Birth Control, Contraception & Medical Termination of Pregnancy | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Population Stabilisation and Birth Control |

|
| Contraceptive Methods |

|
| Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) |

|
| The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017 |

|
Population Stabilisation and Birth Control
Rapid Growth of Population
(a) Population Explosion in the 20th Century
In the 20th century, many things improved, making life better for people. Better health care and living conditions helped more people live longer, which caused the population to grow quickly. The world’s population went from about 2 billion in 1900 to 6 billion in 2000, and 7.2 billion in 2011.
(b) Population Growth in India
- India experienced a similar trend, with the population rising from approximately 350 million at independence to nearly a billion by 2000 and surpassing 1.2 billion by May 2011.
- Factors such as a sharp decline in death rates, maternal mortality rates (MMR), and infant mortality rates (IMR), along with an increase in the number of people of reproductive age, contributed to this growth.
Efforts to Control Population Growth
- The Reproductive Child Health (RCH) programme helped to reduce the population growth rate, but the decline was marginal.
- According to the 2011 census, the population growth rate was below 2 percent, indicating a potentially rapid increase that could lead to a scarcity of basic necessities like food, shelter, and clothing.
- In response, the government implemented measures to curb the population growth rate.
Measures to Encourage Smaller Families
- The government promoted smaller families through various contraceptive methods.
- Campaigns like “ Hum Do Hamare Do. (We Two, Our Two) and the adoption of an “ one child norm. by some urban couples encouraged family planning.
- Legal measures raised the marriageable age for females to 18 years and for males to 21 years, and incentives were offered to couples with small families.
 Hum Do Hamare Do
Hum Do Hamare Do
Contraceptive Methods
Contraceptive methods are designed to prevent unwanted pregnancies and should be user-friendly, easily available, effective, reversible, and have minimal side effects. They should not interfere with the user’s sexual drive or desire.
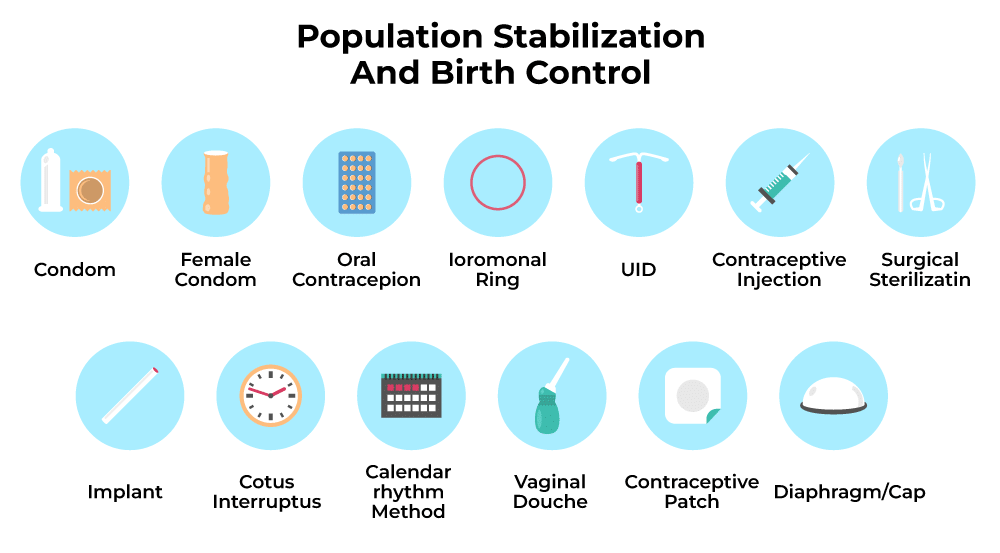
(i) Categories of Contraceptive Methods
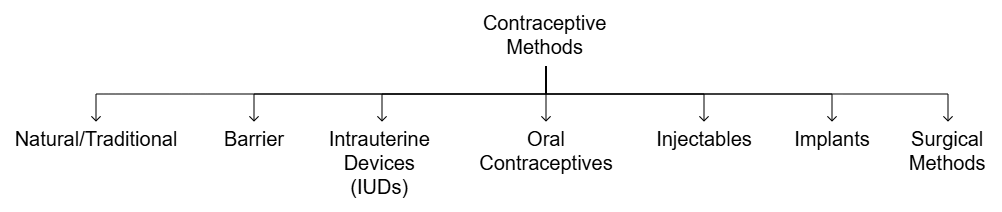 Types of Contraceptive Methods
Types of Contraceptive Methods
1. Natural Methods
Natural methods are based on the principle of preventing the meeting of the ovum and sperm.
