Piezoelectric Transducers: Working and Applications | Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction
The definition of a Piezoelectric transducer is an electrical transducer which can convert any form of physical quantity into an electrical signal, which can be used for measurement. An electrical transducer which uses properties of piezoelectric materials for conversion of physical quantities into electrical signals is known as a piezoelectric transducer.
Piezoelectric materials exhibit the property of piezoelectricity, according to which on the application of any type of mechanical stress or strain leads to the generation of an electric voltage proportional to the applied stress. This produced electric voltage can be measured using voltage measuring instruments to calculate the value of stress or strain applied to the material.
Types of Piezoelectric Materials
Some of the types of piezoelectric materials are:
Naturally Available Ones: Quartz, Rochelle salt, Topaz, Tourmaline-group minerals, and some organic substances as silk, wood, enamel, bone, hair, rubber, dentin. Artificially manufactures piezoelectric materials are Polyvinylidene difluoride, PVDF or PVF2, Barium titanate, Lead titanate, Lead zirconate titanate (PZT), Potassium niobate, Lithium niobate, Lithium tantalate, and other lead-free piezoelectric ceramics.
Not all piezoelectric materials can be used in piezoelectric transducers. There are certain requirements to be met by the piezoelectric materials to be used as transducers. The materials used for measurement purpose should have frequency stability, high output values, insensitive to the extreme temperature and humidity conditions and which can be available in various shapes or should be flexible to be manufactured into various shapes without disturbing their properties.
Unfortunately, there is no piezoelectric material which has all these properties. Quartz is a highly stable crystal which is naturally available but it has small output levels. Slowly varying parameters can be measured with quartz. Rochelle salt gives the highest output values but it is sensitive to environmental conditions and cannot be operated above 1150F.
Piezoelectric Transducer Working
Piezoelectric Transducer works with the principle of piezoelectricity. The faces of piezoelectric material, usual quartz, is coated with a thin layer of conducting material such as silver. When stress has applied the ions in the material move towards one of the conducting surface while moving away from the other. This results in the generation of charge. This charge is used for calibration of stress. The polarity of the produced charge depends upon the direction of the applied stress. Stress can be applied in two forms as Compressive stress and Tensile stress as shown below.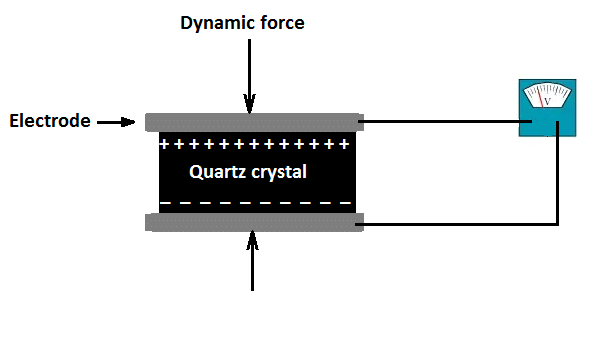
Piezoelectric Transducer Formula
The orientation of the crystal also effects the amount of voltage generated. Crystal in a transducer can be arranged in longitudinal position or transverse position.
Longitudinal and Transverse Effect
In the longitudinal effect, the charge generated is given by
Q = F * d
Where F is the applied force, d is the piezoelectric coefficient of the crystal.
Piezoelectric coefficient d of quartz crystal is around 2.3 * 10-12 C/N.
In the transverse effect, the charge generated is given by Q = F * d * (b/a)
When the ratio b/a is greater than 1 the charge produced by transverse arrangement will be greater than the amount generated by longitudinal arrangement.
Piezoelectric Transducer Circuit
The working of a basic piezoelectric transducer can be explained by the below figure.
Here quartz crystal coated with silver is used as a sensor to generate a voltage when stress is applied on it. A charge amplifier is used to measure the produced charge without dissipation. To draw very low current the resistance R1 is very high. The capacitance of the lead wire that connects the transducer and piezoelectric sensor also affects the calibration. So the charge amplifier is usually placed very near to the sensor.
So in a piezoelectric transducer when mechanical stress is applied a proportional electric voltage is generated which is amplified using charge amplifier and used for calibration of applied stress.
Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducer
The ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer works on the principle of the converse piezoelectric effect. In this effect when electricity is applied to a piezoelectric material, it undergoes physical deformations proportional to applied charge. The circuit of the ultrasonic transducer is given below.
Here, the quartz crystal is placed between two metal plates A and B which are connected to the primary L3 of the transformer. The primary of the transformer is inductively coupled to the electronic oscillator. The coils L1 and L2, which forms secondary of the transformer, are connected to the electronic oscillator.
When the battery is turned ON the oscillator produces high-frequency alternating voltage pulses with a frequency f=1÷(2π√L1C1). Due to this, an e.m.f is induced in L3 which is transferred to the quartz crystal through plates A and B. Due to converse piezoelectric effect the crystal starts contracting and expanding alternatively thus creating mechanical vibrations.
Resonance takes place when the frequency of the electronic oscillator is equal to the natural frequency of the quartz. At this point, quartz produces longitudinal ultrasonic waves of large amplitude.
Piezoelectric Transducer Applications
- As piezoelectric materials cannot measure static values these are primarily used for measuring surface roughness, in accelerometers and as a vibration pickup.
- They are used in seismographs to measure vibrations in rockets.
- In strain gauges to measure force, stress, vibrations etc…
- Used by automotive industries to measure detonations in engines.
- These are used in ultrasonic imaging in medical applications.
Advantages and Limitations of Piezoelectric Transducers
Advantages:
- These are active transducer i.e. they don’t require external power for working and are therefore self-generating.
- The high-frequency response of these transducers makes a good choice for various applications.
Limitations:
- Temperature and environmental conditions can affect the behavior of the transducer.
- They can only measure changing pressure hence they are useless while measuring static parameters.
|
26 videos|28 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on Piezoelectric Transducers: Working and Applications - Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What is the working principle of piezoelectric transducers? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of piezoelectric transducers? |  |
| 3. How does a piezoelectric transducer convert electrical energy into mechanical energy? |  |
| 4. Can piezoelectric transducers generate electricity from vibration or pressure? |  |
| 5. Are there any limitations or challenges associated with piezoelectric transducers? |  |





















