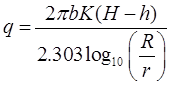Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Notes > Soil Mechanics > Effective Stress, Capillarity & Permeability of Soils
Effective Stress, Capillarity & Permeability of Soils | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Well Hydraulics
- Specific yield (Sy)
The specific yield of an unconfined aquifer is the ratio of volume of water which will flow under saturated condition due to gravity effect to the total volume of aquifer (v).
Sy = Vwy/V where, Vwy = Volume of water yielded under gravity effect and V = total volume of water. - Specific retention: The specific retention of an unconfined aquifer is the ratio of volume of water retained against gravity effect to the total volume of aquifer (v).
SR = VWR/V where, VWR = Volume of water retained under gravity effect.
Coefficient of transmissibility
T = kH where, H = Thickness
k = Coefficient of permeability
Unconfined Aquifer
- Theims Theory
 h1 + s1 = h2 + s2
h1 + s1 = h2 + s2
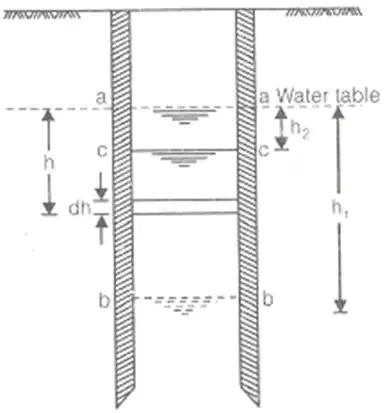
where, q = Rate of flow in m3/s
h1 = Height of water table of 1st observation well
h2 = Height of water table of 2nd observation well
s1 = Drawdown of 1st test well
s2 = Drawdown of 2nd test well.
r1 = and r2 are radius of 1st and 2nd observation wells respectively. - Dupits Theory

R = 3000.S√K and S = H - h
Where, S = Drawdown in the well
k = Permeability coefficient in m/s.
R = Radius of influence in 'm'
150m ≤ R ≤ 300m
r = Radius of tes well in 'm'.
Results of dupits theory are not accurate because 'R' is based on empirical relation.
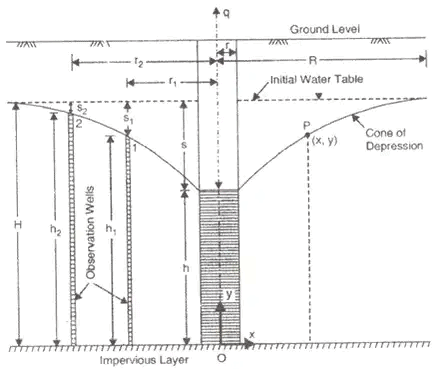
Confined Aquifer
- Theims theory
 where, b = width
where, b = width - Dupits theory

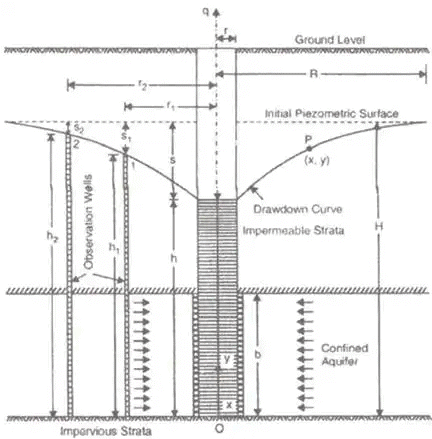
Spherical flow through well
qs = K.2πr.s where, r = Radius of well
S = Drawdown
qs = Rate of flow through spherical well in m3/s qs = 1/30.qradial flow
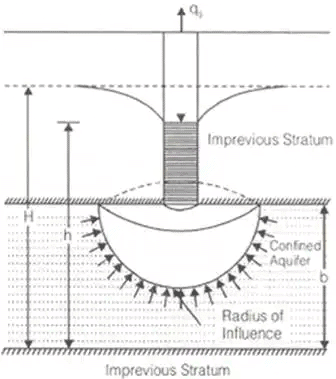
Pumping-In-Test
- Open end test
K = q/5.5rh where, r = Radius of pipe
h = Head of water above the base of pipe, it may include gravity head and pressure head. - Tacker test
K = q/(2πLh)log10(L/r) ... when L > 10r
where, L = Length of perforated section of pipe
k = q/(2πLh)sin - 1(L/2r) ... when L < 10 r
r = Radius of pipe
h = Head of which water is added.
Open well (Recuperation test)
q = (C/A).Volume
Where, C/A = (2.303/T)log10(h1/h2)
C/A = Specific yield or specific capacity of an open well.
T = Time in 'sec'
h1 = Position of water table of t = 0
h2 = Position of water table of t = T
Value of Permeability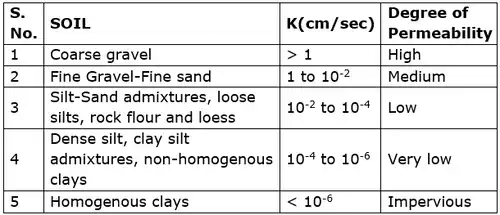
The document Effective Stress, Capillarity & Permeability of Soils | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) is a part of the Civil Engineering (CE) Course Soil Mechanics.
All you need of Civil Engineering (CE) at this link: Civil Engineering (CE)
|
30 videos|76 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Effective Stress, Capillarity & Permeability of Soils - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is effective stress in soils? |  |
Ans. Effective stress in soils refers to the stress that is transmitted through the soil skeleton, excluding the pore water pressure. It is the difference between the total stress and the pore water pressure. Effective stress determines the shear strength and deformation behavior of soils.
| 2. How does capillarity affect soil permeability? |  |
Ans. Capillarity is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces against the force of gravity. In soils, capillarity plays a significant role in determining the soil permeability. Smaller soil particles and narrower pore spaces increase capillary forces, reducing permeability. Conversely, larger particles and wider pore spaces reduce capillary forces, resulting in higher permeability.
| 3. What is soil permeability and why is it important in civil engineering? |  |
Ans. Soil permeability refers to the ability of soil to transmit fluids, such as water or air. It is an essential property in civil engineering as it affects the stability and performance of structures built on or with soil. Understanding soil permeability is crucial for designing drainage systems, evaluating groundwater flow, and determining the suitability of soil for construction projects.
| 4. How can soil permeability be measured? |  |
Ans. Soil permeability can be measured through various laboratory tests, such as the constant head permeability test or the falling head permeability test. In these tests, a soil sample is subjected to a hydraulic gradient, and the rate of fluid flow through the sample is measured. Field tests, such as the pumping test or the slug test, can also be conducted to determine soil permeability in situ.
| 5. How does effective stress influence soil strength and stability? |  |
Ans. Effective stress directly affects the shear strength and stability of soils. As the effective stress increases, the interparticle forces between soil grains strengthen, leading to greater resistance to deformation and shear failure. It is particularly crucial in slope stability analysis, foundation design, and retaining wall design, where the ability of the soil to withstand external loads and maintain stability is of utmost importance.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
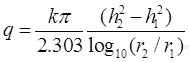 h1 + s1 = h2 + s2
h1 + s1 = h2 + s2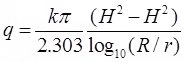
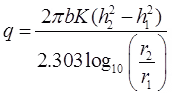 where, b = width
where, b = width