Heat Treatment | Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Introduction
- Heat treatment is a combination of heating and cooling operation and applied to a metal or alloy in the solid-state in a way that will produce desired properties.
- All basic heat-treating processes for steel involve the transformation or decomposition of austenite.
- The nature and appearance of these transformation products determine the physical and mechanical properties of any given steel.
- The difference in temperature use within thick and thin section of articles of variable cross-section should be considered and whenever possible, provision should be made for slowing the heating of the thinner section to minimize thermal stress and dispersion.
Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process generally used to:
- Relieve internal stresses
- Increase, softness, ductility and toughness
- Produce a specific microstructure.
It consists of three stages:
- Heating to a desired temperature
- Holding or Soaking' at that temperature
- Cooling usually to room temperature.
(i) It is employed for low and medium carbon steels that will be experiencing plastic deformation during forming operation.
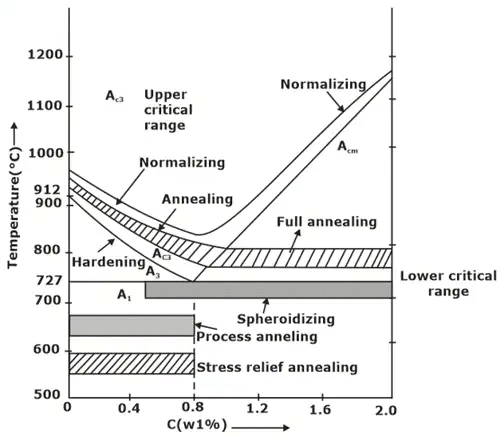
(a) Full annealing: Hypoeutectoid steel and hypereutectoid steel is heated above 50°C of upper critical line and lower critical line respectively. Then component is cooled slowly in furnace. Hence coarse grains are obtained resulting in decreased strength and hardness.
(b) Process annealing: The hypoeutectoid steel is heated below the lower critical line. It relieves the back stresses and no change in microstructure occurs. It is only for low carbon steels.
(c) Spherodise annealing: It improves the machinability of medium and high carbon steel. The specimen is heated just below the lower critical temperature. The carbide in steel is transformed into globular form.
(d) Diffusion annealing: It makes the chemical composition uniform. The sample is heated to 1150°C and kept at that temperature for 6-8 hours and cooled slowly in furnace.
Normalizing
- Steels that have plastically deformed eg: a rolling operation, consists of grains of pearlite and a proeutectoid phase, which are irregularly shaped and relatively large and vary in size.
- Normalizing is used to refine these grains (i.e. to decreases average grain size) and produce more uniform and desirable size distribution.
- The microstructure formed is fine grained pearlite with a proeutectoid Phase.
- It is accomplished by heating alloy (55°C to 85°C) above the upper critical temperature , after sufficient time has been given to alloy to completely transform to austenite, the treatment is terminated by cooling in air. It raises hardness and strength of alloy but decreases ductility of steels.
 Heat treatment
Heat treatment
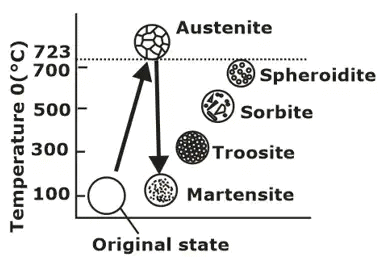
Tempering
It is done:
- To relive residual stress
- To improve ductility
- Toughness is increased.
- High temperature tempering (500-700°C)
Resulting structure is Sorbite, residual stress completely vanished. Tempering of martensite
Tempering of martensite - Medium temperature tempering (300-500°C)>
(i) Resulting in Troostite formation.
(ii) After tempering work is cooled to water, leads to enhanced endurance strength.
(iii) Due to increase in endurance limit, thus used for making "spring steels and die steels". - Low temperature tempering (150°C-300°C):
(i) Holding time is 1-3 hrs.
(ii) Apart from achieved properties in tempering, this process provides additional "wear resistance”.
