Flexible Pavement | Transportation Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Introduction
Flexible pavements are those, which on the whole have low or negligible flexural strength and are rather flexible in their structural action under the loads.
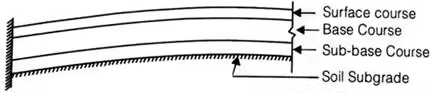
A typical flexible pavement consists of four components:
- soil subgrade
- sub-base course
- base course
- surface course.

(i) Stress Under Road Surface as per Boussineq’s Equation,
where,
σz = vertical stress at depth z.
q = surface pressure.
z = depth at which σz is computed.
a = radius loaded area.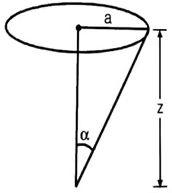
(ii) As per IRC
Maximum legal axle load = 8170 kg
Equivalent single wheel load = 4085 kg.
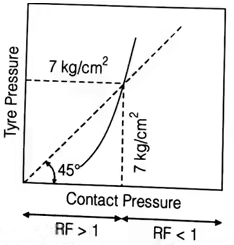
(iii) Contact pressure
(iv) Rigidity factor (R.F)
(v) Equivalent Single Wheel Load (ESWL) 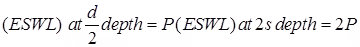
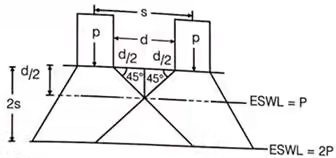
Methods of Flexible Pavement Design
(i) Group Index Method
G.I = 0.2a + 0.005ac + 0.01bd
(ii) C.B.R Method
(a) 
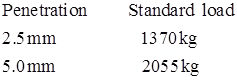
(b) The thickness of Pavement, (T)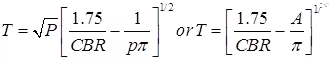
where, P = Wheel load in kg.
CBR = California bearing ratio in percent
p = Tyre pressure in kg/cm2
A = Area of contact in cm2.
A = πa2
a = Radius of contact area.
(c) Number of a heavy vehicle per day for design (A),
A = P[1 + r](n + 10)
where, A = No. of vehicles at the end of design period.
P = Number of heavy vehicles per day at least count.
r = Annual rate of increase of heavy vehicles
n = Number of years between the last count & the year of completion of construction.
(d) CBR Method of pavement design by cumulative standard axle load,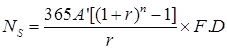
where,
Ns = Cumulative number of standard axle load
A’ = Number of the commercial vehicle per day when construction is completed considering the number of lanes.
n = Design life of the pavement, taken as 10 to 15 years.
F = Vehicle damage factor.
D = Lane distribution factor
(iii) California Resistance Value Method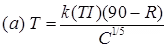
where, T = Total thickness of pavement, (cm)
k = Numerical constant = 0.166
T.I = Traffic Index
T.I = 1.35(EWL)0.11
R = Stabilometer resistance value
C = Choesiometer value.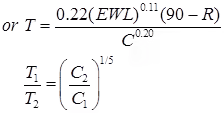
where, T1 & T2 are the thickness values of any two pavement layers & C1 & C2 are their corresponding Cohesiometer values.
(iv) Triaxial Method
(a) Thickness of pavement required for single layer, (TS)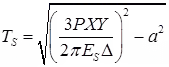
where, TS = Thickness in cm
P = Wind load in kg
X = Traffic coefficient
Y = Rainfall coefficient
ES = Modulus of elasticity of subgrade soil (kg/cm2)
a = Radius of contact area (cm)
Δ = Design deflection (0.25 cm)
(b) Thickness of Pavement Consist of Two layer system,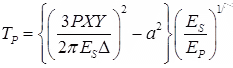
where, EP = Modulus of elasticity of pavement material
T1/T2 = (ES)/(EP)1/3
(v) MC Load Method
T = k.log10(P/S)
where, T = Required thickness of gravel base (cm)
P = Gross wheel load, (kg)
k = Base course constant.
(vi) Burmister Method (Layered System)
Displacement equations given by Burmister are,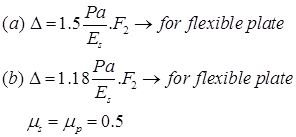
where, μs and μp are Poisons ratio for soil subgrade & pavement.
For single layer, F2 = 1
P = Yielded pressure
ES = Subgrade modulus
a = Radius of loaded area
|
26 videos|91 docs|58 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|