Introduction: C Language | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
C is a procedural programming language. It was initially developed by Dennis Ritchie in the year 1972. It was mainly developed as a system programming language to write UNIX operating system.
Main Features of C language
The main features of the C language include low-level memory access, a simple set of keywords, and a clean style. These features make C language suitable for system programming like an operating system or compiler development.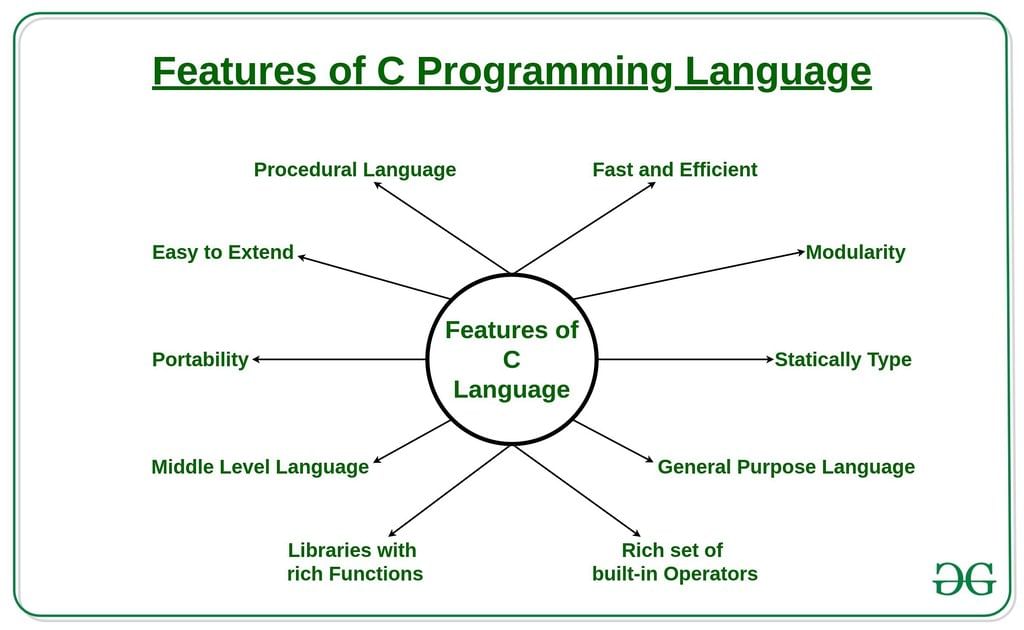
Let's discuss the features of C language in detail:
1. Simple and Efficient - The basic syntax style of implementing C language is very simple and easy to learn. This makes the language easily comprehensible and enables a programmer to redesign or create a new application.
2. Fast - It is a well-known fact that statically typed programming languages are faster than dynamic ones. C is a statically typed programming language, which gives it an edge over other dynamic languages. Also, unlike Java and Python, which are interpreter-based, C is a compiler-based program. This makes the compilation and execution of codes faster.
3. Portability - Another feature of the C language is portability. To put it simply, C programs are machine-independent which means that you can run the fraction of a code created in C on various machines with none or some machine-specific changes.
4. Extensibility - You can easily (and quickly) extend a C program. This means that if a code is already written, you can add new features to it with a few alterations.
5. Function-Rich Libraries - C comes with an extensive set of libraries with several built-in functions that make the life of a programmer easy. You can also create your user-defined functions and add them to C libraries.
6. Dynamic Memory Management - One of the most significant features of C language is its support for dynamic memory management (DMA). It means that you can utilize and manage the size of the data structure in C during runtime. For instance, you can use the free() function to free up the allocated memory at any time.
7. Modularity With Structured Language - C is a general-purpose structured language. This feature of C language allows you to break code into different parts using functions which can be stored in the form of libraries for future use and reusability.
8. Mid-Level Programming Language - Although C was initially developed to do only low-level programming, it now also supports the features and functionalities of high-level programming, making it a mid-level language. And as a mid-level programming language, it provides the best of both worlds. For instance, C allows direct manipulation of hardware, which high-level programming languages do not offer.
9. Pointers - With the use of pointers in C, you can directly interact with memory. As the name suggests, pointers point to a specific location in the memory and interact directly with it. Using the C pointers, you can operate with memory, arrays, functions, and structures.
10. Recursion - It means that you can create a function that can call itself multiple times until a given condition is true, just like the loops. Recursion in C programming provides the functionality of code reusability and backtracking.