(i) Periodic abstinence involves avoiding intercourse from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle when ovulation is likely, known as the fertile period. By abstaining during this time, conception can be prevented.
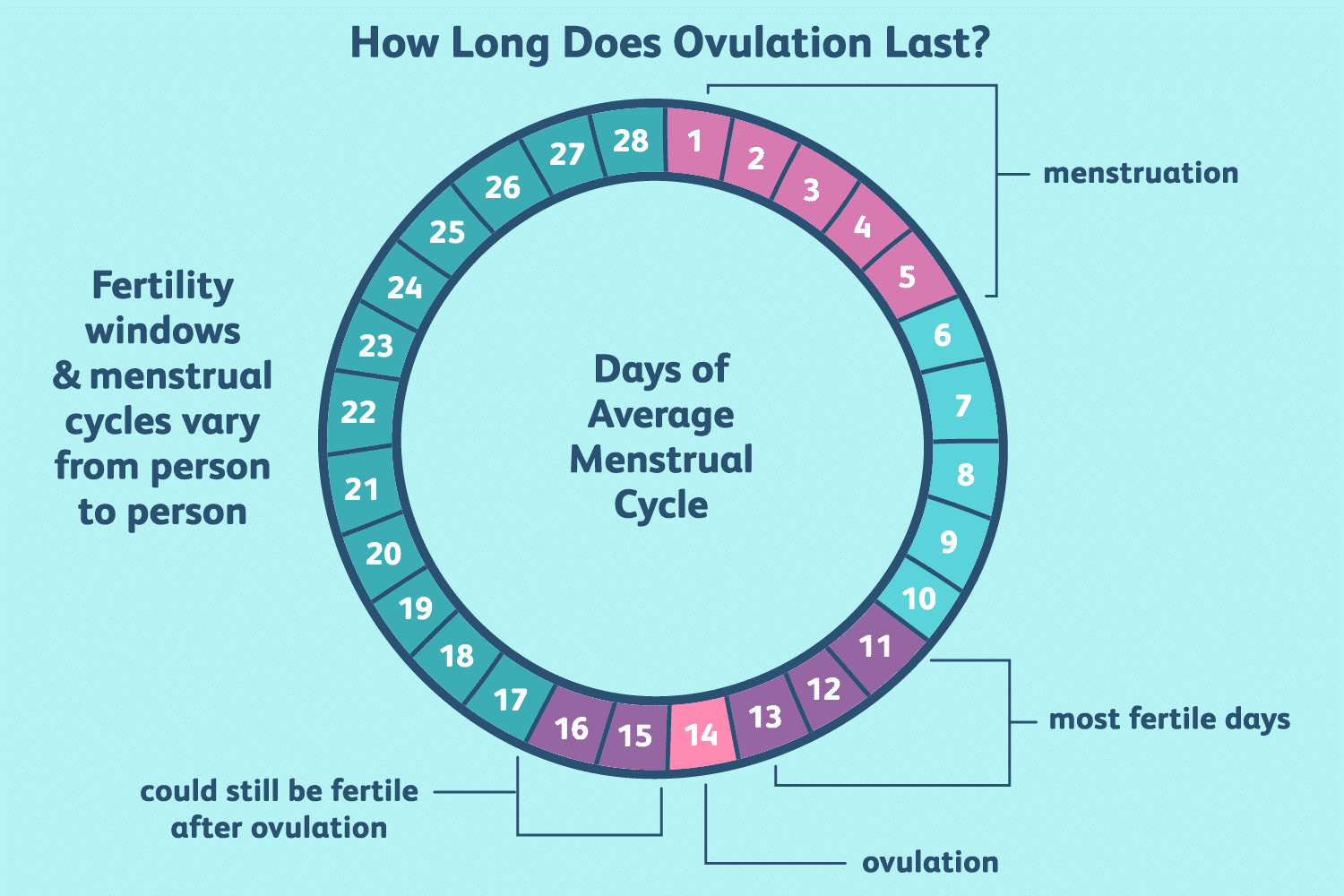
(ii) Withdrawal or coitus interruptus is another method where the male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation to avoid insemination.
(iii) Lactational amenorrhea is based on the fact that ovulation and the menstrual cycle do not occur during intense lactation following childbirth. As long as the mother breastfeeds the child fully, the chances of conception are very low. However, this method is effective for only up to six months after childbirth.
Since natural methods do not involve medicines or devices, they have minimal side effects.However, the chances of failure with these methods can be high.
2. Barrier Methods
Barrier methods prevent the meeting of ovum and sperm by using physical barriers. These methods are available for both males and females.
