Phase Relations of Soils: Soil-Water Relationship | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Properties of Soils
- Phase Diagram
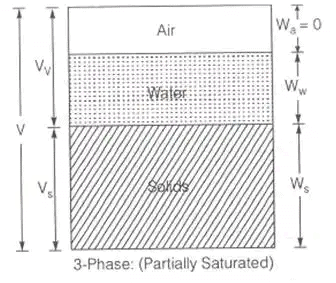
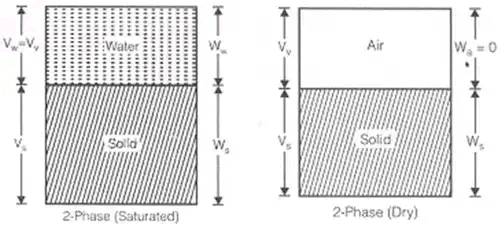
(i) Soil mass is in general a three-phase system composed of solid, liquid and gaseous matter in a blended form with each other.
But in phase diagram – for understanding, these three matters are shown separately.
(ii) In supersaturated, state with change in water content volume of voids changes hence volume of soil changes.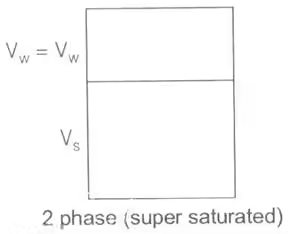
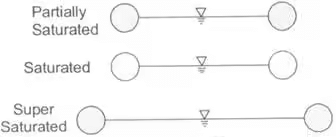 The diagrammatic representation of the different phases in a soil mass is called the "phase diagram".
The diagrammatic representation of the different phases in a soil mass is called the "phase diagram".
- Water content
w = (Ww/Ws) x 100
where, WW = Weight of power
WS = Weight of solids
There can be no upper limit to water content, i.e. w ≥ 0 - Void ratio
e = Vv/Vs
where, Vv = Volume of voids
V = Total volume of soil
Porosity cannot exceed 100% i.e.,
0 < n < 100
Void ratio is more important engineering property. - Degree of Saturation
S = (Vw/Vv) x 100
where, Vw = Volume of water
Vv = Volume of voids
0 ≤ S≤ 100
for perfectly dry soil: S = O
for Fully saturated soil: S = 100%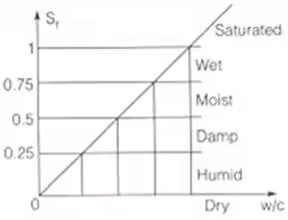
- Air Content
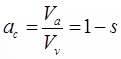 Va = Volume of air
Va = Volume of air
Sr + ac = 1 - % Air Void
%na = (Volume of air/Total volume) x 100 = (Va/V) x 100
na = n.ac
Unit Weight
- Bulk unit weight
γ = W/V = (Ws+Ww)/(Vs+Vw+Va)
Thus Bulk unit weight is total weight per unit volume.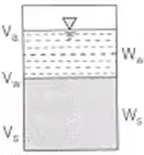
- Dry Unit Weight is the weight of soil solids per unit volume.
γd = Ws/V
Dry unit weight is used as a measure of denseness of soil. More dry unit weight means more compacted soil. - Saturated unit weight: It is the ratio of total weight of fully saturated soil sample to its total volume.
γsat = Wsat/V
(i) Submerged unit weight or Buoyant unit weight (γ): It is the submerged weight of soil solids per unit volume.
γ' = γsat-γw
γsat = unit wt. of saturated soil
γ = unit wt. of water
(ii) Unit wt. of solids:
γs = Ws/Vs
γ is roughly 1/2 of saturated unit weight.
Specific Gravity
- True/Absolute Special Gravity, G
(i) Specific gravity of soil solids (G) is the ratio of the weight of a given volume of solids to the weight of an equivalent volume of water at 4℃.
G = Ws/Vs.γw = γs/γw
G = 2.6 to 2.75 for inorganic solids
= 1.2 to 1.4 for organic solids
(ii) Apparent or mass specific gravity (Gm): Mass specific gravity is the specific gravity of the soil mass and is defined as the ratio of the total weight of a given mass of soil to the weight of an equivalent volume of water.
