Study Notes on CPM & PERT | Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Project
It is a group or combination of interrelated activities that must be executed in a certain fixed order before the entire task is completed. Activities are interrelated in a logical sequence in the sense that some activity can only be started when all activities earlier to it are completed.
Project Network diagram
A network in project management displays the duration of project activities and the dependencies between activities graphically or as a table. In a network, nodes (rectangles) represent activities and events. Arrows connect nodes with each other. Arrows represent the dependency between the activities or events.
Rules for network construction
- An activity can only be started when all the activity earlier to it are completed.
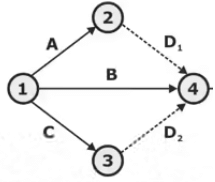
- No two or more activities may have the same head and tail event.
- In this condition to represent the same logic dummy activity will be required.
Application of Network Analysis (PERT and CPM)
- Research and development projects.
- Equipment maintenance and overhauling.
- Construction projects (building, bridges, dams)
- Setting up new industries
- Planning and launching of new products.
- Design of plants, machines and systems
- Organization of big programs
Terminology in Network analysis
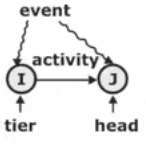
- Activity: It is the recognizable part of a project which consume time and resources for its completion and it may involve physical or mental work when all the activities are executed, then only a project gets completed.
- Event: It denotes the point of time or accomplishment occurring at a moment and is used to denote the starting and end point of an activity, event neither consume any time nor resources for its completion.
- Dummy Activity: An activity which use to show logic, dependency or relationship of one activity over the other but doesn’t consume any time or resources for its completion it termed as dummy activity it is represented by dotted line arrow. Dummy activities only be used when it is necessary but there is no restriction on the no. of dummy activity used. There should be no looping & dangling on the network diagram.
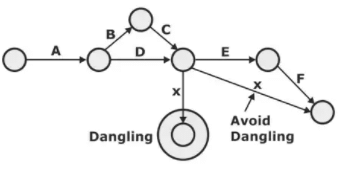
- Dangling: It is the condition when activity other than the final activity doesn’t have any successor activity. Such activity should be connected directly to the last event of network diagram.
Types of Network diagram
- Event on Node (EON) or Activity on Arrow (AOA): An arrow diagram is defined as a process diagramming tool used to determine optimal sequence of events, and their interconnectivity. It is used for scheduling and to determine the critical path through nodes.
- Activity on node (AON): The Activity-on-Node, or Precedence Diagram uses similar logic to Activity-on-Arrow (A-O-A), but it is represented differently. With this technique, the activity is represented by a box or node, with the arrows showing logic relationship between boxes.
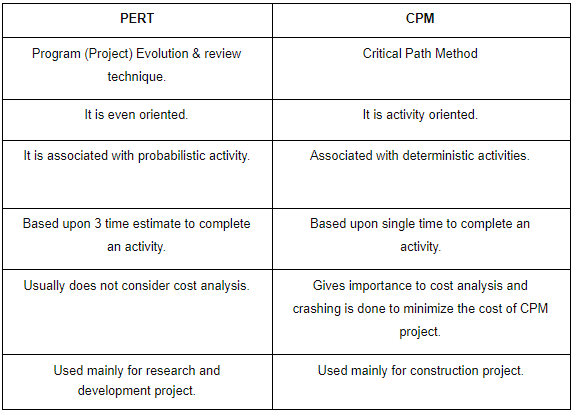
- PERT(Programme Evaluation and Review Technique)
(a) PERT is event oriented.
(b) PERT is a probabilistic model i.e. it takes into account uncertainties involved in the estimation of time of a job or an activity.
(c) It uses three estimates of the activity time - optimistic, Pessimistic and Most Likely.
(i) Optimistic time (t0 or a): It is the minimum time required to complete an activity when everything goes acc. to the plan.
(ii) Pessimistic time (tp or b): It is the maximum time required to complete an activity when everything goes against the plan.
(iii) Most likely time (tm or m): It is a time required to complete an activity when executed under normal working condition.
(d) Thus, the expected duration of each activity is probabilistic and expected duration indicates that there is 50% probability of getting the job done within that time.
(e) PERT is primarily concerned with project time. It enables the project manager to schedule and coordinates the various activities so that the project can be completed on scheduled time.
(f) PERT is generally used for those projects, which are not of repetitive in nature (e.g. Research and Development Projects) and where time required to complete Various activities are not known in advance.
(g) The process of PERT analysis includes
(i) Identification of the activities of the project.
(ii) Estimation of activity time.
(iii) Defining inter-dependence relationships between the
(iv) Drawing the net work.
(v) Using the network to obtain the scheduling data activities
(h) PERT is majorly applied for scheduling, organization and integration of different tasks within a project.
(i) It provides the blueprint of project and is efficient technique for project evaluation.
