Surface Chemistry & Adsorption | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Surface chemistry is referred to as the study of the phenomenon occurring on the surfaces of substances. This is very applicable in industries and day to day lives. In other words, surface chemistry deals with all types of surface phenomenon.
What is Surface Chemistry?
It is the study of the chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two surfaces which can be solid-liquid, solid-gas, solid-vacuum, liquid-gas, etc. Some applications of surface chemistry are known as surface engineering. There are various phenomena taking place on the surface of substances and some of them are:
- Adsorption
- Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Corrosion
- Crystallization
Applications of Surface Chemistry
In a wider perspective, surface chemistry deals with the interaction of surfaces of one system with that of the other system. Some phenomena work on this principle such as:
- Catalysis
- Colloid Formation
- Electrode Reactions
- Chromatography
Surface Chemistry has a major role in various chemical processes such as:
- Enzymatic reactions at the biological interfaces found in the cell walls and membranes.
- In the electronics industry, they are used in the surface and interface of microchips found in computers.
- In automobile exhausts, the heterogeneous catalysts found in the catalytic converter for cleaning emissions.
Role of Adsorption in Surface Chemistry
Accumulation of species on higher concentration on the surface of a substance due to intermolecular force is known as adsorption. For Example, gases such as H2, O2, N2 adsorbs on the surface of activated charcoal.
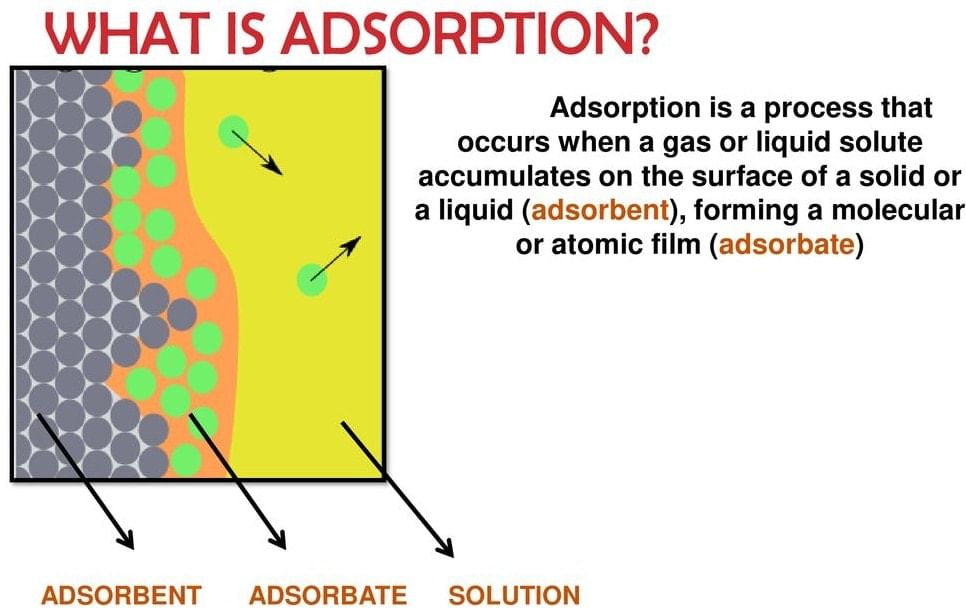
Enthalpy of Adsorption: The amount of heat energy liberated when one mole of gas is adsorbed on the unit surface area of adsorbent is known as enthalpy of adsorption.
Types of Adsorption
Due to the force of interaction between adsorbate and adsorbent, adsorption in surface chemistry is classified into two types.
1. Physical Adsorption or Physisorption
There exists a weak van der Waals force between adsorbate and adsorbent.
Characteristics:
- Nature of forces: weak van der Waals forces
- Specificity: It is not specific in nature
- Reversibility: The process is reversible
- Layer: It is a multi-layered process
- Enthalpy of adsorption: Low enthalpy of adsorption [ 20 – 40 KJ/mole ]
- The energy of activation: Very low
- Desorption: Very easy
- Factors affecting: Surface area of adsorbent nature of adsorbate, pressure, temperature.
