Morphology of Flowering Plants (Only in NEET) | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Modifications of Roots (Only in NEET) |

|
| Modifications of Stem (Only in NEET) |

|
| Modifications of Leaves (Only in NEET) |

|
| Description Of Some Important Families (Only NEET) |

|
Introduction
- The structure of higher plants is incredibly diverse, which is always fascinating to observe. Despite the wide variety in their external appearance or morphology, all angiosperms share certain fundamental features: they all have roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Additionally, we need to be aware of the various adaptations that different parts of plants may exhibit in response to their environment, such as adaptations for different habitats, protection, climbing, storage, and so on.
- For instance, if you were to pull out a weed, you would notice that it, like all flowering plants, has roots, stems, and leaves. It may also bear flowers and fruits.
- The part of the flowering plant that is underground is called the root system, while the portion that is above the ground is known as the shoot system.
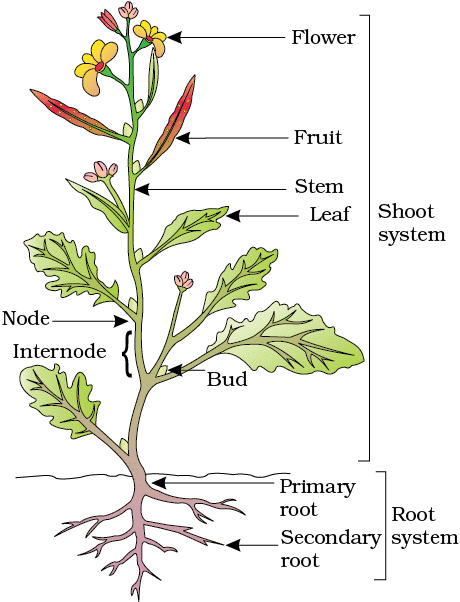 Parts of Flowering Plant
Parts of Flowering Plant
Modifications of Roots (Only in NEET)
Roots in certain plants undergo changes in their shape and structure, becoming modified to perform functions beyond just the absorption and conduction of water and minerals. These modifications are for purposes such as support, food storage, and respiration.
(i) Storage Roots:
- Tap Roots: Plants like carrot and turnip have tap roots that swell and store food.
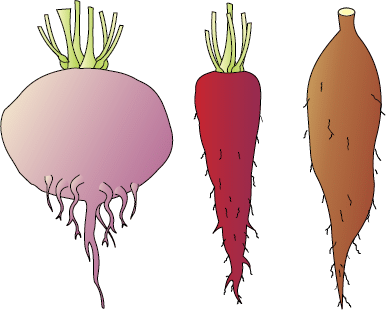
- Adventitious Roots: Sweet potato has adventitious roots that also swell and store food.
(ii) Support Roots:
- Prop Roots: These are the hanging structures that support a banyan tree.
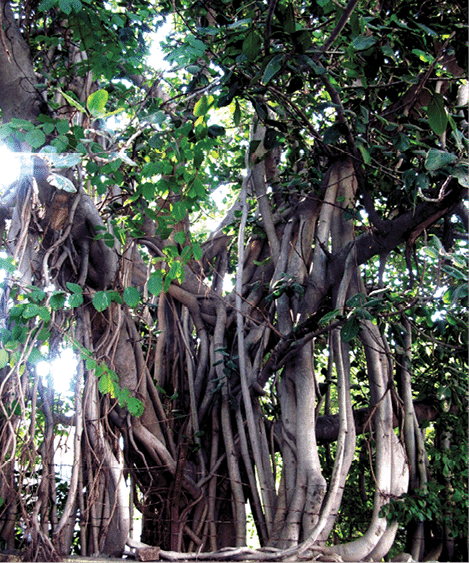 Modification of root for support: Banyan tree
Modification of root for support: Banyan tree- Stilt Roots: Found in plants like maize and sugarcane, these are supporting roots that come out of the lower nodes of the stem.