(j) Avg or expected time to complete an activity is given by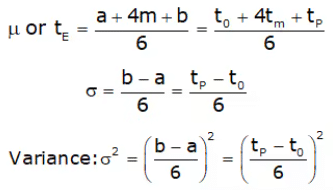
(k) Probability of completing project within scheduled time: If TE is expected project completion time, s is std. deviation along the critical path then the prob. of completing project within a scheduled time (TS) is given by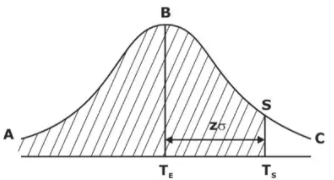 P(Ts) = Area(ABS)
P(Ts) = Area(ABS)
Z = (Ts - TE)/σ Where Z is std. normal variant
ROL =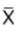 + Zσ
+ Zσ
Std deviation along critical path ⇒ σ =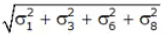
Where σ1, σ3, σ6, σ8 are standard deviation along critical path
CPM (Critical Path Method)
- CPM is a technique which is used for the projects where the time needed for completion of project is already known.
- It is majorly used for determining the approximate time within which a project can be completed.
- A network is a graphical representation of a project, depicting the flow as well as the sequence of well-defined activities and events. A network path consists of a set of activities that connects the networking beginning event to the network terminal event.
- The longest path through the network is called the critical path and its length determines the minimum duration in which the said project can be completed.
- An activity in a network diagram is said to be critical, if the delay in its start will further delay the project completion time. In this activity times are known with certainity.
- Critical path is the largest path in project management which always provide minimum time taken for completion of project.
Prepare Project Scheduling
The project scheduling can be done in the following steps:
- Time schedule for each activity.
- Earlier and latest start time as well as earlier finish and latest finish of each activity.
- Float for each activity.
- Critical activities and critical path for the network.
1. Earliest and Latest Time
- Earliest Start Time (EST) of Activity: It is earliest event time of tail and event.
- Earliest Finish Time (EFT) of Activity: It is the sum of earliest start time and activity time.
EFT = EST + activity time - Latest Start Time (LST) of Activity: It is the latest possible time by which an activity can start without delaying the date of completion of the project.
- Latest Finish Time (LFT) of Activity: It is latest possible time by which the activity must be completed so that the scheduled date for the completion of the project may not be delayed.
LFT = LST + activity time
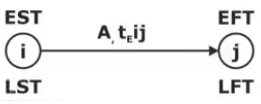
- Earliest Event Time (Ei): It is the maximum of earliest finish times of all activities ending into that event.
Ej = max. of all {Ei + tEij} - Latest Event Time (Li): It is the minimum of the latest start time of all activities originating from that event.
Li = min. of all {Lj - tEij}

2. Float or Slack
Float or slack means a margin of extra time over and above its duration which a non-critical activity can consume without delaying the date of completion of the project.
- Slack term used for PERT (event), It is amount of time by which particular event can be delayed without delaying the project schedule.
Si = Li - Ei - Float term used for CPM (activity)
- Total Float: It is extra time available for an activity without delaying the project schedule.
TF = LFT - EFT = LST - EST - Free Float: It is that part of total float which can be used without affecting the float of succeeding activity.
FF = TF - Head event slack - Independent Float: It is the amount of time which can be used without affecting either the head or the tail event.
IF = FF - Tail event slack
TF ≥ FF ≥ IF - Interfering Float: It can be defined as that part of the total float which causes a reduction in the float of the successor activities. It can be defined as the difference between the latest finish time of the activity under consideration and earliest start time of the following activity or zero whichever is larger.
3. Crashing or Time Cost Model
It is an extension of critical path method that consider a compromise between the time and cost required to complete a project the total cost of any project consists of direct and indirect cost involves in its execution.
Cost time Slope = 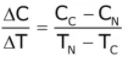
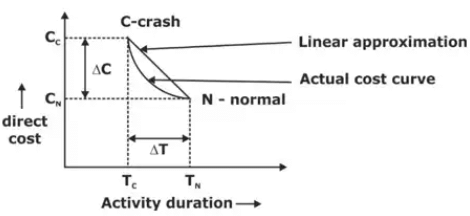
The objective of crashing a network is to determine optimum project duration corresponding to minimum cost of project and the steps involved are:
- In the critical path select the critical activity having minimum cost slope.
- Reduce the duration of this activity by one-time unit.
- Revise the network diagram by adjusting the time & cost of crashed activity again find critical path, project duration and total cost of project.
- If the optimum project duration is obtained then stop otherwise repeat from step i.
|
30 videos|64 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Study Notes on CPM & PERT - Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is CPM (Critical Path Method) in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. How does CPM help in managing mechanical engineering projects? |  |
| 3. What is PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 4. How does PERT help in estimating project timelines in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of using CPM and PERT in mechanical engineering projects? |  |
















