NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Chemistry Class 12 > Mindmap: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic acids
Mindmap: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic acids | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
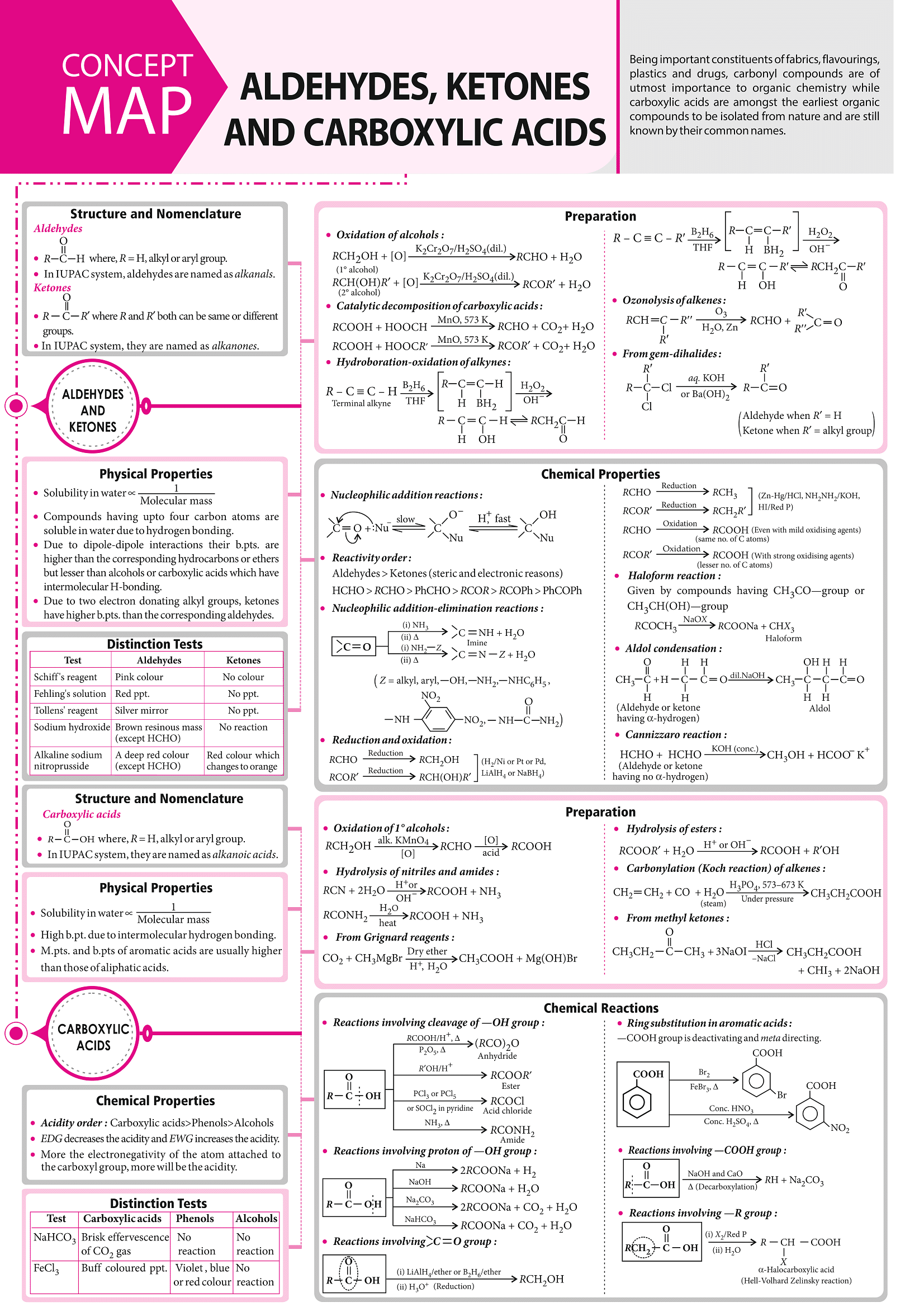
The document Mindmap: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic acids | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Chemistry Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
100 videos|282 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Mindmap: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic acids - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids? |  |
Ans. Aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain the carbonyl functional group. Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, ketones have it in the middle, and carboxylic acids have it at the end of the carbon chain with a hydroxyl group attached.
| 2. What are some common examples of aldehydes? |  |
Ans. Some common examples of aldehydes include formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and benzaldehyde. Formaldehyde is used as a disinfectant, acetaldehyde is found in alcoholic beverages, and benzaldehyde is used in the production of fragrances and flavors.
| 3. How do ketones differ from aldehydes and carboxylic acids? |  |
Ans. Ketones differ from aldehydes and carboxylic acids in terms of the position of the carbonyl group. While aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain and carboxylic acids have it at the end with a hydroxyl group, ketones have the carbonyl group in the middle of the carbon chain.
| 4. What are some important reactions of aldehydes and ketones? |  |
Ans. Some important reactions of aldehydes and ketones include nucleophilic addition, oxidation, reduction, and condensation reactions. Nucleophilic addition reactions involve the addition of a nucleophile to the carbonyl carbon, oxidation reactions convert aldehydes to carboxylic acids, reduction reactions convert aldehydes and ketones to alcohols, and condensation reactions form larger molecules by eliminating water.
| 5. How are carboxylic acids formed? |  |
Ans. Carboxylic acids can be formed through the oxidation of aldehydes or primary alcohols. In the case of aldehyde oxidation, the aldehyde is further oxidized to a carboxylic acid. Similarly, primary alcohols can be oxidized to carboxylic acids through a two-step process, where the alcohol is first converted into an aldehyde and then into a carboxylic acid.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