Gm = (W/V.γw) = (γ or γd or γsat)/γw
where, γ is bulk unit wt. of soil
γ = γsat for saturated soil mass
γ = γd for dry soil mass
Gm < G
In India, G is reported at 27℃,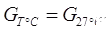
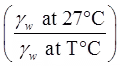
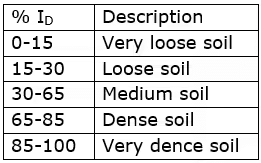
- Relative density (ID)
To compare the degree of denseness of two soils.
ID ∞ Shear strength ∝ (1/Compressibility)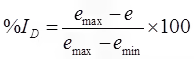
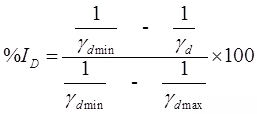
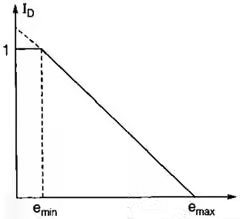 A. when particles are arranged in cubical array
A. when particles are arranged in cubical array
emax = 91%, nmax = 47.6%
B. When particles are arranged in prismoidal array (Rhomohedral Array)
emin = 35%, nmin = 25.9% - Relative Compaction
Indicate: Degree of denseness of cohesive + cohesionless soil
Rc = γD/γDmax
Relative Density
Indicate: Degree of denseness of natural cohesionless soil
Some Important Relationships
- Relation between γd, γ
γd = γ/(1+w) ,
Vs = V/(1+e) & Ws = W/(1+w) - Relation between e and n
n = e/(1+e) or e = n/(1-n) - Relation between e, w, G and S:Se = w. G
- Bulk unit weight (γ) in terms of G, e, w and γw γ, G, e, Sr, γw
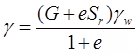
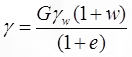
{Se = w. G} - Saturated unit (γsat.) weight in terms of G, e & γwSr = 1
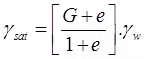
- Dry unit weight γd in terms of G, e and γwSr = 0
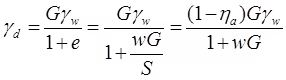
- Submerged unit weight (γ') in terms of G, e and γw
γ = γsat - γw =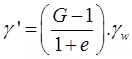
- Relation between degree of saturation (s) w and G
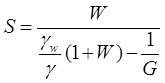
Methods for determination of water content
- Oven Drying Method
(i) Simplest and most accurate method
(ii) Soil sample is dried in a controlled temperature (105-110℃)
(iii) For organic soils, temperature is about 60℃. Soil having gypsum, temperature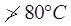
(iv) Sample is dried for 24 hrs.
(v) For sandy soils, complete drying can be achieved in 4 to 6 hrs.
(vi) Water content is calculated as:
where, W1 = weight of container
W2 = weight of container + moist sample
W3 = weight of container + dried sample
Weight of water = W2 – W3
Weight of solids = W3 – W1 - Pycnometer Method
(i) quick method
(ii) capacity of pycnometer = 900 m/.
(iii) this method is more suitable for cohesionless soils.
(iv) used when specific gravity of soil solids is known
(v) Let W1 = Wt. of empty dried pycnometer bottle
W2 = Wt. of pycnometer + Soil
W3 = Wt. of pycnometer + Soil + Water
W4 = Wt. of pycnometer + Water.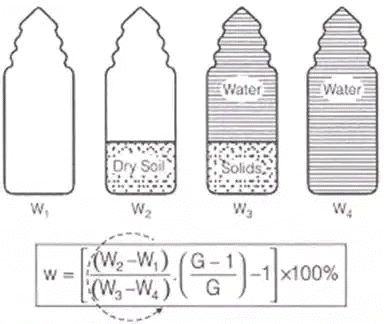 (W1, W2, W3 and W4 are in anticlockwise order)
(W1, W2, W3 and W4 are in anticlockwise order) - Calcium Carbide Method/Rapid moisture Meter Method Field Method
(i) Quick method (requires 5 to 7 minutes); but may not give accurate results.