Note - Many later languages have borrowed syntax/features directly or indirectly from the C language. Like syntax of Java, PHP, JavaScript, and many other languages are mainly based on the C language. C++ is nearly a superset of C language (Few programs may compile in C, but not in C++).
Beginning with C programming
Structure of a C program: After the above discussion, we can formally assess the structure of a C program. By structure, it is meant that any program can be written in this structure only. Writing a C program in any other structure will hence lead to a Compilation Error.
The structure of a C program is as follows:
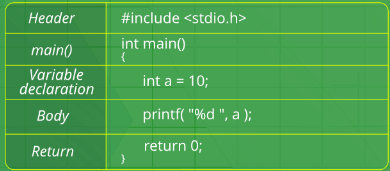 Structure of a C program
Structure of a C program
1. The components of the above structure are:
(i) Header Files Inclusion: The first and foremost component is the inclusion of the Header files in a C program.
A header file is a file with extension .h which contains C function declarations and macro definitions to be shared between several source files.
Some of C Header files:
- stddef.h: Defines several useful types and macros.
- stdint.h: Defines exact width integer types.
- stdio.h: Defines core input and output functions
- stdlib.h: Defines numeric conversion functions, pseudo-random network generator, memory allocation
- string.h: Defines string handling functions
- math.h: Defines common mathematical functions
(ii) Main Method Declaration: The next part of a C program is to declare the main() function. The syntax to declare the main function is:
Syntax to Declare the main method:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{}
(iii) Variable Declaration: The next part of any C program is the variable declaration. It refers to the variables that are to be used in the function. Please note that in the C program, no variable can be used without being declared. Also in a C program, the variables are to be declared before any operation in the function.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
.
.
(iv) Body: The body of a function in the C program, refers to the operations that are performed in the functions. It can be anything like manipulations, searching, sorting, printing, etc.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
printf("%d", a);
.
.
(v) Return Statement: The last part of any C program is the return statement. The return statement refers to the returning of the values from a function. This return statement and return value depend upon the return type of the function. For example, if the return type is void, then there will be no return statement. In any other case, there will be a return statement and the return value will be of the type of the specified return type.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
(vi) Writing first program:
Following is first program in C:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("GeeksQuiz");
return 0;
}
(vii) Let us analyze the program line by line.
- Line 1: [ #include <stdio.h> ]
1. In a C program, all lines that start with # are processed by a preprocessor which is a program invoked by the compiler.
2. In a very basic term, the preprocessor takes a C program and produces another C program.
3. The produced program has no lines starting with #, all such lines are processed by the preprocessor.
4. In the above example, the preprocessor copies the preprocessed code of stdio.h to our file.
5. The .h files are called header files in C. These header files generally contain declarations of functions. We need stdio.h for the function printf() used in the program.Question for Introduction: C LanguageTry yourself:The C-preprocessors are specified with _________ symbol.View Solution - Line 2 [ int main(void) ]
1. There must be a starting point from where the execution of compiled C program begins.
2. In C, the execution typically begins with the first line of main().
3. The void written in brackets indicates that the main doesn’t take any parameter (See this for more details). main() can be written to take parameters also. We will be covering that in future posts.
4. The int that was written before main indicates the return type of main(). The value returned by main indicates the status of program termination. - Line 3 and 6: [ { and } ]
In C language, a pair of curly brackets defines the scope and are mainly used in functions and control statements like if, else, and loops. All functions must start and end with curly brackets. - Line 4 [ printf(“GeeksQuiz”); ]
printf() is a standard library function to print something on standard output. The semicolon at the end of printf indicates line termination. In C, a semicolon is always used to indicate the end of a statement. - Line 5 [ return 0; ] The return statement returns the value from main(). The returned value may be used by an operating system to know the termination status of your program. The value 0 typically means successful termination.
2. How to execute the above program:
In order to execute the above program, we need a compiler to compile and run our programs. There are certain online compilers that can be used to start C without installing a compiler.
- Windows: There are many compilers available freely for the compilation of C programs like Code Blocks and Dev-CPP. We strongly recommend Code Blocks.
- Linux: For Linux, gcc comes bundled with Linux, Code Blocks can also be used with Linux.
|
158 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction: C Language - Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What are the main features of the C programming language? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of portability in the C programming language? |  |
| 3. How does C programming support modularity? |  |
| 4. How does C programming achieve efficiency? |  |
| 5. Why is C programming widely used in various applications? |  |






