(iii) Respiratory Roots:
Pneumatophores: In plants like Rhizophora, which grow in swampy areas, roots emerge from the ground and grow vertically upwards. These roots help the plant obtain oxygen for respiration.
 Respiration: Pneumatophores in Rhizophora
Respiration: Pneumatophores in Rhizophora
Modifications of Stem (Only in NEET)
(i) Underground Stems
- Rhizomes: These are underground stems that grow horizontally. They are capable of producing new shoots and roots from their nodes. Examples include ginger, turmeric, and ginger.
- Corms: Corms are swollen, vertical, underground stems that store nutrients. They have a basal plate from which roots and shoots can grow. Examples include crocus and gladiolus.
(ii) Subaerial Stems
- Stolons: Stolons are horizontal stems that grow above ground. They produce new plants at their nodes, which can root down into the soil. Examples include strawberries and spider plants.
- Runners: Runners are similar to stolons but tend to grow just below the soil surface. They also produce new plants at their nodes. Examples include couch grass and some varieties of mint.
(iii) Aerial Stems
- Offset: An offset is a lateral shoot that grows horizontally just below the water surface. It produces new plants at its nodes. Examples include water hyacinth and certain types of pond lilies.
- Suckers: Suckers are vertical shoots that arise from the base of a plant or from its roots. They can develop into new plants. Examples include banana plants and some varieties of bamboo.
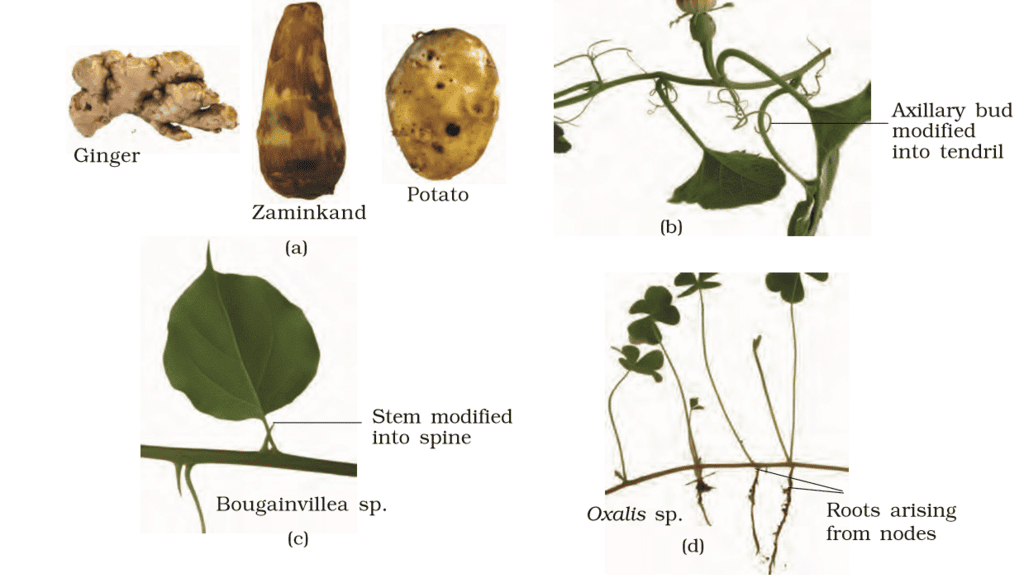 Modifications of stem for : (a) storage (b) support (c) protection (d) spread and vegetative propagation
Modifications of stem for : (a) storage (b) support (c) protection (d) spread and vegetative propagation
Modifications of Leaves (Only in NEET)
- Leaves can be changed to do jobs other than photosynthesis. For example, in pea plants, leaves become tendrils that help the plant climb. In cacti, leaves become spines that protect the plant.
- Some plants, like onion and garlic, have fleshy leaves that store food.
- In Australian acacia, the leaves are small and do not last long. In these plants, the petioles (the part of the leaf stalk) get bigger, turn green, and make food through photosynthesis.
- Leaves of certain insect-eating plants, such as the pitcher plant and Venus flytrap, are also modified leaves that have adapted to catch and digest insects.