(ii) The reaction involved is
CaC2 + 2H2O → C2H2 ↑ + Ca(OH)2
(iii) Soil sample weights 4-6 gms.
(iv) The gauge reads water content with respect to total mass of soil. i.e., wr = Ww/(Ws)wet
(In this equipment pressure calibrated against water content with respect to total mass)
(v) Actual water content w = (wr/(1-wr)) x 100%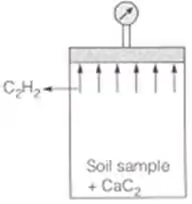 wr is moisture content recorded, expressed as fraction of moist wt. of solid.
wr is moisture content recorded, expressed as fraction of moist wt. of solid.
w is actual water content. - Sand Bath Method (Field Method)
(i) quick, field method
(ii) used when electric oven is not available.
(iii) soil sample is put in a container & dried by placing it in a sand bath, which is heated on the kerosene store.
(iv) water content is determined by using same formula as in oven drying method. - Torsion Balance Moisture Meter Method
(i) quick method for use in laboratory.
(ii) Infrared radiations are used for drying sample.
(iii) Principle: The torsion wire is prestressed accurately to an extent equal to 100% of the scale reading. Then the sample is evenly distributed on the balance pan to counteract the prestressed torsion and the scale is brought back to zero. As the sample dries, the loss in weight is continuously balanced by the rotation of a drum calibrated directly to read moisture% on wet basis. - Alcohol Method
(i) It is a quick method adopted in field.
(ii) Should not be used for organic soil and soils containing calcium compound.
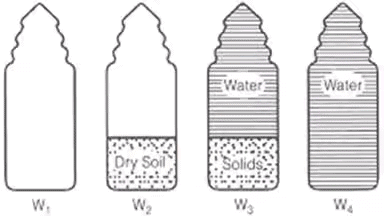
Determination of specific gravity of soil solids
- Pycnometer method is used.
- Instead of pycnometer, Density bottle (50 ml) OR Flask (500 ml) can also be used.
Let, W1 = Weight of empty pycnometer
W2 = Weight of pycnometer + soil sample (oven dried)
W3 = Weight of pycnometer + soil soilds + water
W4 = Weight of pycnometer + water
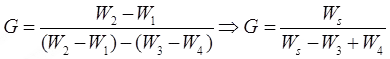
Methods for the determination of in sity unit weight
1. Core-Cutter Method
- Used in case of cohesive soils.
- Cannot be used in case of hard and gravelly soils.
γ = W/V - The method consists of driving a core-cutter (Volume = 1000 cc) into the soil and removing it, the cutter filled with soil is weighted. Volume of cutter is known from its dimensions and in situ unit weight is obtained by dividing soil weight by volume of cutter.
- If water content is known in the laboratory, the dry unit weight can also be computed.
γd = γ/(1+w)
2. Sand Replacement Method
- Used in case of hard and gravelly soils.
- A hole in ground is made. The excavated soil is weighted. The volume of hole is determined by replacing it with sand. Insitu unit weight is obtained by dividing weight of excavated soil with volume of hole.
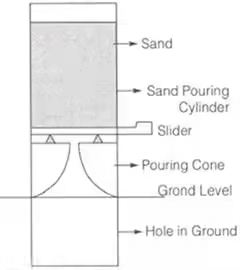
3. Water Displacement Method
- Suitable for cohesive soils only, where it is possible to have a lump sample.
