Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Notes > Structural Analysis > Analysis of Arches & Cables
Analysis of Arches & Cables | Structural Analysis - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
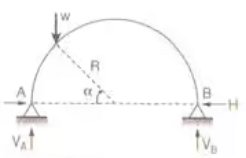
Arches
Three Hinged Arches
- Three Hinged Parabolic Arch of Span L and rise 'h' carrying a UDL over the whole span
Ds = 0
BMc = 0
H = wl2/8h
Mx = VAx - wx2/2 - Hy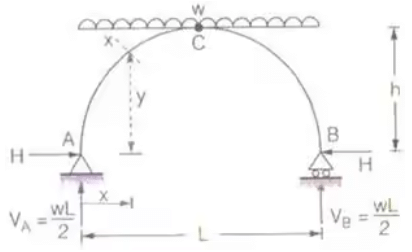 where, H = Horizontal thrust
where, H = Horizontal thrust
VA = Vertical reaction at A = wl/2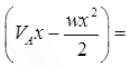 Simply supported beam moment i.e., moment caused by vertical reactions.
Simply supported beam moment i.e., moment caused by vertical reactions.
Hy = H-moment
DS = Degree of static indeterminacy
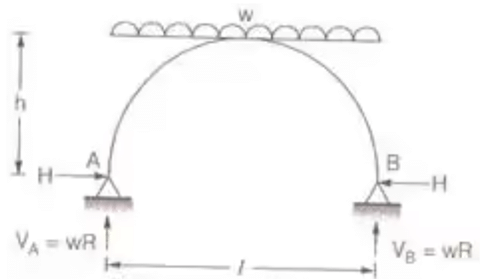
BMC = Bending Moment at C. - Three Hinged Semicircular Arch of Radius R carrying a UDL over the whole span.
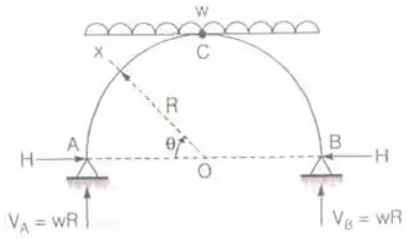 H = wR/2
H = wR/2
Mx = -wR2/2 [sin θ - sin2 θ]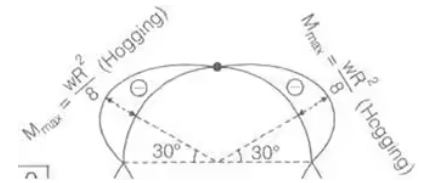 Mmax = -wR2/8
Mmax = -wR2/8
BMc = 0
Point of contraflexure = 0 - Three Hinged Parabolic Arch Having Abutments at Different Levels
(i) When it is subjected to UDL over whole span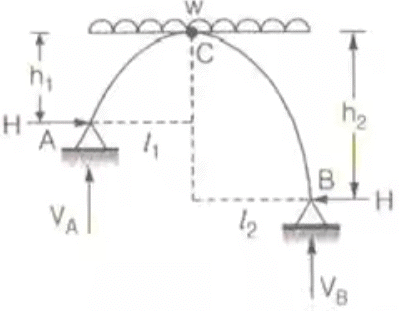
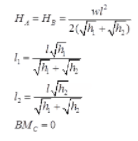
(ii) When it is subjected to concentrated load W at crown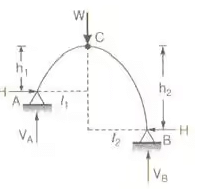
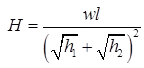
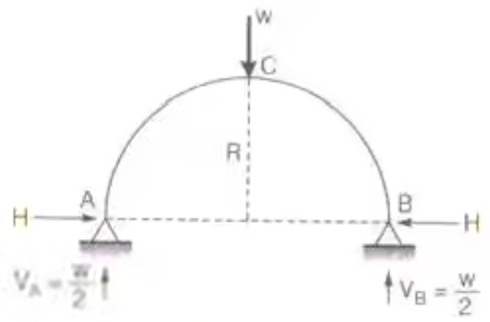
- Three Hinged Semicircular Arch Carrying Concentrated Load W at Crown
 H = VA = VB = W/2
H = VA = VB = W/2
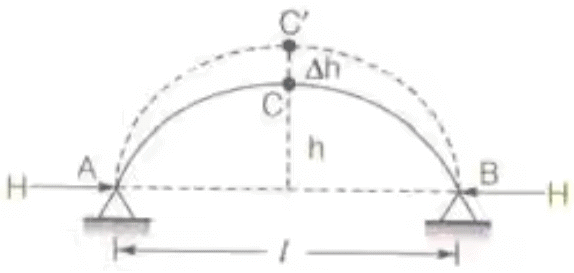
Temperature Effect on Three Hinged Arches
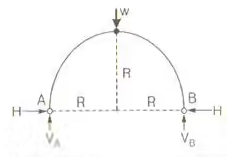
Where, Δh = free rise in crown height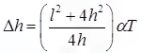
l = length of arch
h = rise of arch
α = coefficient of thermal expansion
T = rise in temperature in 0C- H α 1/h
Where, H = horizontal thrust
and h = rise of arch - % Decrease in horizontal thrust = δh/h x 100
Two Hinged Arches
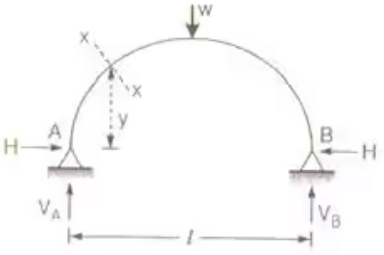 Two hinged arch of any shape
Two hinged arch of any shape
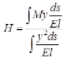
DS = 1
Where, M = Simply support Beam moment caused by vertical force.
