Kingdom Monera, Protista And Fungi - NEET PDF Download
Billions of years of evolution have led to a mind-numbing variety of species on earth. Classification of these organisms was a serious challenge for the biologists.
Many researchers had come forward with different categories to classify living things. Among them, Ernst Haeckel (1894), Robert Whittaker (1959) and Carl Woese (1977) are few, whose contributions are notable.
Modern-day of taxonomy have accepted the five-kingdom classification which was proposed by R. H. Whittaker.
The basis of his classification is the cell structure, mode, and source of nutrition and the structure of the body. The classification of living organisms according to Whittaker is divided into five kingdoms namely: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia
Let’s learn about kingdoms Monera, Protista, and Fungi and the differences between the three.
Kingdom Monera
Kingdom Monera is considered as the most primitive group of organisms and monerans are most abundant of all. It generally comprises unicellular organisms with a prokaryotic cell organization. They lack well-defined cell structures including the nucleus and other cell organelles.
They consist of prokaryotes which include species like the Cyanobacteria, archaebacteria, mycoplasma, and bacteria are a few members of this kingdom.
The general features of Monerans are:
- Monerans are present in both aerobic and anaerobic environment.
- Some have rigid cell walls, while some do not.
- The membrane-bound nucleus is absent in monerans.
- Habitat – Monerans are found everywhere in hot or thermal springs, in the deep ocean floor, under ice, in deserts and also inside the body of plants and animals.
- They can be autotrophic, i.e., they can synthesize food on their own while some others have a heterotrophic, saprophytic, parasitic, symbiotic, commensalistic and mutualistic modes of nutrition.
- Locomotion is with the help of flagella.
- Circulation is through diffusion.
- Respiration in these organisms vary, few are obligate aerobes, while some are obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes
- Reproduction is mostly asexual and few also reproduce by sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is by conjugation, transformation, and transduction. Asexual reproduction is by binary fission.
 Kingdom Monera
Kingdom Monera
Kingdom Protista
All unicellular eukaryotic organisms are placed under the Kingdom Protista.
The term Protista was first used by Ernst Haeckel in the year 1886. This kingdom forms a link between other kingdoms of fungi, plants, and animals.
Kingdom Protista is an important phase in early evolution and the very first protist probably evolved 1.7 billion years ago.
Kingdom Protista is a very large group comprising of at least 16 phyla. Many species of this kingdom are the primary producers in the aquatic ecosystem and some are responsible for serious human diseases like malaria.
General features of Kingdom Protista are as follows:
- They are simple, unicellular, eukaryotic organisms.
- Most of the protists live in water, some in moist soil or even the body of human and plants.
- These organisms have a membrane-bound nucleus, endomembrane systems, mitochondria for cellular respiration and some have chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- Nuclei contain multiple DNA strands and the number of nucleotides is significantly less.
- Respiration – cellular respiration is the primarily aerobic process, but some living in the moist soil underneath ponds or in digestive tracts of animals are facultative anaerobes.
- Locomotion is often by flagella or cilia.
- Nutrition- include both heterotrophic and autotrophic.
- Reproduction – Some reproduce sexually and others asexually.
- Some protists are pathogens of both plants and animals. Example: Plasmodium falciparum causes malaria in humans.
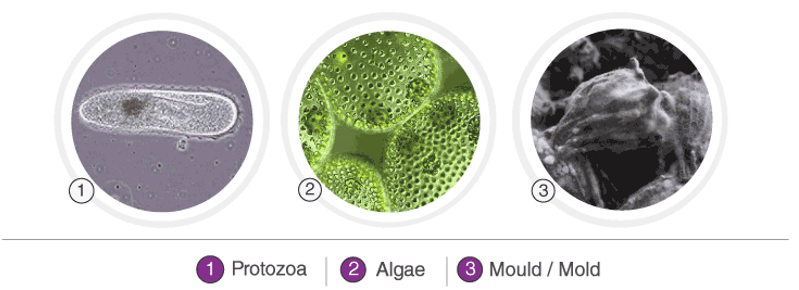
Kingdom Fungi
Fungi are a group of organisms that are found everywhere from air, water, land to the soil. They are also found in plants and animals.
Some fungi are microscopic and others are gargantuan – almost extending over a thousand acres. And even though fungi appear like plants, they are in fact closely related to animals.
