Introduction: Arrays | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction to Arrays
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array). The base value is index 0 and the difference between the two indexes is the offset.
For simplicity, we can think of an array as a fleet of stairs where on each step is placed a value (let’s say one of your friends). Here, you can identify the location of any of your friends by simply knowing the count of the step they are on.
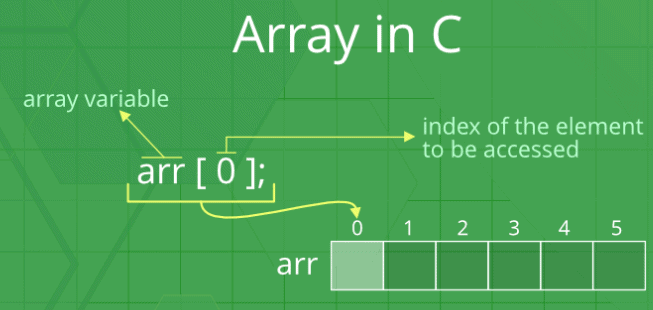
Remember: “Location of next index depends on the data type we use”. The above image can be looked at as a top-level view of a staircase where you are at the base of the staircase. Each element can be uniquely identified by its index in the array (in a similar way as you could identify your friends by the step on which they were on in the above example).
The above image can be looked at as a top-level view of a staircase where you are at the base of the staircase. Each element can be uniquely identified by its index in the array (in a similar way as you could identify your friends by the step on which they were on in the above example).
Array’s size
In C language array has a fixed size meaning once the size is given to it, it cannot be changed i.e. you can’t shrink it neither can you expand it. The reason was that for expanding if we change the size we can’t be sure ( it’s not possible every time) that we get the next memory location to us as free. The shrinking will not work because the array, when declared, gets memory statically, and thus compiler is the only one to destroy it.
Types of indexing in an array:
- 0 (zero-based indexing): The first element of the array is indexed by a subscript of 0.
- 1 (one-based indexing): The second element of the array is indexed by the subscript of 1.
- n (n-based indexing): The base index of an array can be freely chosen. Usually, programming languages allowing n-based indexing also allow negative index values, and other scalar data types like enumerations, or characters may be used as an array index.
C++
C
Output 5 Here the value 5 is printed because the first element has index zero and at zeroth index we already assigned the value 5.
Advantages of using arrays:
- Arrays allow random access to elements. This makes accessing elements by position faster.
- Arrays have better cache locality that can make a pretty big difference in performance.
- Arrays represent multiple data items of the same type using a single name.
Disadvantages of using arrays:
You can’t change the size i.e. once you have declared the array you can’t change its size because of static memory allocated to it. Here Insertion and deletion are difficult as the elements are stored in consecutive memory locations and the shifting operation is costly too.
Now if take an example of implementation of data structure Stack using array there are some obvious flaw.
Let’s take the POP operation of the stack. The algorithm would go something like this:
- Check for the stack underflow
- Decrement the top by 1
So there what we are doing is that the pointer to the topmost element is decrement meaning we are just bounding our view actually that element stays there talking up of the memory space if you have any primitive datatype then it might be ok but the object of an array would take a lot of memory.
Examples:
// A character array in C/C++/Java
char arr1[] = {'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's'};
// An Integer array in C/C++/Java
int arr2[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// Item at i'th index in array is typically accessed
// as "arr[i]". For example arr1[0] gives us 'g'
// and arr2[3] gives us 40.
Usually, an array of characters is called a ‘string’, whereas an array of ints or floats is simply called an array.
Applications on Arrays:
- Array stores data elements of the same data type.
- Arrays can be used for CPU scheduling.
- Used to Implement other data structures like Stacks, Queues, Heaps, Hash tables, etc.
|
120 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction: Arrays - Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is an array in programming? |  |
| 2. How do you declare an array in C programming? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between an array and a linked list? |  |
| 4. How do you access elements in an array? |  |
| 5. Can arrays store elements of different data types? |  |























