Can Matter change its state? - Class 9 PDF Download
Can Matter Change its State?
We all know from our observation that water can exist in three states of matter–
- solid, as ice,
- liquid, as the familiar water, and
- gas, as water vapour.
What happens inside the matter during this change of state? What happens to the particles of matter during the change of states? How does this change of state take place? We need answers to these questions, isn’t it?
Effect of Change of Temperature
Activity
- Take about 150 g of ice in a beaker and suspend a laboratory thermometer so that its bulb is in contact with the ice, as in Fig.
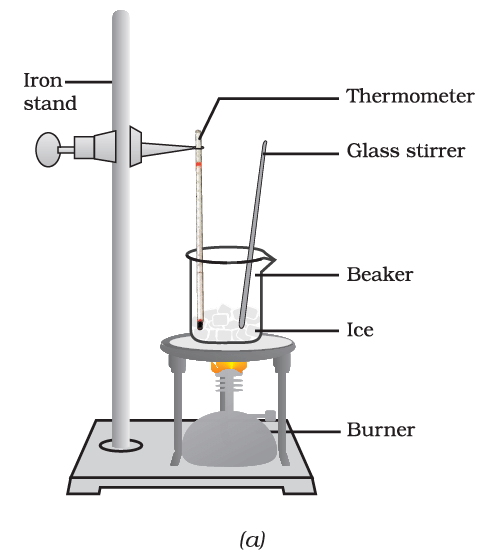 Conversion of ice to water,
Conversion of ice to water,
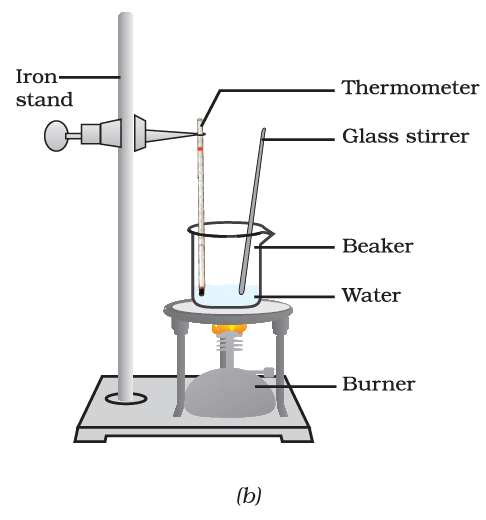 conversion of water to water vapour
conversion of water to water vapour
- Start heating the beaker on a low flame.
- Note the temperature when the ice starts melting.
- Note the temperature when all the ice has converted into water.
- Record your observations for this conversion of solid to liquid state.
- Now, put a glass rod in the beaker and heat while stirring till the water starts boiling.
- Keep a careful eye on the thermometer reading till most of the water has vaporised.
- Record your observations for the conversion of water in the liquid state to the gaseous state.
On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the particles start vibrating with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. The particles leave their fixed positions and start moving more freely. A stage is reached when the solid melts and is converted to a liquid. The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The melting point of a solid is an indication of the strength of the force of attraction between its particles.
The melting point of ice is 273.15 K*. The process of melting, that is, change of solid state into liquid state is also known as fusion.
When a solid melts, its temperature remains the same, so where does the heat energy go?
You must have observed, during the experiment of melting, that the temperature of the system does not change after the melting point is reached, till all the ice melts. This happens even though we continue to heat the beaker, that is, we continue to supply heat. This heat gets used up in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. As this heat energy is absorbed by ice without showing any rise in temperature, it is considered that it gets hidden into the contents of the beaker and is known as the latent heat. The word latent means hidden. The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion. So, particles in water at 0oC (273 K) have more energy as compared to particles in ice at the same temperature.
When we supply heat energy to water, particles start moving even faster. At a certain temperature, a point is reached when the particles have enough energy to break free from the forces of attraction of each other. At this temperature the liquid starts changing into gas. The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Particles from the bulk of the liquid gain enough energy to change into the vapour state.
For water this temperature is 373 K (100 0C = 273 + 100 = 373 K).
Can you define the latent heat of vaporisation? Do it in the same way as we have defined the latent heat of fusion. Particles in steam, that is, water vapour at 373 K (100o C) have more energy than water at the same temperature. This is because particles in steam have absorbed extra energy in the form of latent heat of vaporisation.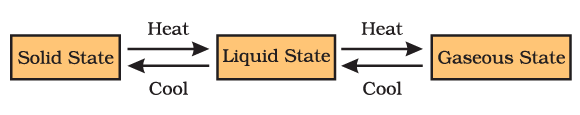
So, we infer that the state of matter can be changed into another state by changing the temperature.
We have learnt that substances around us change state from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas on application of heat. But there are some that change directly from solid state to gaseous state and vice versa without changing into the liquid state.
Activity
- Take some camphor or ammonium chloride. Crush it and put it in a china dish.
- Put an inverted funnel over the china dish.
- Put a cotton plug on the stem of the funnel, as shown in Fig.
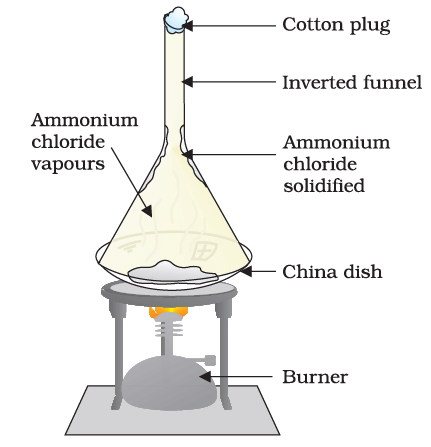 Sublimation of ammonium chloride
Sublimation of ammonium chloride
- Now, heat slowly and observe.
