Digital Modulation Schemes | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Digital Modulation Schemes
This is possible to transmit the analog signal i.e., speech, video etc, in digital format. Some digital modulation schemes are given below
- Digital Carrier Modulation: Commonly used digital modulation schemes are Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) and Phase Shift Keying (PSK).
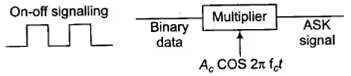
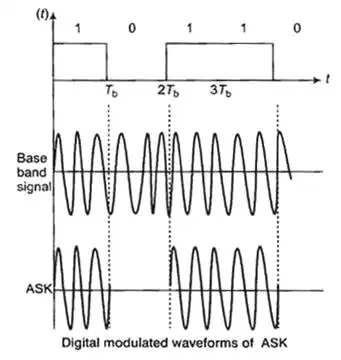
- Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK): The amplitude of a high-frequency carrier is varied in accordance with digital data (0 or 1).
S(t) = Ac cos 2πfct; 0 ≤ t ≤ Tb
= 0; otherwise
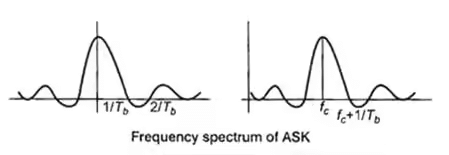
Bandwidth = 2 × 1/Tb
= 2 × bit rate
- For digital input 1 amplitude level is high and for digital input 0 amplitude level is low.
- Signalling used is on-off signalling.
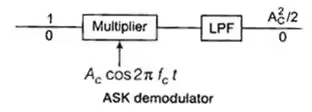
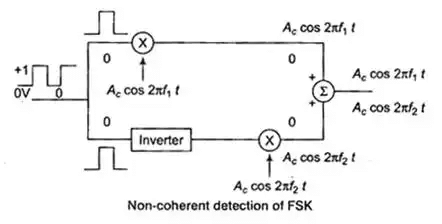
Demodulation of ASK
For binary digit 1, Ac cos 2π fct × Ac cos 2πfct = (A2c /2)[1 + cos 4πfct]
Output of LPF = (A2c /2)
For binary digit 0 output of LPF = 0
In ASK, probability of error (Pe) is high.
In ASK, SNR is less.
Example: Consider a simple ASK modulation scheme where two digital symbols, 0 and 1, are transmitted using two different amplitudes. When transmitting '0,' the amplitude is 0, and when transmitting '1,' the amplitude is 1.
When receiving the signal, a receiver can use a threshold detector to distinguish between the two amplitudes. If the received amplitude is greater than a certain threshold, it is decoded as '1,' and if it's below the threshold, it's decoded as '0.'
Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
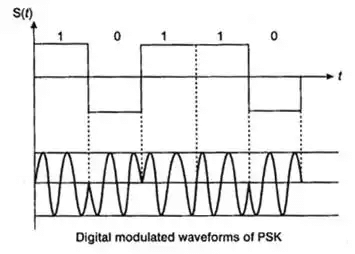
In phase shift, keying phase of high-frequency carrier is varied in accordance with digital data 1 or 0.
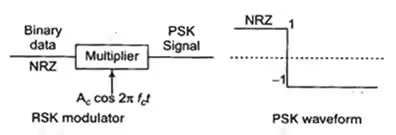
- NRZ signalling is used.
S(t) = Ac cos 2πfct for bit 1
= – Ac cos 2pfct for bit 0
A frequency of the carrier must be a multiple of a bit rate.
Tb = n/fc
Fc = nrb
- In case of PSK, a probability of error is less.
- In case of PSK, SNR is high.
- Mainly used a technique in wireless transmission.
Example: PSK uses different phases of the carrier signal to represent digital symbols. Let's say '0' is represented by a phase of 0 degrees, and '1' is represented by a phase of 180 degrees.
