Protista & Kingdom Fungi - NEET PDF Download
Protista
What are Protists?
Protists are simple eukaryotic organisms that are neither plants nor animals or fungi. Protists are unicellular in nature but can also be found as a colony of cells. Most protists live in water, damp terrestrial environments or even as parasites.
The term ‘Protista’ is derived from the Greek word “protistos”, meaning “the very first“. These organisms are usually unicellular and the cell of these organisms contains a nucleus which is bound to the organelles. Some of them even possess structures that aid locomotion like flagella or cilia.
Scientists speculate that protists form a link between plants, animals and fungi as these three kingdoms diverged from a common protist-like ancestor, billions of years ago. Though this “protists-like” ancestor is a hypothetical organism, we can trace some genes found in modern animals and plants to these ancient organisms.
Therefore, these organisms are traditionally considered as the first eukaryotic forms of life and a predecessor to plant, animals and fungi.
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista
The primary feature of all protists is that they are eukaryotic organisms. This means that they have a membrane-enclosed nucleus. Other characteristic features of Kingdom Protista are as follows:
- These are usually aquatic, present in the soil or in areas with moisture.
- Most protist species are unicellular organisms, however, there are a few multicellular protists such as kelp. Some species of kelp grow so large that they exceed over 100 feet in height. (Giant Kelp).
- Just like any other eukaryotes, the cells of these species have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- They may be autotrophic or heterotrophic in nature. An autotrophic organism can create their own food and survive. A heterotrophic organism, on the other hand, has to derive nutrition from other organisms such as plants or animals to survive.
- Symbiosis is observed in the members of this class. For instance, kelp (seaweed) is a multicellular protist that provides otters, protection from predators amidst its thick kelp. In turn, the otters eat sea urchins that tend to feed on kelp.
- Parasitism is also observed in protists. Species such as Trypanosoma protozoa can cause sleeping sickness in humans.
- Protists exhibit locomotion through cilia and flagella. A few organisms belonging to kingdom Protista have pseudopodia that help them to move.
- Protista reproduces by asexual means. The sexual method of reproduction is extremely rare and occurs only during times of stress.
Classification of Protista
Kingdom Protista is classified into the following:
Protozoa
Protozoans are unicellular organisms. Historically, protozoans were called “animal” protists as they are heterotrophic and showed animal-like behaviours.
There are also parasitic protozoans which live in the cells of larger organisms. Most of the members do not have a predefined shape. For instance, an amoeba can change its shape indefinitely but a paramecium has a definite slipper-like shape. The most well-known examples of protozoans are amoeba, paramecium, euglena. Unlike other members of this group, euglena is a free-living protozoan that has chlorophyll, which means it can make its own food.
The protozoans can be divided into four major groups:
- Amoeboid protozoans – Mostly found in water bodies, either fresh or saline. They have pseudopodia (false feet) which help to change their shape and in capturing and engulfing food. E.g. Amoeba
- Flagellated protozoans – As the name suggests, the members of this group have flagella. They can be free-living as well as parasitic. E.g. Euglena
- Ciliated protozoans – They have cilia all over their body which help in locomotion as well as nutrition. They are always aquatic. E.g. Paramecium
- Sporozoans – These organisms are so-called because their life cycle has a spore-like stage. For example, the malarial parasite, Plasmodium.
Slime Moulds
Slime moulds are saprophytic organisms (they feed on the dead and decaying matter). These are tiny organisms that have many nuclei.
Usually, Slime moulds are characterized by the presence of aggregates called plasmodium and are even visible to the naked eye.
Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates and Euglenoids
These form another category under kingdom Protista. These are generally single-celled or multicellular organisms. These are photosynthetic, found mostly in freshwater sources or marine lakes. They are characterized by a stiff cell wall.
Example of chrysophytes include diatoms and golden algae. They are characterised by the presence of a hard siliceous cell wall. Diatomaceous earth is formed due to the accumulation of cell wall deposits. They are photosynthetic organisms.
Dinoflagellates are photosynthetic and found in various different colours, according to the pigment present in them. They show bioluminescence and known to cause red tide.
Euglenoids are the link between plants and animals. They lack a cell wall but perform photosynthesis. In the absence of sunlight, they act as a heterotroph and feed on small organisms. The outer body covering is a protein-rich layer known as a pellicle. E.g. Euglena, Trachelomonas, etc.
Economic Importance of Protists
- Protists serve as the foundation of the food chain.
- Protists are symbionts – having a close relationship between two species in which, one is benefited.
- Some protists also produce oxygen and may be used to produce biofuel.
- Protists are the primary sources of food for many animals.
- In some rare cases, Protists are harvested by humans for food and other industrial applications.