(iii) It enhances true tensile strength and hardness change by small extent.
(iv) It is used for measuring & cutting tools.
Case Hardening or Surface Hardening Methods
- Its main objective is to achieve hard surfaces with relatively soft core and hard surface is called case.
- Hard surface provides good wear resistance while good toughness is the result of soft core. There are various treatments to impart surface hardness which are discussed below:
(a) Carburizing
- It is applied to low carbon steels having up to 0.18% C.
- Temperature range is between 870-950°C and result in the formation of Austenite phase, which has maximum solubility of carbon.
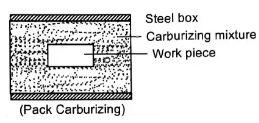
(i) Pack carburizing
- Here, the pieces to be hardened are surrounded by a carburizing mixture and then packed in a steel box.
- It is heated to around 870-950°C.
- Carburizing mixture: 50% charcoal + 20% BaCO3 + 5% CaCO3 + 5-12% Na2CO3
 Pack carburizing
Pack carburizing
(ii) Gas carburizing
- Here work part is treated in a atmosphere of gases containing carbon and hydrocarbon gases such as CH4, butane etc.
- Here, the workpiece is heated to temperature of 950°C and held for 3-12 hours.
- CH4 → 2H2 + C (atomic)
(iii) Liquid carburizing
- Here, the part is heated to 950°C and it is kept in a molten salt bath having 20% NaCN, which gives Carbon (C) & Nitrogen (N).
- Carbon and small amount of Nitrogen diffuses into surface at this temperature.
- In carburizing operations carbon can be penetrated up to the depth of 0.3 mm with hardness obtained around (55-65 HRC).
(b) Nitriding
- It is done by heating steel in the atmosphere of NH3 gas.
- Piece to be nitrided are placed in an airtight container, workpieces are heated to a temperature in range (500-600°C), at which NH3 dissociates into 2NH3 → 2N + 3H2
- This atomic nitrogen diffuses to the surface making case hardened.
- Here work part is immersed in molten salt bath containing sodium cyanide (NaCN). which is heated to 820-860°C.
- This is usually followed by water quenching.
- The cyanide both consists of:
20-30% NaCN + 25-50% NaCl + 25-50% Na2CO3
Induction Hardening
- Workpieces heated in an induction furnace surrounded by copper coils which are water cooled. High frequency AC current is passed through Cu coils and thus alternate magnetic field set up which induce eddy currents on the surfaces.
- Heat is generated on the surface by eddy currents.
- The surface of work piece is heated in austenitic range then quenched immediately to form martensite.
- The structure of core remains unchanged because it is not affected by heat.
- Heating rate is 300°/sec for hypoeutectoid steel and subsequently heating time is very small (2-50 sec.) quenching temperature depend upon rate of heating if the rate is 500°C/sec, it is 1000°C & if it is 250°C then 900°C.
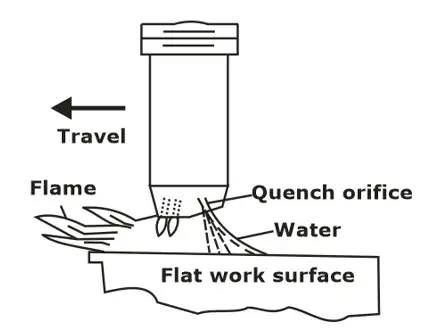
Flame Hardening
- Process consists of heating the surface of high carbon steels by a high temperature gas flame at 2400-3500°C, followed by immediate cooling is air or water.
- Heat is supplied by oxy-acetylene torch. The heat is supplied so quickly to the surface that the core remains unaffected.
- The thickness of hardened layer is 2-4 mm and its structure is martensite.
 Flame hardening
Flame hardening
|
15 videos|19 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Heat Treatment - Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is heat treatment in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. What are the common methods of heat treatment? |  |
| 3. What factors influence the choice of heat treatment method? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of heat treatment in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of heat treatment in mechanical engineering? |  |