- A regular shape, well-trimmed sample is weighted. (W1). It is coated with paraffin wax & again weighted (W2). The sample is now placed in a metal container filled with water upto the brim. Let the volume of displaced water be Vm. Then volume of uncoated specimen is calculated as,
V = V - (W2-W1)/γP
where, = unit wt. of paraffin wax
Thus, bulk unit wt. of soil - Sands + Gravels: Bulky grains
Bulk grains classified as – angular, Subangular, Sub rounded, rounded, well rounded
Higher angularity ∝ Higher Shear Strength - Clay Minerals: Flaky grains
Grain size distribution
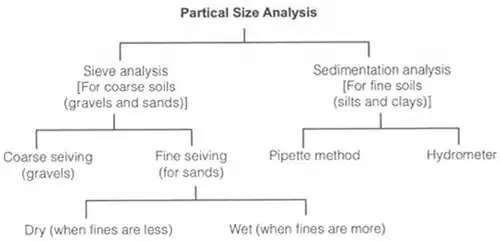
- Sieve Analysis: (For Coarse Grained Soils)
The fraction retained on 4.75 mm sieve is called the gravel fraction which is subjected to coarse sieve analysis.
The material passing 4.75 mm sieve is further subjected to fine sieve analysis if it is sand or to a combined sieve and sedimentation analysis if silt and clay sizes are also present. - Coarse Sieves: 4.75 mm, 10 mm, 20 mm, 80 mm.
- Fine Sieves: 75 μ, 150 μ, 212 μ, 425 μ, 600 μ, 1 mm, 2 mm.
- Concept of "Percentage finer"
% retained on a particular sieve = (Weight of soil retained on that sieve/Total weight of soil taken) x 100
Cumulative % retained = sum of % retained on all sieves of larger sizes and the % retained on that particular sieve. "Percentage finer" than the sieve under reference = 100% - Cumulative % retained. - Sedimentation Analysis
According to stokes law, the terminal velocity is given by,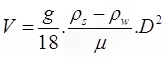 = density of grains (g/cm3)
= density of grains (g/cm3)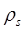 = density of water (g/cm3)
= density of water (g/cm3)
μ = viscosity of water
g = acceleration due to gravity (cm/s2)
D = Diameter of grain (cm)
If 'h' the height through which particle falls in time 't', then h/t = k.D2
∴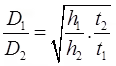
- Pipette Method
In this method, the weight of solids per cc of suspension is determined directly by collecting 10 cc of soil suspension from a specified sampling depth.
If md = dry mass (obtained after drying the sample) then, mass present in unit vol. of pipette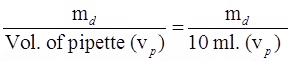
If Md = total mass of soil dissolved in total volume of water (V) then mass/unit volume
= Md/V
Therefore, % finer is given by = %
N = mdNp/mdN
In m is the mass of dispersing agent dissolved in the total volume V, then actual % finer,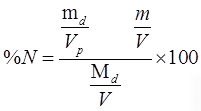
- Hydrometer Method
In this method the weight of solids present at any time is calculated indirectly by reading the density of soil suspension. - Calibration of Hydrometer
Establishing a relation between the hydrometer reading RH and effective depth (He).
The effective depth is the distance from the surface of the soil suspension to the level at which the density of soil suspension is being measured.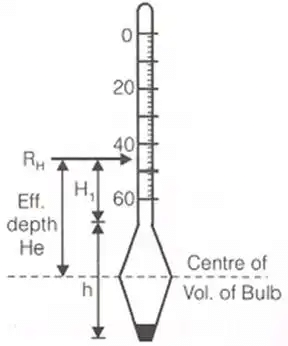 Effective depth is calculated as
Effective depth is calculated as
He = H1 + 1/2(h - VH/AJ)
where, H1 = distance (cm) between any hydrometer reading and neck.
h = length of hydrometer bulb
VH = volume of hydrometer bulb
AJ = area of the cross section of the jar.
Reading of Hydrometer is related to sp. gr. or density of soil suspension as:
GSS = 1 + (RH/1000)
Thus a reading of RH = 25 means, Gss = 1.025 and a reading of RH = -25 means, Gss = 0.975% finer is given as: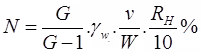
where, G = sp. gr. of soil solids
RH = final corrected value of hydrometer
V = Total volume of soil suspension
W = weight of soil mass dissolved. - Corrections to Hydrometer Reading
(i) Meniscus correction: (Cm)
Hydrometer reading is always corresponding to the upper level of meniscus.