- Two hinged semicircular arch of radius R carrying a concentrated load 'w' at the town.
H = w/π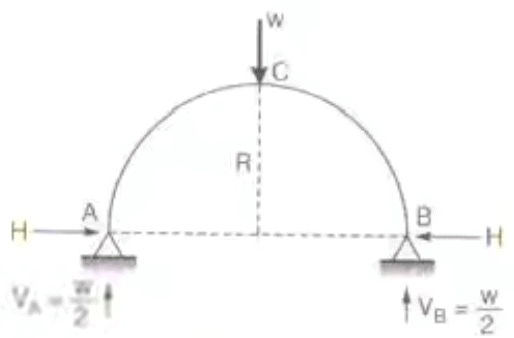 Two Hinged Circular arch
Two Hinged Circular arch - Two hinged semicircular arch of radius R carrying a load w at a section, the radius vector corresponding to which makes an angle α with the horizontal.
 Two Hinged Circular archH = w/π sin2 α
Two Hinged Circular archH = w/π sin2 α - A two hinged semicircular arch of radius R carrying a UDL w per unit length over the whole span.
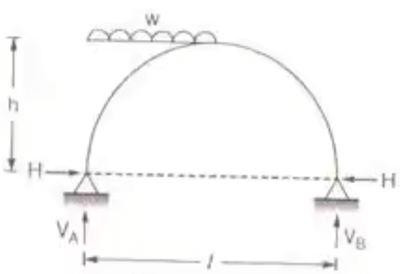
 Two Hinged Semicircular arch
Two Hinged Semicircular arch - A two hinged semicircular arch of radius R carrying a distributed load uniformly varying from zero at the left end to w per unit run at the right end.
 Two Hinged Semicircular archH = 2/3.wR/π
Two Hinged Semicircular archH = 2/3.wR/π - A two hinged parabolic arch carries a UDL of w per unit run on entire span. If the span off the arch is L and its rise is h.
 Two Hinged parabolic archH = wl2/8h
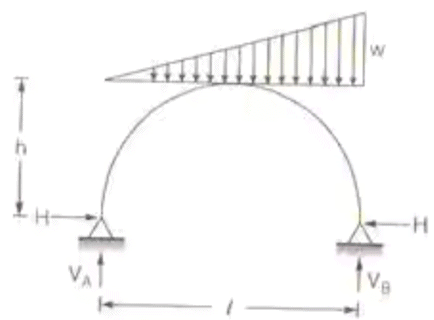
Two Hinged parabolic archH = wl2/8h - When half of the parabolic arch is loaded by UDL, then the horizontal reaction at support is given by
 Two Hinged parabolic arch
Two Hinged parabolic arch - When two hinged parabolic arch carries varying UDL, from zero to w the horizontal thrust is given by
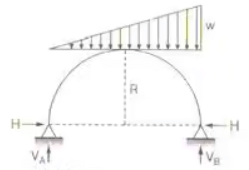
 Two Hinged parabolic archH = wl2/16h
Two Hinged parabolic archH = wl2/16h - A two hinged parabolic arch of span l and rise h carries a concentrated load w at the crown.