 Modifications of leaf for : (a) support: tendril (b) protection: spines (c) storage: fleshy leaves
Modifications of leaf for : (a) support: tendril (b) protection: spines (c) storage: fleshy leaves
Description Of Some Important Families (Only NEET)
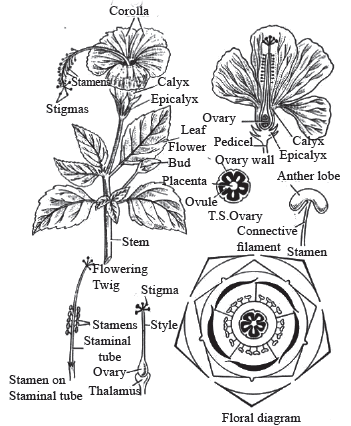
1. Malvaceae
Malvaceae is a family of plants that includes mallows, Hibiscus, and monkshood (order Malvales),
Containing at least 4,000 species of herbs, shrubs, and trees.
Vegetative characters
- Stem: It has branched, erect, branched at the nodes, cylindrical, solid, with stellate hairs usually on the stem.
- Leaves: simple or alternate, rounded, palmately divided, stipulate, generally palmately veined forms.
Floral characters
- Inflorescence: cymose(rare), racemose(mostly), solitary
- Flower: Bracteate. Flowers are bisexual, actinomorphic, hypogynous and pentamerous.
- Calyx: sepals five, gamosepalous, valvate aestivation. In some of the plants persistant calyx are present, it means they are present on fruit.
- Corolla: Petals five, polypetalous, twisted aestivation, mucilagenous and attractive.
- Androecium: Typically, 5-10 stamens are arranged in a tube around the pistil connate at, their bases. Stamens are monoadelphous.
- Gynoecium: Pentacarpellary or polycarpellary, syncarpous but stigma’s are free, so gynoecium is in completely syncarpous. Pentalocular or multilocular, ovary hypogynous, rarely perigynous.
- Fruit: Loculicidal capsule, rarely berry.
- Seed: Non-endospermic seeds.
- Floral Formula:
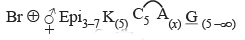
- Economic importance: In horticulture, the family Malvaceae has been used for centuries to make fibres, food,medicine, and timber. Some of the important species with the products they produce are listed below.
(i) Gossypium sp. (cotton), Corchorus sp. (tossa and white jute), Hibiscus sp., Theobroma cacao (cacao), Abelomoschus esculentus (okra).
Need to Know: The Epi in floral formula of Malvaceae denotes epicalyx (Bracteoles) which are present as 3-7 in number. These are the transformed bracteoles & are free and green in colour
2. Cruciferae
Brassicaceae, formerly Cruciferae, the mustard family of flowering plants(order Brassicales), composed of 338 genera and some 3,700 species. Brassicaceae can be found almost on the entire land surface of the earth, but the family is absent.
Vegetative characters
- Stem: erect, herbaceous, slightly hairy
- Leaves: The leaves are mostly simple and alternately arranged, and many are peppery-flavoured.
Floral characters
- Inflorescence: Raceme, indeterminate growth
- Flower: flowers are bisexual, actinomorphic (radial or regular).
- Calyx: sepals four (separate)
- Corolla: petals four (separate), often clawed, cruciform
- Androecium: 6, tetradynamous (4 tall, 2 short)
- Gynoecium: 2 united carpels, superior ovary (hypogynous flower); ovules have parietal placentation
- Fruit: dry, dehiscent. silicle (short, squat), silique (longer than wide by 3X)
- Seeds: Non endospermic
- Floral Formula:
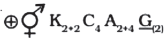
- Economic importance: Crops-many; Brassica (mustard and cabbage), kale, brussel sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, turnip.