- Phytoplankton is one of the sole food sources for whales
- Seaweed is an alga, which is considered a plant-like protist.
- Zooplankton is fed on by various sea creatures including shrimp and larval crabs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Protists?
Protists include a vast collection of single-celled and multicellular organisms that have a nucleus. They also possess highly specialized cellular machinery called cell organelles that aid in performing various life processes. Most protists are free-living autotrophs (such as algae) while others are heterotrophic (Amoeba) or even parasitic (Trypanosoma protozoa).
State a few examples of Protists.
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena Plasmodium, etc.
How are Protists classified?
Protists are broadly classified into 5 subdivisions based on their general characteristic features. They are classified as:
- Chrysophytes
- Dinoflagellates
- Euglenoids
- Slime moulds
- Protozoans
Outline the characteristics of Kingdom Protista.
- All protists are eukaryotic organisms. This means that they have a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other cell organelles.
- Most protists are aquatic, others are found in moist and damp environments.
- Most are unicellular, however, there are a few multicellular protists such as the giant kelp.
- They may be autotrophic or heterotrophic in nature.
- Parasitism is also observed in some protists.
- Others exhibit symbiosis.
Are all Protists unicellular?
No, not all Protists are unicellular. Protists such as moulds and algae are multicellular, i.e., they are made up of more than one cell. Amoeba, paramecium and euglena are unicellular organisms belonging to kingdom Protista.
What is Fungi?
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include microorganisms such as yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. These organisms are classified under kingdom fungi. The organisms found in Kingdom fungi contain a cell wall and are omnipresent. They are classified as heterotrophs among the living organisms.
 Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Fungi
To name a few – the appearance of black spots on bread left outside for some days, the mushrooms and the yeast cells, which are commonly used for the production of beer and bread are also fungi. They are also found in most of the skin infections and other fungal diseases.
If we observe carefully, all the examples that we cited involve moist conditions. Thus, we can say that fungi usually grow in places which are moist and warm enough to support them.
Let us have a detailed overview of the structure, classification and characteristics of fungi.
Structure of Fungi
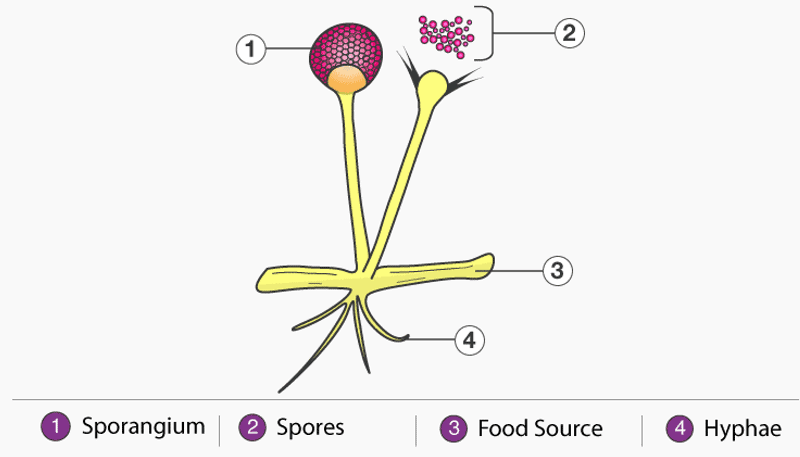 Structure of Fungi
Structure of Fungi
The structure of fungi can be explained in the following points:
- Almost all the fungi have a filamentous structure except the yeast cells.
- They can be either single-celled or multicellular organism.
- Fungi consist of long thread-like structures known as hyphae. These hyphae together form a mesh-like structure called mycelium.
- Fungi possess a cell wall which is made up of chitin and polysaccharides.
- The cell wall comprises protoplast which is differentiated into other cell parts such as cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell organelles and nuclei.
- The nucleus is dense, clear, with chromatin threads. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Characteristics of Fungi
Following are the important characteristics of fungi:
- Fungi are eukaryotic, non-vascular, non-motile and heterotrophic organisms.
- They may be unicellular or filamentous.
- They reproduce by means of spores.
- Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation.
- Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesis.
- Fungi store their food in the form of starch.
- Biosynthesis of chitin occurs in fungi.
- The nuclei of the fungi are very small.
- The fungi have no embryonic stage. They develop from the spores.
- The mode of reproduction is sexual or asexual.
- Some fungi are parasitic and can infect the host.
- Fungi produce a chemical called pheromone which leads to sexual reproduction in fungi.
- Examples include mushrooms, moulds, yeast.
Classification of Fungi
Kingdom Fungi are classified based on different modes. The different classification of fungi is as follows:
Based on Mode of nutrition
On the basis of nutrition, kingdom fungi can be classified into 3 groups.
