Sheet Metal | Manufacturing Engineering - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Sheet Metal Operations
A sheet is a plate with thickness less than 5 mm. Sheet metal operations are performed over metal sheet when length and width is very large compared to thickness. The basic cutting operations which come under Sheet Metal Operations are Punching Operation and Blanking Operation. For both punching and blanking operations, the punch and die combination will be used as tools.
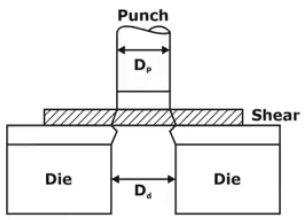 Punching and Blanking Setup
Punching and Blanking Setup
When the force is applied by using the punch on to the sheet, the cutting or shearing action will be taking place in the sheet producing a piece/blank leaving a hole in the sheet.
- In punch and die working, if the hole produced in the sheet is useful, it is called Punching or Piercing operation.
- To ensure that the cutting or shearing action is taking place on the sheet, the Punch size is always less than the Die size.
- In punching operation, the punch size is made equal to hole size and clearance is provided on the die.
- Punch Size < Die Size (Basic Requirement)
- Punch Size = Hole Size (Needed)
- Clearance → Die.
- Shear → Punch.
When the force is applied by using the punch on to the sheet, the cutting or shearing action will be taking place in the sheet producing a piece/blank.
In punch and die working, if the Piece/blank produced in the sheet is useful, it is called as Blanking operation.
- In blanking Operation, the die size is made equal to blank size and clearance is provided only on the Punch.
- Die Size = blank Size.
- Clearance → Punch.
Analysis of Punching and Blanking
Let, C is the amount of clearance per side of the die opening. The optimum clearance can be determined with the help of the following relation,
Optimum clearance, C = 0.0032t * sqrt(τ)
Where, t = sheet thickness in mm, τu = ultimate shear stress in N/mm2
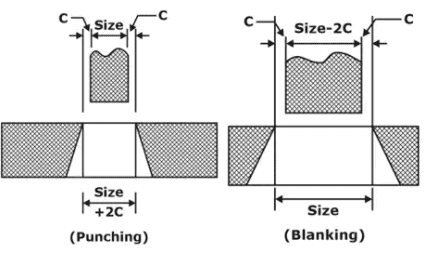
Load Estimation of Punching and Blanking Operation
The distance which the punch enters into the work material to cause rupture to take place is called ‘penetration’ and is usually given as the percentage of the stock thickness.
Fmax = As × τu
where As = shearing area = p × t
τu = ultimate shear stress
t = thickness of plate
p = perimeter, p = πd for Circular cross-section
As = πdt for circular cross-section
For rectangular blanks with length L and width b, it is Fmax = 2(L + b)t.τu
Energy Required Or Work Done in Punching/Blanking
Work done = Force × distance = Fmax × Kt
In general K = 0.2 to 0.6, K = % penetration required for completing the shearing action.
Methods of Reducing Punch Force
The working faces of the punch or die are ground off so that these do not remain parallel to the horizontal plane but are inclined to it. The angle of inclination is called shear. This has the effect of reducing the sheared area at any one time and the maximum force is much less.
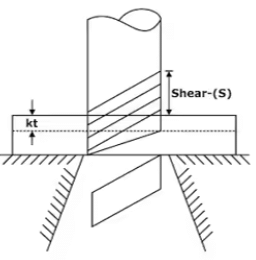
Stock Strip Layout
Another important aspect of the blanking operation is to minimize the scrap by an optimum layout design (also known as nesting).