Therefore, meniscus correction is always positive (+Cm).
(ii) Temperature correction: (Ct)
Hydrometers are generally calibrated at 27℃. If the test temperature is above the standard (27℃) the correction is added and, if below, it is subtracted.
(iii) Dispersing/Deflocculating agent correction: (Cd)
The correction due to rise in specific gravity of the suspension on account of the addition of the deflocculating agent is called Dispersing agent correction (Cd).
Cd is always negative.
The corrected hydrometer reading is given by
(RH) = RH + Cm±Ct-Ca - Grain Size Distribution Curves
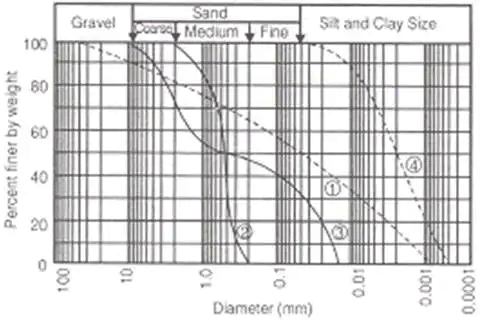 Curve-1: Well graded soil: good representation of grain sizes over a wide range and its gradation curve is smooth.
Curve-1: Well graded soil: good representation of grain sizes over a wide range and its gradation curve is smooth.
Curve-2: Poorly graded soil/ Uniform gradation:
It is either an excess or a deficiency of certain particle sizes or has most of the particles about the same size.
Curve-3: Gap graded soil: In this case some of the particle sizes are missing.
Curve-4: Predominantly coarse soil.
Curve-5: Predominantly fine soil.
The diameter D10 corresponds to 10% of the sample finer in weight on the Grain size distribution curve. This diameter D10 is called effective size.
Similarly, D30 and D60 are grain dia. (mm) corresponding to 30% fine and 60% finer.
The shape parameters related to these are:
(i) Coefficient of Uniformity Cu = D60/D10
(ii) Coefficient of Curvature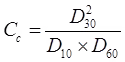
(a) for a soil to be well graded: [1 < Cc < 3] and [Cu > 4] for gravels:
[Cu > 6] for sands.
(b) Cu = 1 for uniform soils/poorly graded soils.
Consistency of clays: Atterberg limits
LL = WI = liquid limit
PL = Wp = plastic limit
SL = Ws = Shrinkage limit
V1 = Volume of soil mass at LL
Vp = Volume of soil mass at PL
Vd = Volume of soil mass at SL
Vs = Volume of solids
Plasticity Index (Ip)
It is the range of moisture content over which a soil exhibits plasticity.
Ip = WL - Wp
WL = water content at LL
Wp = water content at PL
If PL ≥ LL, Ip is reported as zero.
Soil classification related to plasticity index: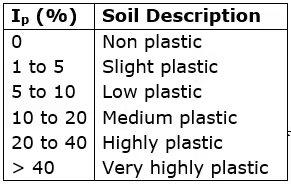
Relative Consistency or Consistency – index (Ic)
To study behaviour saturated fine grained soil at its natural water content IC = (WL-WN)/(IP)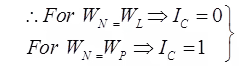
If IC < 0, the natural water content of soil (wN) is greater than wL and the soil mass behaves like a liquid, but only upon disturbance.
If IC > 1, soil is in semi solid state and will be very hard or stiff.
