Inventory Control | Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Inventory Control
In inventory control our aim is to manage inventory in such a manner that day to day working run smoothly without any delay but at the minimum of cost.
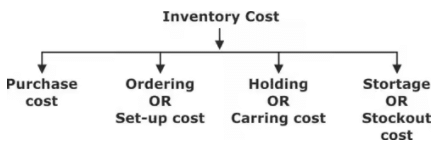
Type of inventory costs
- Purchase Cost: It is the cost of purchasing inventory it depends upon quantity or bulk purchased.

- Ordering Cost:

- Set up cost:

- Holding or Carrying Cost:

- Shortage or Stock out cost:

Types of inventory
- Transit or Pipeline: Inventory can’t provide service while in transportation such inventory is called transit inventory.
- Buffer or safety stock: It is the reserve stock kept throughout the year and it is held for protecting against the fluctuation in the demand rate and lead time.
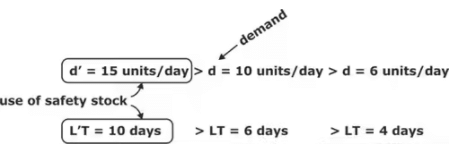 Lead Time: It is the time gap between placing an order and inventory on-hand so that it can be used or consumed.
Lead Time: It is the time gap between placing an order and inventory on-hand so that it can be used or consumed. - Seasonal Inventory: The demand of the inventory changes with seasons of the year.
- Anticipation inventory: The inventory is build-up to meet anticipated demand in the future like big selling forecast, govt. policy change, price hike, strike shut down etc.
- Decoupling inventory: It is extra inventory kept between two interdependent operations or workstations and it works as a buffer during breakdown and maintenance.
Characteristic of Inventory Model
- Dependent: The demand for these item is directly related or linked to any other item, usually of a higher level of which it becomes a part.
- Independent: The demand for this items is not directly related or linked to any other item it is difficult to compute and it is projected with the help of forecasting.
Deterministic & Probabilistic
- Deterministic: In these model demand rate and lead time remain fixed and constant and therefore we need not to carry safety stock.
- Probabilistic: This model represents real-world condition where there is variation and fluctuation in the demand rate and lead time. In this model we need to carry safety stock to prevent stock out.
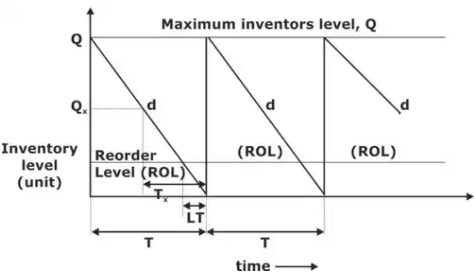
- Notations: D : Annual or yearly demand of inventory (units/year)
Q : Quantity to be ordered at each order point (units/order)
N : Number of orders placed in a year (order/year).
T : Time length of one inventory cycle or time gap between 2 successive order (year/order)
[same unit]
C : Cost of purchasing one unit of inventory (Rs/unit)
C0 : Cost of placing one order (Rs/order)
Ch : Cost of holding one unit in inventory for one complete year (Rs/unit/year)
Type of Inventory Models
Deterministic Models or Economic Order Quantity or Harris Wilson model or Infinite Rate of Replenishment
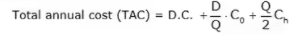
The ordering quantity Q* where holding cost becomes equal to ordering cost and total inventory cost is minimum is known as economic order quantity [EOQ].
only for EOQ
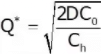
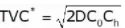
only for EOQ
When holding cost is given in terms of interest or % it always correspond to unit price of inventory and interest rate should be always yearly.
Ch = i % of C
EOQ with price break or Quantity discount
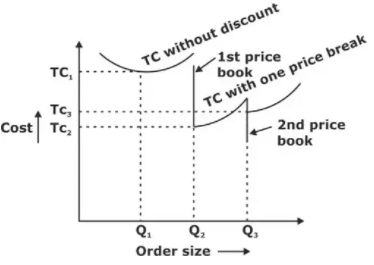
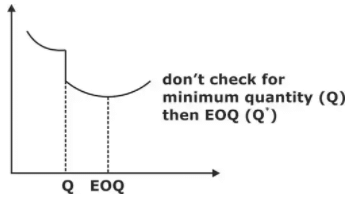
In this problem, first we compute feasible EOQ and then total cost is computed at EOQ and next higher order size having price break whenever the total cost comes out to be minimum gives the best order size.
Production or Build up model
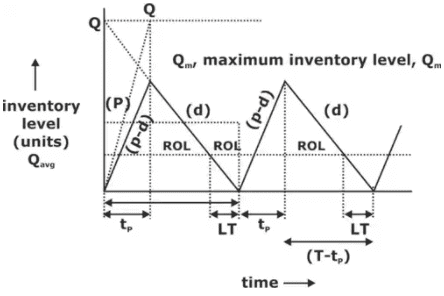
Q: Quantity to be produced/manufactured in every set up (unit/setup)
C0: (Rs/setup) cost of each set up
tP: production/manufacturing time
P: production/built-up rate
d: demand/consumption rate
Qm = Q(p-d/p)
TVC = Setup cost (S.C.) + Holding cost (H.C.)
S.C. = No. of setup × cost/setup
SC = D/Q x Co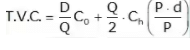
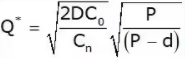
Production factor > 1
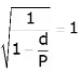
case when P→∞
S.C. = H.C.
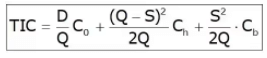
Shortage or Stockout or Back order
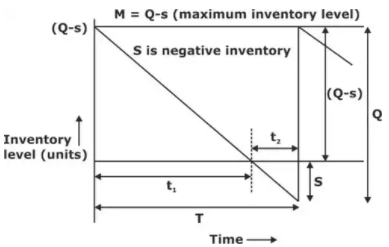
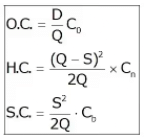
Annual SC = S2/2Q.Cb
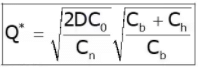