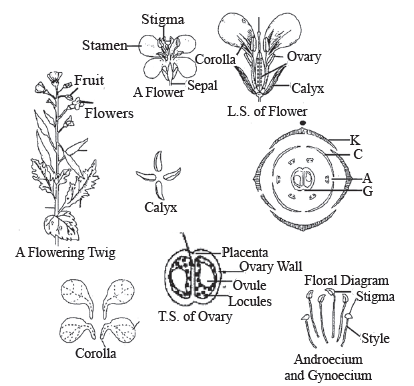 Floral diagram with floral formula of mustard
Floral diagram with floral formula of mustard
3. Leguminosae (Fabaceae)
- Leguminosae family is devided into 3 – subfamilies:
- Papilionoideae,/Caesalpinioideae and Mimosoideae
- It is distributed all over the world.
Vegetative Characters
- Trees, shrubs, herbs; root with root nodules.
- Stem: erect or climber
- Leaves: alternate, pinnately compound or simple; leaf base, pulvinate; stipulate; venation reticulate.
Floral characters
- Inflorescence: Racemose
- Flower: Bisexual, Zygomorphic
- Calyx: Sepals five, gamosepalous; imbricate/valvate aestivation
- Corolla: Petals five, polypetalous, papilionaceous, consisting of a posterior standard, two lateral wings, two anterior ones forming a keel (enclosing stamens and pistil), Vexillary aestivation.
- Androecium: Ten, diadelphous, anther dithecous
- Gynoecium: Ovary superior, Monocarpellary, unilocular with many ovules, style single, marginal placentation.
- Fruit: Legume;
- Seed: one to many, non-endospermic
- Floral Formula:
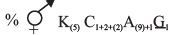
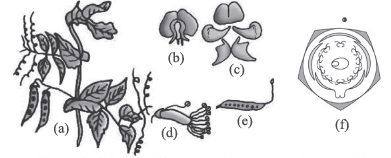 Pisum sativum (pea) plant: (a) Flowering twig (b) Flower (c) Petals (d) Reproductive parts (e) L.S.carpel (f) Floral diagram
Pisum sativum (pea) plant: (a) Flowering twig (b) Flower (c) Petals (d) Reproductive parts (e) L.S.carpel (f) Floral diagram
Economic importance
- Pulses: E.g., Gram, Arhar, Sem, Moong, Soyabean
- Edible oil: E.g., Soyabean, Groundnut
- Dye: E.g., Indigofera
- Fibres: E.g., Sunhemp
- Fibres: E.g., Sesbania, Trifotium
- Ornamentals: E.g., Lupin, Sweet pea
- Medicine: E.g., Muliathi
4. Poaceae/Graminae
Poaceae, earlier called Gramineae (grass) family of monocotyledonous flowering plants. They grow on all parts of the world, in desert to freshwater and marine habitats, and tundra.
Vegetative characters
- Stem: The stem may be underground as in rhizome or runner, herbacius (Wheat, Rice, Doob), shrub like or woody and tall (Bamboo)
- Leaves: are alternate, simple, exstipulate, and distichous.
Floral characters
Inflorescence: The primary inflorescence of grasses is the spikelet, a small structure consisting of a short axis, the rachilla, to which are attached chaffy, overlapping scales (glumes) that cover the florets.
- Flower: Flowers are zygomorphic, may be bisexual or unisexual (Rarely).
- Perianth: two perianths.
- Androecium: three stamens, Polyandrous
- Gynoecium: monocarpellary gynoecium, superior unilocular ovary with single ovule on basal placentation.
- Fruit: Mostly one-seeded Caryopsis (fruit wall is completely fused with the seed coat).
- Floral Formula:
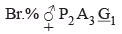
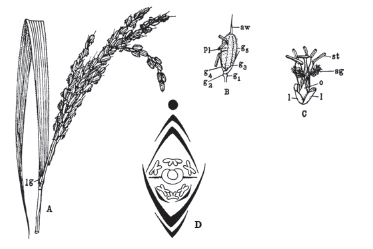 Oryza sativa (Poaceae). (A) Terminal part of plant bearing panicle and spikelet and ligule, (B) Single spikelet, (C) Structure of the bisexual flower, (D) Floral diagram
Oryza sativa (Poaceae). (A) Terminal part of plant bearing panicle and spikelet and ligule, (B) Single spikelet, (C) Structure of the bisexual flower, (D) Floral diagram
Economic importance
- Food: These from the basic food of mankind. These plants are: Triticum aestivum (Wheat), Avena sativa, Zeamays(corn), Oryza sativa (rice), Hordeum vulgare(barley), Penisetum typhoideum(Pearlmillet, Bajra), Sorghum vulgare(Jowar).