- Liquidity Index (IL)
IL = (WN - WP) / (IP)
For a soil in plastic state IL varies from 0 to 1.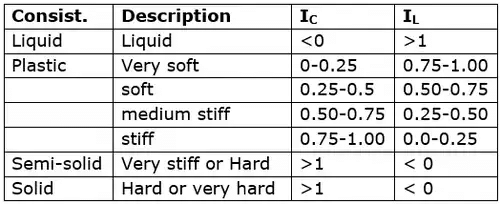
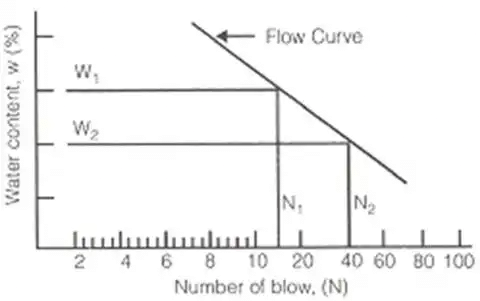
- Flow Index (If)
If = (W1 - W2) / log10(N2 / N1)
- Toughness Index (It)
IT = IP / IF
For most of the soils: 0 < IT < 3
When IT < 1, the soil is friable (easily crushed) at the plastic limit. - Shrinkage Ratio (SR)
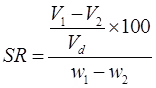
where, V1 = Volume of soil mass at water content w1%.
V2 = volume of soil mass at water content w2%.
Vd = volume of dry soil mass
Now, at SL, w2 = ws and V2 = Vd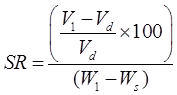
If w1 & w2 are expressed as ratio,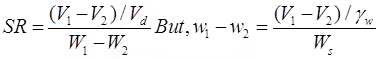
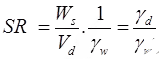
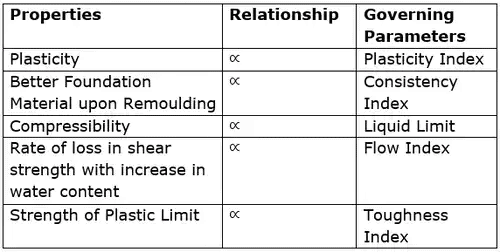
Stress-strain curve for different consistency states
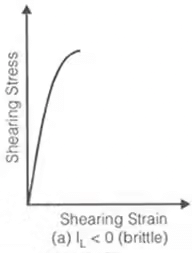
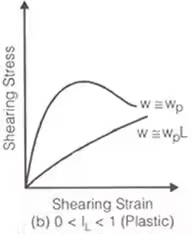
- Unconfined Compressive Strength (qu)
Defined as the load per unit area at which an unconfined prismatic or cylindrical specimen of standard dimensions of a soil fails in a simple compression test.
qu = 2 x shear strength of a clay soil (under undrained condition).
qu is related to consistency of clays as: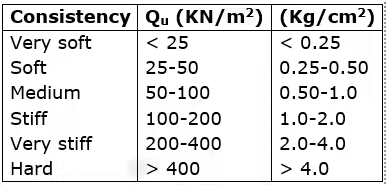
- Sensitivity (St): It is defined as the ratio of the unconfined compressive strength of an undisturbed specimen of the soil to the unconfined compressive strength of a specimen of the same soil after remolding at unaltered water content.
St = (qu)undisturbed/(qu)remoulded
St ≤ 1: in case of stiff clay having cracks and fissures.
Soil classification based on sensitivity: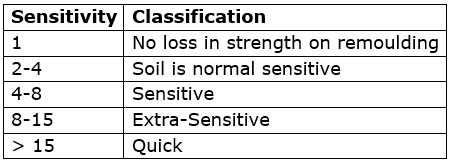
- Thixotropy: It is the property of certain clays by virtue of which they regain, if left alone for a time, a part of the strength lost due to remoulding, at unaltered moisture content.
Higher the sensitivity, larger the thixotropic hardening.
- Active
Activity of clay = Plasticity index/%by weight finer 2μ
Activity based classification of clays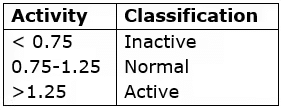
Volume change during swelling or shrinkage = (Ip and % clay) of Activity
|
30 videos|126 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Phase Relations of Soils: Soil-Water Relationship - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the significance of phase relations in soils? |  |
| 2. How is the soil-water relationship relevant to civil engineering? |  |
| 3. What are the different phases in soil-water relationships? |  |
| 4. How does water content affect the behavior of soils? |  |
| 5. What role does porosity play in soil-water relationships? |  |

