- Saprophytic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by feeding on dead organic substances. Examples: Rhizopus, Penicillium and Aspergillus.
- Parasitic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by living on other living organisms (plants or animals) and absorb nutrients from their host. Examples: Taphrina and Puccinia.
- Symbiotic – These fungi live by having an interdependent relationship association with other species in which both are mutually benefited. Examples: Lichens and mycorrhiza. Lichens are the symbiotic association between algae and fungi. Here both algae and fungi are mutually benefited as fungi provide shelter for algae and in reverse algae synthesis carbohydrates for fungi.
Based on Spore Formation
Kingdom Fungi are classified into the following based on the formation of spores:
- Zygomycetes – These are formed by the fusion of two different cells. The sexual spores are known as zygospores while the asexual spores are known as sporangiospores. The hyphae are without the septa.
- Ascomycetes – They are also called as sac fungi. They can be coprophilous, decomposers, parasitic or saprophytic. The sexual spores are called ascospores. Asexual reproduction occurs by conidiospores. Example – Saccharomyces
- Basidiomycetes – Mushrooms are the most commonly found basidiomycetes and mostly live as parasites. Sexual reproduction occurs by basidiospores. Asexual reproduction occurs by conidia, budding or fragmentation. Example- Agaricus
- Deuteromycetes – They are otherwise called imperfect fungi as they do not follow the regular reproduction cycle as the other fungi. They do not reproduce sexually. Asexual reproduction occurs by conidia. Example – Trichoderma.
Reproduction in Fungi
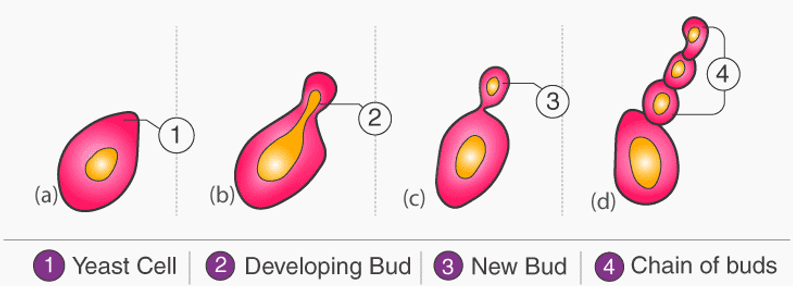 Reproduction in Fungi
Reproduction in Fungi
Reproduction in fungi is both by sexual and asexual means. The sexual mode of reproduction is referred to as teleomorph and the asexual mode of reproduction is referred to as anamorph.
- Vegetative reproduction – By budding, fission and fragmentation
- Asexual reproduction – This takes place with the help of spores called conidia or zoospores or sporangiospores
- Sexual reproduction – ascospores, basidiospores, and oospores
The conventional mode of sexual reproduction is not always observed in the kingdom Fungi. In some fungi, the fusion of two haploid hyphae does not result in the formation of a diploid cell. In such cases, there appears an intermediate stage called the dikaryophase. This stage is followed by the formation of diploid cells.
Uses of Fungi
Fungi are one of the most important groups of organisms on the planet as it plays a vital role in the biosphere and has great economic importance on account of their both benefits and harmful effects.
Following are some of the important uses of fungi:
- Recycling – They play a major role in recycling the dead and decayed matter.
- Food – Mushrooms species are edible which are cultured and are used as food by humans.
- Medicines – There are many fungi which are used to produce antibiotics, to control diseases in humans and animals. Penicillin antibiotic is derived from a common fungi Penicillium.
- Biocontrol Agents – Fungi are involved in exploiting insects, other small worms and help in controlling pests. Spores of fungi are used as spray-on crops.
- Food spoilage – Fungi play a major role in recycling organic material and are also responsible for major spoilage and economic losses of stored food.
Examples of Fungi
Following are the common examples of fungi:
- Yeast
- Mushrooms
- Moulds
- Truffles
Frequently Asked Questions on Fungi
Which organisms belong to kingdom fungi?
Kingdom fungi include mushrooms, yeast, moulds containing filamentous structures called hyphae.
What are the different types of fungi?
The different types of fungi include- Zygomycetes Basidiomycetes, Ascomycetes, and Deuteromycetes.
Which kingdom is closely related to kingdom fungi?
Kingdom fungi are closely related to the animal kingdom. This has been determined by phylogenetic studies. The phylogenetic tree explains how animals diverged from fungi millions of years ago.
What is common between plants and fungi?
Plants and fungi, both have a cell wall.
Which class of kingdom fungi can move?
Chytridiomycota produces flagellated gametes and is the only exception to the group that can move with the help of flagella. These are ancient fungi and are believed to be a connecting link between fungi and animals.