2. Chemical Adsorption or Chemisorption
It is due to strong chemical forces between adsorbate and adsorbent.
Characteristics:
- Nature of forces: Strong chemical forces
- Specificity: Highly specific nature
- Reversibility: It is irreversible
- Layer: It is a single-layered process
- Enthalpy of adsorption: High enthalpy of adsorption [40 – 400 KJ/mole]
- The energy of activation: Very high
- Desorption: Very difficult
- Factors affecting: Surface area of adsorbent, nature of adsorbate Temperature.
Effects of Pressure and Temperature on Adsorption
1. Effect of Pressure
The fraction of gas adsorbed is proportional to the pressure of the gas. Adsorption increase with pressure reaches the maximum and becomes constant.
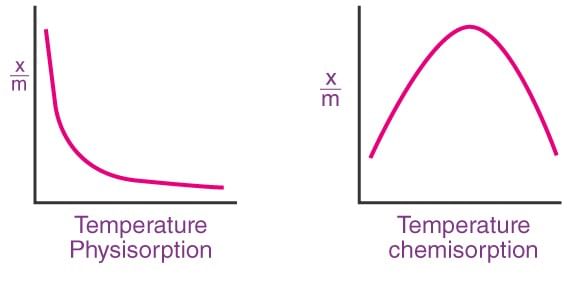
2. Effect of Temperature
- Adsorption of gases on solid is always exothermic.
- Physical adsorption follows the Lechatlier Principle, the amount of gas adsorbed decrease with the increase of temperature.
- Chemisorption increases with an increase in temperature. It reaches the maximum and then decreases.
- The curve obtained by plotting fraction of gas adsorbed and temperature at constant pressure is adsorption isobars.
Different Adsorption Isotherm Models
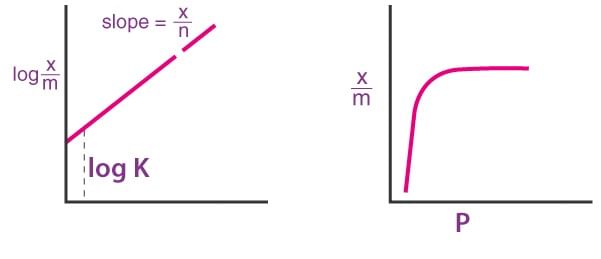
1. Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
x/m = K [P^(1/n)]
‘x’ is the mass of adsorbate on the mass of adsorbent
⇒ log K/m = 1/n (log P + log K)
It does not apply to the adsorption of gases on solids at a higher pressure
2. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
- The layer of gas adsorbed on the solid adsorbent is one molecule thick.
- The adsorbed layer is uniform all over the adsorbent.
- There is no interaction between the adjacent adsorbed molecules.
Emulsions in Surface Chemistry
The colloidal solutions in which both dispersed phase and dispersion medium are liquids are called Emulsions.
Example: Paints, dyes, milk, vanishing cream. On the basis of dispersion medium emulsions in surface chemistry are classified into two types:
Oil in Water Emulsions
In this, the oil or fat droplets are dispersed in water. Example: Milk.
Water in Oil Emulsions
In this, the water droplets are dispersed in oil. Example: Vanishing cream.
Emulsions are unstable, to increase the stability another substance called emulsifiers are added. Example: Milk contains natural emulsion casein.
Applications of Emulsions
- These are used in syrups
- Paints
- Toothpaste
- Digestion of fats
- Pigment and dye
|
117 videos|226 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Surface Chemistry & Adsorption - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is surface chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of surface chemistry? |  |
| 3. What is the role of adsorption in surface chemistry? |  |
| 4. How do pressure and temperature affect adsorption? |  |
| 5. What are different adsorption isotherm models? |  |





