(i) Condoms: Condoms are made of thin rubber or latex and act as a barrier to prevent sperm from entering the female reproductive tract.
- In males, condoms are worn on the penis before intercourse to collect ejaculate and prevent conception. - Male condoms, such as 'Nirodh,' have gained popularity not only for contraception but also for protecting against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and AIDS.
 Male Condom
Male Condom
- Female condoms are inserted into the vagina and cervix before intercourse, serving the same purpose.
 Female Condom
Female Condom
- Both male and female condoms are disposable, can be self-inserted, and offer privacy to the user.
(ii) Diaphragms, Cervical Caps, and Vaults: These are barriers made of rubber that are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix during intercourse. - They prevent sperm from entering the uterus by blocking the cervix. - Diaphragms, cervical caps, and vaults are reusable.
(iii) Spermicidal Creams, Jellies, and Foams: These products are often used in conjunction with barrier methods to enhance their contraceptive effectiveness.
3. Intra Uterine Devices (IUDs)
IUDs are a highly effective and popular method of contraception. These devices are inserted into the uterus by qualified doctors or nurses through the vagina. There are different types of IUDs available:
(i) Non-medicated IUDs: Such as the Lippes loop.
(ii) Copper-releasing IUDs: Including CuT, Cu7, and Multiload 375.
(iii) Hormone-releasing IUDs: Such as Progestasert and LNG-20.
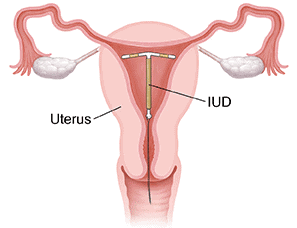 Placement of IUD in the Uterus
Placement of IUD in the Uterus
- IUDs work by increasing the phagocytosis of sperm within the uterus. Copper ions released from the IUDs suppress sperm motility and their ability to fertilise an egg. Hormone-releasing IUDs further make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to sperm.
- IUDs are ideal for women who want to delay pregnancy or space their children. They are one of the most widely accepted methods of contraception in India.
4. Oral Contraceptives
Progestogens or Progestogen-Estrogen Combinations: These are taken in small doses orally. They come in the form of tablets, commonly known as "pills."
- Dosage: Pills need to be taken daily for 21 days, preferably starting within the first five days of the menstrual cycle.
- Cycle: After 21 days, there is a 7-day gap during which menstruation occurs. This cycle is repeated until the woman wishes to prevent conception.
- Mechanism: Pills work by inhibiting ovulation and implantation. They also alter the quality of cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to enter.
- Effectiveness: Pills are very effective with fewer side effects and are well accepted by women.
- Saheli: This is a new oral contraceptive for women that contains a non-steroidal preparation. It is a "once a week" pill with minimal side effects and high contraceptive efficacy.
5. Injectables & Implants
- Progestogens are a type of hormone that can be given to females either on their own or in combination with estrogen.
- These hormones can be administered through injections or implants placed under the skin.
- While the way they work is similar to that of pills, the effectiveness of injections and implants lasts much longer.
 Implants
Implants
Emergency Contraception:Using progestogens, progestogen-estrogen combinations, or intrauterine devices (IUDs) within 72 hours after intercourse has been proven to be highly effective as emergency contraceptives.
These methods can help prevent potential pregnancy resulting from situations such as rape or unprotected casual intercourse.
6. Surgical Methods
Surgical methods, commonly known as sterilisation, are often recommended for either the male or female partner as a definitive way to prevent future pregnancies. These procedures work by blocking the transport of gametes, thereby preventing conception.
Sterilisation in Males: Vasectomy
- In a vasectomy, a small section of the vas deferens, the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, is either removed or tied off.
- This is done through a small incision in the scrotum.
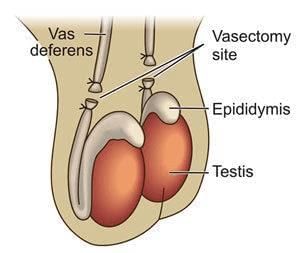 Vasectomy
Vasectomy
Sterilisation in Females: Tubectomy
- In a tubectomy, a small portion of the fallopian tube, which carries eggs from the ovaries to the uterus, is removed or blocked.
- This procedure is done through a small incision in the abdomen or the vagina.
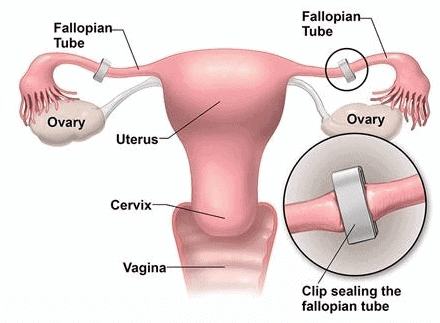 Tubectomy
Tubectomy
Effectiveness and Reversibility
- Both vasectomy and tubectomy are highly effective methods of sterilisation.