The receiver uses a phase detector to measure the phase of the received signal. If the phase is 0 degrees, it's decoded as '0,' and if it's 180 degrees, it's decoded as '1.'
 |
Test: Modem Digital Modulation & Detection Techniques
|
Start Test |
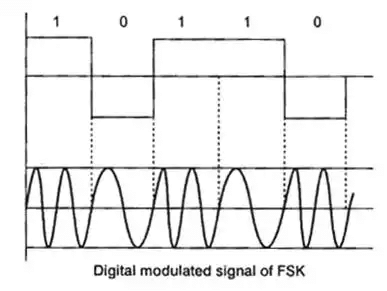
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
In frequency shift keying, a frequency of the carrier is varied in accordance with digital data (1 or 0).
For digital data 1 we use frequency f1 and for digital data 0 we use frequency f2.
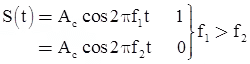
- NRZ signalling is used here
- VCO The schematic diagram of VCO is given below
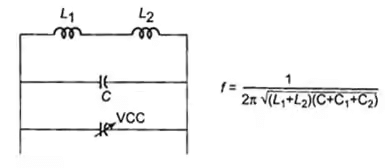
Bandwidth = 2Δf + 2fm

Bandwidth = f1 + (1/Tb) – f2 + (1/Tb)
= f1 – f2 + (2/Tb); f1 – f2 = 2Δf
Key Points
- In case of FSK, Pe is less but SNR is high.
- Multiplexing is difficult in FSK.
Example: In FSK, two digital symbols are transmitted by using two different carrier frequencies. For example, '0' might be transmitted at 1 kHz, and '1' at 2 kHz.
The receiver uses a frequency detector to determine which frequency is present in the received signal. If the detected frequency is 1 kHz, it's decoded as '0,' and if it's 2 kHz, it's decoded as '1.'
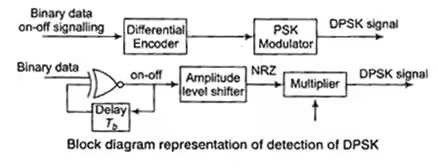
Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK)
In PSK it needs a complicated synchronising circuit at the receiver, this disadvantage of PSK is removed in DPSK.
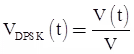
A cos ω0t = ± A cos ω0t
Note: Advantage of DPSK over PSK is, DPSK does not require a coherent carrier for demodulation.
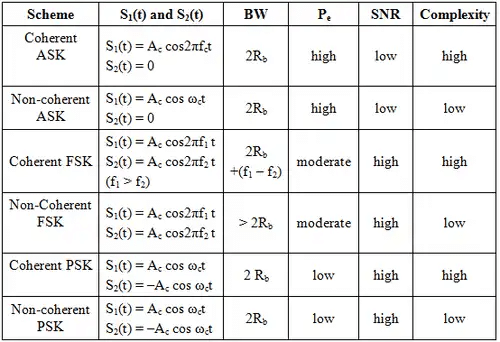
Comparison of Digital Modulation Schemes
 |
Download the notes
Digital Modulation Schemes
|
Download as PDF |
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM)
In QAM, digital information is content in a both amplitude and phase of the signal. It is used in both digital modulation scheme and analog modulation scheme. Digital cable television and in cable modem applications QAM is used.
Example: QAM combines both amplitude and phase modulation. In a simple 4-QAM scheme, '00' is represented by a signal with a certain amplitude and phase, '01' by a different phase, '10' by another amplitude, and '11' by another amplitude and phase.
The receiver uses both amplitude and phase detectors to decode the received signal. It simultaneously measures both the amplitude and phase of the signal to determine which pair of bits (00, 01, 10, or 11) is transmitted.
|
13 videos|39 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Digital Modulation Schemes - Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What is digital modulation? |  |
| 2. What is ASK modulation and demodulation? |  |
| 3. How does PSK modulation work? |  |
| 4. What is FSK modulation? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between DPSK and PSK modulation? |  |