NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 11 > Mind Map: Waves
Mind Map: Waves | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
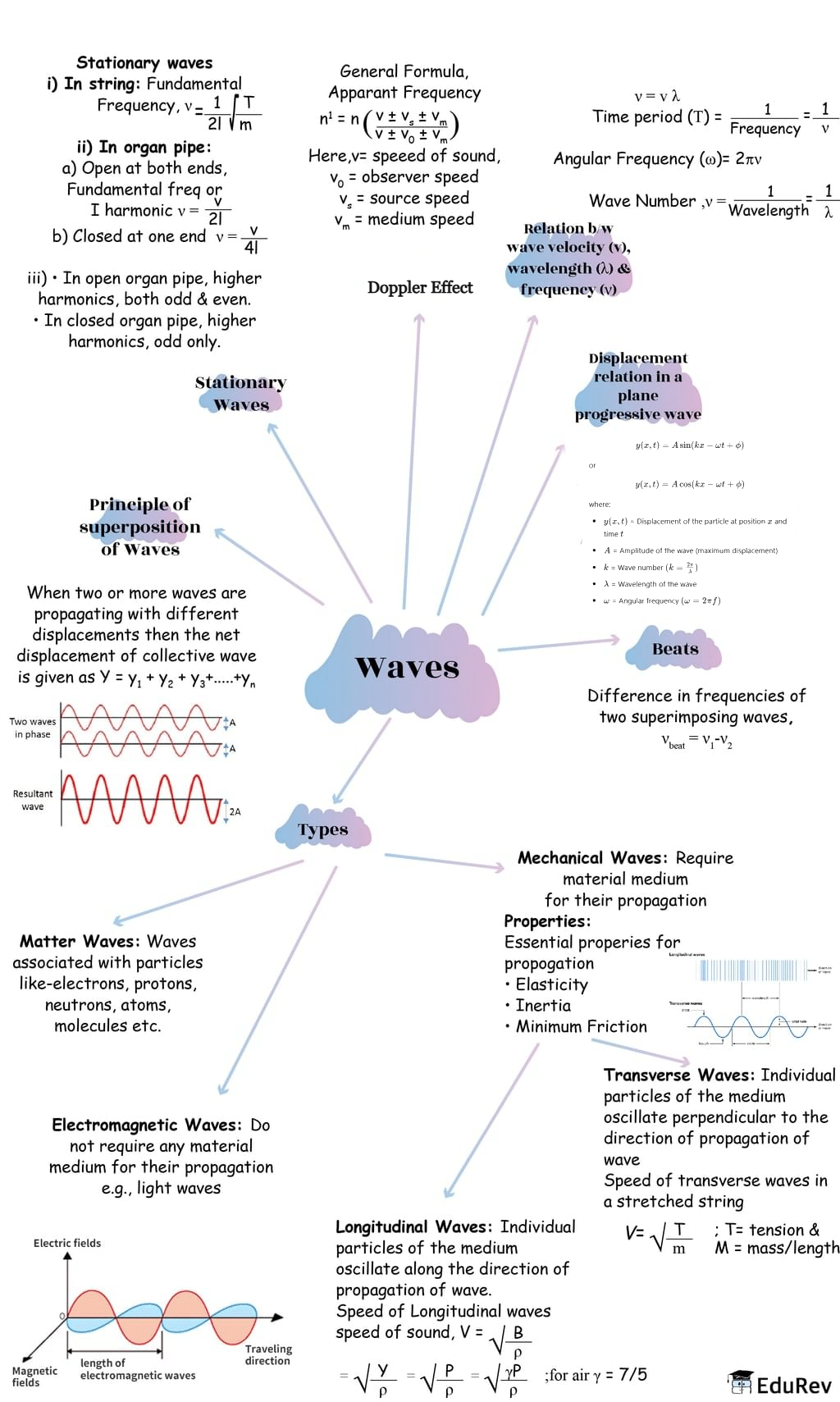
The document Mind Map: Waves | Physics Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Waves - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the different types of waves in physics? |  |
Ans. In physics, waves can be classified into two main types: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through, such as sound waves and water waves. Electromagnetic waves, on the other hand, do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum, like light waves and radio waves.
| 2. What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves? |  |
Ans. Longitudinal waves are characterized by particle displacement parallel to the direction of wave propagation. An example is sound waves, where compressions and rarefactions move along the direction of the wave. Transverse waves have particle displacement perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, like waves on a string or light waves, where the oscillations occur at right angles to the direction of energy transfer.
| 3. How do waves carry energy? |  |
Ans. Waves carry energy through the movement of particles in the medium (for mechanical waves) or through electric and magnetic fields (for electromagnetic waves). As the waves propagate, they transfer energy from one location to another without permanently displacing the medium itself. The energy is carried by the oscillations of the particles or fields.
| 4. What factors affect wave speed? |  |
Ans. The speed of a wave is influenced by several factors including the type of wave, the medium through which it travels, and the properties of that medium such as temperature, density, and elasticity. For instance, sound travels faster in water than in air due to the greater elasticity and density of water.
| 5. What is wave interference and how does it occur? |  |
Ans. Wave interference occurs when two or more waves overlap and combine to form a new wave pattern. This can result in constructive interference, where the amplitudes of the waves add together, creating a larger wave, or destructive interference, where the waves cancel each other out, resulting in a smaller wave or no wave at all. Interference is a fundamental principle in understanding wave behavior.
Related Searches

