- What do you infer from the above activity?
A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called sublimation and the direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called deposition.
Effect of Change of Pressure
We have already learnt that the difference in various states of matter is due to the difference in the distances between the constituent particles. What will happen when we start putting pressure and compress a gas enclosed in a cylinder? Will the particles come closer? Do you think that increasing or decreasing the pressure can change the state of matter?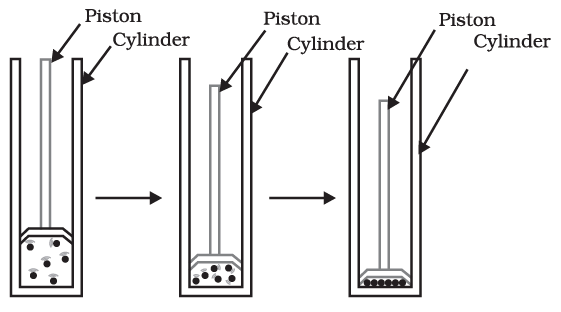 By applying pressure, particles of matter can be brought close together.
By applying pressure, particles of matter can be brought close together.
Applying pressure and reducing temperature can liquefy gases.
Have you heard of solid carbon dioxide (CO2)?It is stored under high pressure. Solid CO2 gets converted directly to gaseous state on decrease of pressure to 1 atmosphere* without coming into liquid state. This is the reason that solid carbon dioxide is also known as dry ice.
Thus, we can say that pressure and temperature determine the state of a substance, whether it will be solid, liquid or gas.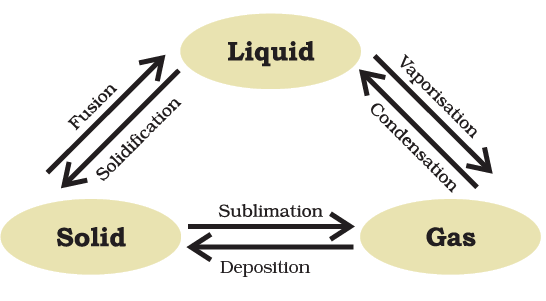 Interconversion of the three states of matter
Interconversion of the three states of matter
Evaporation
Do we always need to heat or change pressure for changing the state of matter? Can you quote some examples from everyday life where change of state from liquid to vapour takes place without the liquid reaching the boiling point? Water, when left uncovered, slowly changes into vapour. Wet clothes dry up. What happens to water in the above two examples?
We know that particles of matter are always moving and are never at rest. At a given temperature in any gas, liquid or solid, there are particles with different amounts of kinetic energy. In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Factors Affecting Evaporation
Let us understand this with an activity.
Activity
- Take 5 mL of water in a test tube and keep it near a window or under a fan.
- Take 5 mL of water in an open china dish and keep it near a window or under a fan.
- Take 5 mL of water in an open china dish and keep it inside a cupboard or on a shelf in your class.
- Record the room temperature.
- Record the time or days taken for the evaporation process in the above cases.
- Repeat the above three steps of activity on a rainy day and record your observations.
- What do you infer about the effect of temperature, surface area and wind velocity (speed) on evaporation?
You must have observed that the rate of evaporation increases with–
- an increase of surface area: We know that evaporation is a surface phenomenon. If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases. For example, while putting clothes for drying up we spread them out.
- an increase of temperature: With the increase of temperature, more number of particles get enough kinetic energy to go into the vapour state.
- a decrease in humidity: Humidity is the amount of water vapour present in air. The air around us cannot hold more than a definite amount of water vapour at a given temperature. If the amount of water in air is already high, the rate of evaporation decreases.
- an increase in wind speed: It is a common observation that clothes dry faster on a windy day. With the increase in wind speed, the particles of water vapour move away with the wind, decreasing the amount of water vapour in the surrounding.
How Does Evaporation Cause Cooling?
In an open vessel, the liquid keeps on evaporating. The particles of liquid absorb energy from the surrounding to regain the energy lost during evaporation. This absorption of energy from the surroundings make the surroundings cold.
What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm? The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool.
After a hot sunny day, people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground because the large latent heat of vaporisation of water helps to cool the hot surface.
Can you cite some more examples from daily life where we can feel the effect of cooling due to evaporation?
Why should we wear cotton clothes in summer?
During summer, we perspire more because of the mechanism of our body which keeps us cool. We know that during evaporation, the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings or body surface and change into vapour. The heat energy equal to the latent heat of vaporisation is absorbed from the body leaving the body cool. Cotton, being a good absorber of water helps in absorbing the sweat and exposing it to the atmosphere for easy evaporation.
Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water?
Let us take some ice-cold water in a tumbler. Soon we will see water droplets on the outer surface of the tumbler. The water vapour present in air, on coming in contact with the cold glass of water, loses energy and gets converted to liquid state, which we see as water droplets.
FAQs on Can Matter change its state? - Class 9
| 1. Can matter change its state? |  |
| 2. What causes matter to change its state? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of state changes in matter? |  |
| 4. Can matter change from a gas to a solid without going through the liquid state? |  |
| 5. Can matter change its state at any temperature? |  |