Fungi have great economic importance and show a great diversity in morphology and habitat. More than 70,000 species of fungi have been recognized and the organisms of kingdom fungi include mushrooms, smuts, yeasts, puffballs, rusts, smuts, truffles, morels, and moulds.
General features of fungi are as follows:
- Fungi are eukaryotic, non-vascular and non-motile organisms.
- The growth rate of fungi is slower than that of bacteria.
- Fungi grow best in an acidic environment.
- The Kingdom Fungi consist of both unicellular (e.g. Yeast, Molds) and multicellular (e.g. mushrooms) organisms.
- Like plant cells, fungi have cell walls made up of complex sugar molecules called chitin. But unlike plants, they do not undergo photosynthesis.
- The cell wall is composed of chitin. The vegetative body of the fungi may be unicellular or composed of microscopic threads called hyphae.
- They have a heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Few species are saprophytes i.e., they feed on dead and decaying organic matters.
- Some fungi are parasitic while some are symbionts. They can live in a symbiotic relationship with algae, like blue-green algae. These are called lichens.
- Reproduction in fungi is both by sexual and asexual means. Asexual reproduction takes place by means of spores and sexual reproduction takes place by means of gametic copulation, somatic copulation, and Spermatization.
 Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Monera, Protista and Fungi- Comparison Chart
The difference between kingdom Protista, monera and fungi are as follows:
Kingdom Monera | Kingdom Protista | Kingdom Fungi |
Unicellular Prokaryotes | Unicellular Eukaryotes. | Unicellular or Multicellular eukaryotes |
No cellular organelles | Membrane-bound cell organelles | Cell organelles are present |
Simple structure | Complex structure | Complex cellular organization |
Cell wall is present but not well developed. | Well-developed cell wall is present. | Cell wall is made up of chitin |
No true nucleus | Has a true nucleus | Possess a true nucleus |
Autotrophic or heterotrophic mode of nutrition | Holozoic, parasitic or photosynthetic mode of nutrition. | Heterotrophic or saprophytic mode of nutrition. |
Flagella and cilia absent | Flagella and cilia present | Flagella are present for locomotion |
Reproduction is asexual | Reproduction is sexual or asexual | Reproduction is sexual and asexual |
Found everywhere | Found in aquatic, moist and shady places. | Found mostly in an acidic environment |
Example: Mycobacterium, Bacillus, | Example: Dinoflagellates, protozoan, slime moulds | Example: yeast, mushrooms |
Frequently Asked Questions
What does kingdom monera include?
Kingdom monera include single-celled prokaryotic organisms called bacteria. These are the most ancient microorganisms present on earth.
Why was the kingdom monera divided?
Kingdom Monera was divided because the scientists observed a few differences between the two groups of Monera. Archaebacteria and Eubacteria are two such groups.
Why is the kingdom monera no longer used?
Kingdom Monera is no longer used because it includes members from two domains. Also, domain Archaea is more closely related to domain Eukarya than it is to domain bacteria.
Give a few examples of kingdom Protista.
Kingdom Protista includes diatoms, euglena, amoeba, Plasmodium, slime moulds, etc. The photosynthetic protists include various types of dinoflagellates and euglena.
What belongs to kingdom Protista?
Kingdom Protista includes unicellular eukaryotes, diatoms, protozoans, euglenoids, dinoflagellates, slime moulds, etc.
Who proposed kingdom Protista?
Kingdom Protista was proposed by Ernst Hackel in 1866.
How can you define fungi?
Fungi are living organisms with complex eukaryotic cells. These are neither plants nor animals or bacteria. They are classified in their own kingdom.
How are fungi important?
Fungi are one of the most important decomposers in the ecosystem. They are saprophytes and feed on dead and decaying organic matter. They break down plant fibres such as dead leaves and wood and allow the nutrients to release into the soil.
FAQs on Kingdom Monera, Protista And Fungi - NEET
| 1. What are the characteristics of Kingdom Monera? |  |
| 2. What are the major differences between Kingdom Monera and Kingdom Protista? |  |
| 3. How do fungi obtain their nutrition? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristic features of Kingdom Protista? |  |
| 5. How do bacteria play an important role in the environment? |  |



