 (a) Improper Layout
(a) Improper Layout
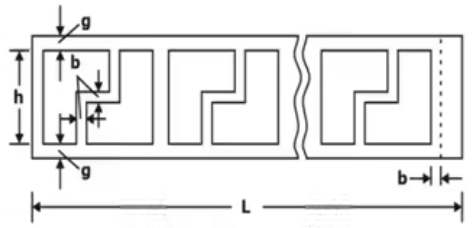 (b) Optimum Layout
(b) Optimum Layout
In a circular blank, some saving in the scrap may be achieved only through a choice of multiple rows. Since the components are to be ultimately blanked out of a stock strip, precaution is to be taken while designing the dies for utilizing as much of stock as possible. It is also necessary in progressive dies, to ensure continuous handling of the scrap on the die block, which means that the scrap strip should have sufficient strength.
Spring Back
Spring Back is the elastic recovery leading to the increase of the included angle when the bending pressure is removed. To compensate for spring back two methods are commonly used:
- Overbending: The punch angle and radius are smaller than the final ones.
- Bottoming: Squeezing the part at the end of the stroke.
Deep Drawing
It is a Sheet Metal forming process in which a sheet metal blank is radially drawn into a forming die by the mechanical action of a punch. Deep drawing is mainly used for producing Cup-shaped components. Drawing is called deep drawing when the height of the cup if greater than half of the diameter of the cup, otherwise shallow drawing. Most of the utensils used in the kitchen are produced by using Deep Drawing Operation only.
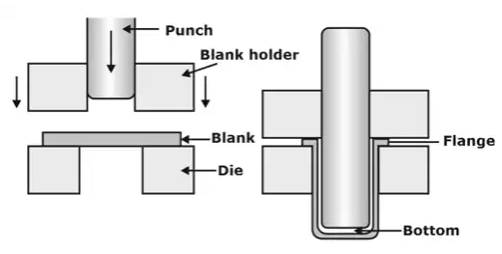
Clearance
Clearance c is the distance between the punch and die and is about 10% greater than the stock thickness: c = 1.1t
Measures of Drawing
Two measures of the severity of a deep drawing operation following measures are used,
- Drawing ratio DR defined as DR = Db/Dp, Here Db is the blank diameter and Dp is the punch diameter. DR must be less than 2.0 for a feasible operation. If it is more than 2.0, the progressive deep drawing is applied .
- Thickness-to-diameter ratio t/Db- It is desirable to be greater than 1% to avoid wrinkling.
Blank size determination
The blank diameter can be calculated by setting the initial blank volume equal to the final volume of the part and solving for diameter Db.
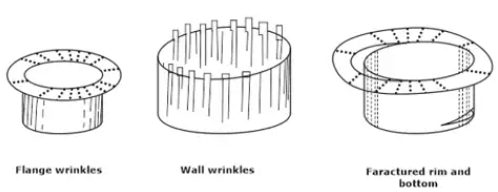
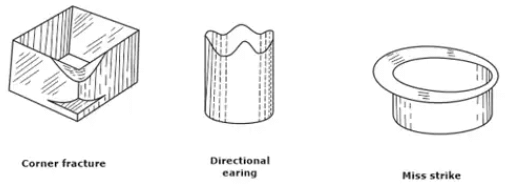
Deep Drawing Defects
As already noted, many types of deformations are involved in the deep drawing operation on sheet metals.
- An insufficient blank holder pressure causes wrinkles to develop on the flange, which may also extend to the wall of the cup.
- Too much of a blank holder pressure and friction may cause a thinning of the walls and a fracture at the flange, bottom, and the corners(if any).
- While drawing a rolled stock, ears a lobes tend to occur because of the anisotropy induced by the rolling operation.
- Due to this misplacement of the stock, unsymmetrical flanges may result. This type of defect is commonly referred to as a miss strike.
- The effect of a large grain size is to produce a dull surface (orange peel effect). This effect is also common in the bending operations.
|
52 videos|54 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on Sheet Metal - Manufacturing Engineering - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is sheet metal engineering and what are its applications? |  |
| 2. What are the common sheet metal forming processes? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using sheet metal in engineering applications? |  |
| 4. What are the common materials used in sheet metal engineering? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of tolerances in sheet metal engineering? |  |






