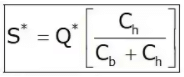
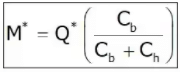
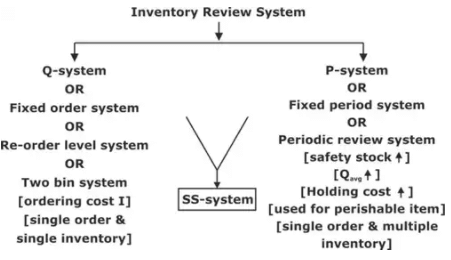
Probabilistic Models
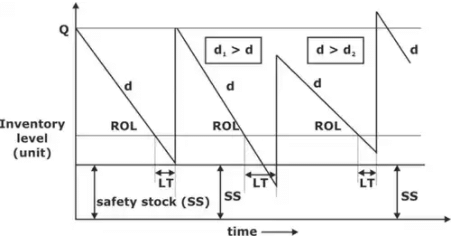 Re-order level = Average demand during LT (ADDLT) + Safety Stock (SS)
Re-order level = Average demand during LT (ADDLT) + Safety Stock (SS)
Qavg = Q/2 + SS
Service Level Model
This model is preferred when the different cost factor involved with inventory are not known exactly it is based upon probability theory and amount of safety stock is kept according to level of service management wants to active.
Service Level = Number of units Supplied without delay/total number of units demanded
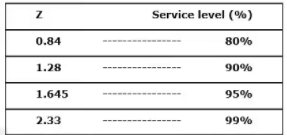
When the demand during lead time may be approximated by a normal distribution with certain avg. and std. deviation (s), then re-order level is given by,
ROL = 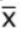 + Zσ
+ Zσ
Inventory Classification and Control
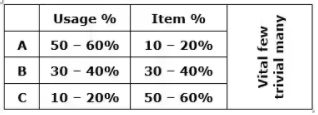
1. ABC Control (Always better control)
- In ABC control, inventory items are classified into A,B & C category depending upon their usage value.
- It is based on Pareto law or 80 – 20 law.
2. VED (Vital essential & desirable)
- Inventory is classified on the basis of importance of inventory for the production system.
3. HML (High Medium & Law)
- Inventory are classified on the basis of unit price of inventory.
4. SDE (Source difficult & Easy)
- Inventory are classified on the basis of availability of inventory for the production system.
- e.g. Nuclear power plant
|
30 videos|64 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Inventory Control - Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is inventory control in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. Why is inventory control important in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 3. What are the common challenges in inventory control for mechanical engineering companies? |  |
| 4. What are some inventory control techniques used in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 5. How can technology aid in inventory control for mechanical engineering companies? |  |