- However, the reversibility of these procedures is very limited, making them permanent solutions for contraception.
(ii) Consultation and Considerations in Contraceptive Use
Consultation with Medical Professionals
- It is crucial to emphasize that choosing and using a suitable contraceptive method should always be done in consultation with qualified medical professionals.
- Contraceptives are not regular requirements for maintaining reproductive health; rather, they are used to prevent, delay, or space pregnancies due to personal reasons.
Role in Population Control
- While contraceptives play a significant role in controlling population growth, it is essential to acknowledge their potential side effects.
- These side effects may include nausea, abdominal pain, breakthrough bleeding, irregular menstrual bleeding, and, although not very common, an increased risk of breast cancer.
Balancing Benefits and Risks
- The widespread use of contraceptive methods has a substantial impact on population control.
- However, individuals should be aware of the possible ill effects, even if they are not very significant.
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP), also known as induced abortion, refers to the intentional or voluntary termination of a pregnancy before full term.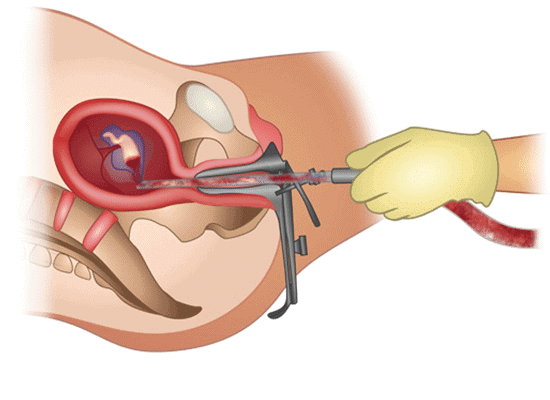 Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Every year, approximately 45 to 50 million MTPs are performed worldwide, accounting for about one-fifth of all conceived pregnancies in a year. The acceptance and legalization of MTP are subjects of debate in many countries due to the emotional, ethical, religious, and social issues involved.
- In India, the government legalized MTP in 1971 under strict conditions to prevent misuse. These restrictions are particularly important to curb indiscriminate and illegal female foeticides, which are reported to be high in the country.
(i) Reasons for MTP
- Unwanted Pregnancies: MTP is sought to terminate unwanted pregnancies resulting from casual unprotected intercourse, contraceptive failures, or cases of rape.
- Health Risks: MTP is also essential in situations where the continuation of the pregnancy poses health risks or could be fatal to the mother, the fetus, or both.
(ii) Safety of MTP
- First Trimester: MTP is considered relatively safe during the first trimester, up to 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Second Trimester: Abortions in the second trimester are significantly riskier.
(iii) Illegal and Unsafe Practices
- Unqualified Practitioners:. disturbing trend is the prevalence of illegal MTPs performed by unqualified individuals, which poses serious health risks and can be fatal.
- Misuse of Amniocentesis: Another dangerous trend is the misuse of amniocentesis to determine the sex of the unborn child. If the fetus is found to be female, it often leads to MTP, which is illegal and harmful.
(iv) Importance of Counseling and Healthcare Facilities
Effective counseling on the risks of unprotected intercourse and the dangers of illegal abortions, along with improved healthcare facilities, could help reverse the unhealthy trends associated with MTP.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017
 Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017
- The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017, was introduced by the Indian government to decrease the number of illegal abortions and the associated risks of maternal mortality and morbidity.
- This Act allows for the termination of pregnancy under specific circumstances within the first 12 weeks, based on the opinion of a single registered medical practitioner.
- If the pregnancy has exceeded 12 weeks but is less than 24 weeks, the opinion of two registered medical practitioners is required, and they must genuinely believe that the necessary grounds for termination are met.
The grounds for terminating a pregnancy under this Act include:
1. Risk to the Pregnant Woman: If continuing the pregnancy poses a risk to the life of the pregnant woman or could cause severe physical or mental harm to her.
2. Risk of Severe Abnormality: If there is a significant risk that the child, if born, would suffer from serious physical or mental disabilities.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Birth Control, Contraception & Medical Termination of Pregnancy - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the difference between birth control and contraception? |  |
| 2. What are the natural methods of contraception? |  |
| 3. How do barrier methods of contraception work? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of oral contraceptives? |  |
| 5. When should emergency contraceptives be used? |  |
















