimens are preserved in jars containing preservative solution, insects are kept in insect boxes, large animals, birds and mammals are preserved by stuffing. Museums do have the collection of skeletons of various animals.
4) Zoological parks:- These are the places where the wild animals are kept under captivity and protection of the humans (ex-situ conservation).
Ex:- Jayachamarajendra zoological park, Mysore.
Zoos are setup by providing conditions that are similar to natural habitat for animals.
Zoos help in,
✓ To learn about the behavior of the animals.
✓ Entertainment and captive breeding.
5) Key:- It is a taxonomic aids used to identify plants and animals based on similarities and dissimilarities. The keys are based on a pair of contrasting characters called couplet. It represents acceptance of only one and the rejection of the other. Each statement in the key is called lead. There are various keys for each taxonomic category like family, genus etc..,
Note:
1) Flora, manuals,monographs are the other taxonomic aids which helps in the correct
identification.
Flora:- It contains actual account of habitat and distribution of plants in a given area, and also provides the index to plant species, present in that area.
Monographs:- They provide information for identification of names of species found in an area.
Manuals:- Contains information of any one taxon.
FAQs on Notes of "The Living World" Class 11th.
| 1. What is the concept of biodiversity? |  |
| 2. How is biodiversity important for human beings? |  |
| 3. What are the major threats to biodiversity? |  |
| 4. How can we conserve biodiversity? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of conserving biodiversity? |  |