- Fodders: The dried stems and leaves of the cereal crops are used as fodder for the cattle.
- Sugar: Sugar is obtained from the juice of Saccharum officinarum(sugarcane).
- Ornamental plants: Many grasses are used in lawns, e.g. Agrostis (floringrass), Poa annua (meadow grass).
- Alcohol and beverages: Ethyl alcohol and many other beverages are prepared form cereals and sugarcane molasses.
- Uses of Bamboo: Bambusa (bamboo) are used as building material. These are used for huts, making boats, carts pipes etc.
5. Compositae- Sunflower family
It is largest family of angiosperms, having largest geographical distribution. It is also known as Asteraceae. The name of this family is based on its inflorescence. i. e. Star-like
Vegetative characters:
- Stem: Erect, or prostrate, herbaceous or woody (Artemisia), hairy, sometimes with latex. Stem tubers are also present (Helianthus).
- Leaves: Alternate rarely opposite or whorled. Leaves may be radical, petiolate or sessile, exstipulate, mostly simple sometimes scale-like (Senecio), unicostate or multicostate reticulate venation.
Floral characters:
- Inflorescence: inflorescence capitulum or head surrounded by involucre of bracts; ray and disc florets, flower tubular or ligulate.
- Flower: flowers are bi - or unisexual or outer male or female, pentamerous, actinomorphic or zygomorphic.
- Calyx: Sepals are modified into pappus or absent or scale like, valvate aestivation is present.
- Corolla: corolla gamopetalous, petal five.
- Androecium: stamens 5, epipetalous, usually dithecous, filament free and anthers united i.e. syngenesious.
- Gynoecium: bicarpellary, syncarpous, ovary unilocular, inferior (epigynous), with basal placentation.
- Fruit: cypsela.
- Floral Formula:
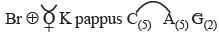
Floral formula of ray florets:
Parts of an Sunflower Head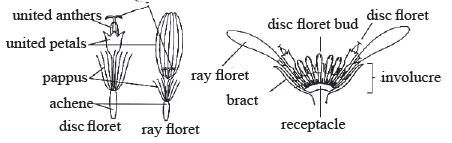 Sunflower : Infloresence with ray and disc florets
Sunflower : Infloresence with ray and disc florets
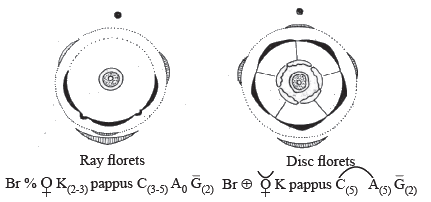 Sunflower : Floral formula of ray and disc florets
Sunflower : Floral formula of ray and disc florets
Economic importance:
- Food: Leaves of Lactuca sativa are used as salad. The roots of Helianthus tuberosus are edible.
- Oil: The seeds of Helianthus and Artemisia yield oil.
- Medicinal: Solidago used in dropsy. Artemisia yields santonin which is used as vermifuge. The roots of Taraxacum used in bowel disorders. The juice of Emillia sonchifolia leaves has cooling effect and is used in eye inflammation and also for night blindness.
- Insecticide: The capitula of Chrysanthemum roseum and C. cinerariifolium are dried, powdered and used as insecticide.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Morphology of Flowering Plants (Only in NEET) - Biology Class 11
| 1. What is the purpose of inflorescence in flowering plants? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of inflorescence? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of venation in flowering plants? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a special type of inflorescence? |  |
| 5. How does the morphology of flowering plants contribute to their reproductive success? |  |





