H = 25 wl/ 128 h
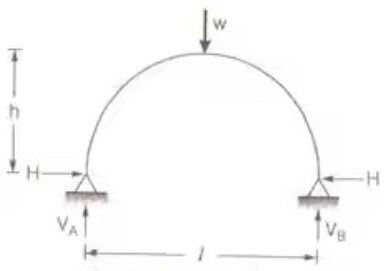
Two Hinged parabolic arch
Temperature Effect on Two Hinged Arches
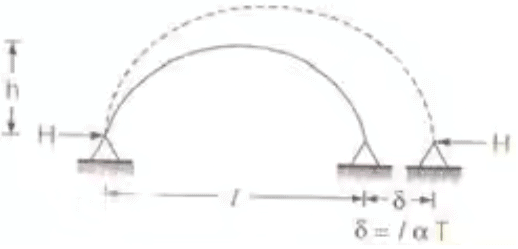
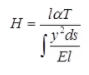
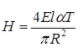
where H = Horizontal thrust for two hinged semicircular arch due to rise in temperature by T 0C.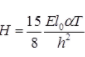
where l0 = Moment of inertia of the arch at crown.
H = Horizontal thrust for two hinged parabolic arch due to rise in temperature T 0C.
Reaction Locus for a Two Hinged Arch
- Two Hinged Semicircular Arch
Reaction locus is straight line parallel to the line joining abutments and height at πR/2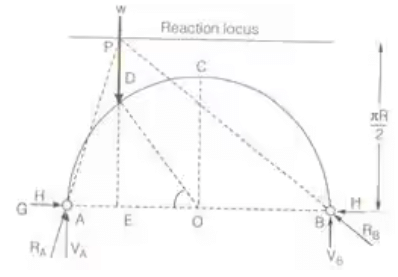
- Two Hinged Parabolic Arch
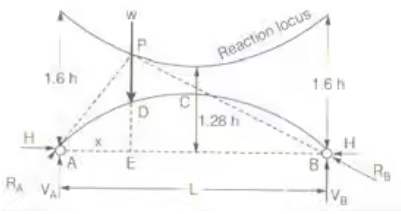
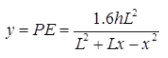
Eddy's Theorem
Mxαy
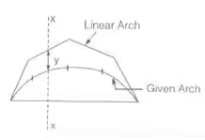 where, MX = BM at any section
where, MX = BM at any section
y = distance between given arch linear arch
The document Analysis of Arches & Cables | Structural Analysis - Civil Engineering (CE) is a part of the Civil Engineering (CE) Course Structural Analysis.
All you need of Civil Engineering (CE) at this link: Civil Engineering (CE)
|
32 videos|154 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Analysis of Arches & Cables - Structural Analysis - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the concept of arches and cables in structural engineering? |  |
Ans. Arches and cables are structural elements commonly used in architecture and engineering to support loads and distribute forces. Arches are curved structures that transmit loads in compression, while cables are tensioned elements that carry loads through tensile forces.
| 2. How do arches and cables differ in terms of their structural behavior? |  |
Ans. Arches rely on the inherent strength of their curved shape to distribute loads and resist bending moments. They transfer the forces to the supports or abutments at their ends. On the other hand, cables are prestressed elements that rely on tension forces to resist the loads. They are suspended between supports and can carry loads over long spans without the need for intermediate supports.
| 3. What are the advantages of using arches in structural design? |  |
Ans. Arches offer several advantages in structural design. They have a visually appealing aesthetic and can create large open spaces without the need for columns or intermediate supports. Arches also provide excellent resistance to bending moments and can withstand both vertical and horizontal loads. Additionally, arches can be constructed using a variety of materials, including stone, brick, concrete, or steel.
| 4. How are cables used in structural systems? |  |
Ans. Cables are commonly used in structural systems where long-span structures are required, such as suspension bridges or cable-stayed bridges. They are also used in tensegrity structures and in the construction of lightweight roofs and canopies. Cables are tensioned and anchored at their ends, providing stability and load-carrying capacity.
| 5. Are there any limitations or considerations when using arches and cables in structural design? |  |
Ans. Yes, there are certain limitations and considerations when using arches and cables in structural design. Arches require proper support at their ends to resist the horizontal thrust generated by the curved shape. The choice of materials and construction techniques is crucial to ensure the stability and durability of arches. Cables, on the other hand, require precise tensioning and anchoring to maintain their structural integrity. The dynamic behavior of cables under wind or seismic loads must also be carefully analyzed in the design process.
Related Searches