Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Envelope & Components of Bacterial Cell | Biology for ACT PDF Download
What is a Cell Envelope?
- Most prokaryotic cells, particularly bacterial cells, have a chemically complex cell envelope.
- The cell envelope consists of a tightly bound three-layered structure i.e., the outermost glycocalyx followed by the cell wall and then the plasma membrane.
- Although each layer of the envelope performs a distinct function, they act together as a single protective unit.
- The cell envelope is a combination of the cell membrane, cell wall, and outer membrane if it is present.
- Usually, this envelope is a characteristic of prokaryotes like bacteria.
- It comprises the inner cell wall and the cell wall of a bacterium.
- The cell envelope provides structural integrity to the cell.
- In prokaryotes, it protects the cell from the internal turgor pressure caused due to a high concentration of macromolecules inside the cell.
There are two types of bacterial cell envelopes:
- Gram-positive cell wall
- Gram-negative cell wall
Types of Bacterial Cell Envelopes
Gram-positive Cell Envelope
- The cell envelope of a gram-positive bacteria comprises a cell wall with a thick peptidoglycan layer.
- This helps in retaining the crystal violet dyes during gram-staining.
- The cell wall is embedded with teichoic acids and lipoteichoic acids.
Gram-negative Cell Envelope
- The gram-negative cell envelope contains a cell wall with a thin peptidoglycan layer due to which the cell wall is unable to retain crystal violet stain upon decolourisation during gram staining.
- The outer membrane is composed of lipopolysaccharides and phospholipids.
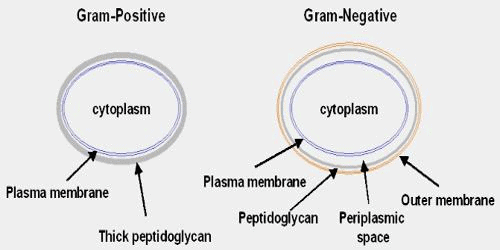
Differences between Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria
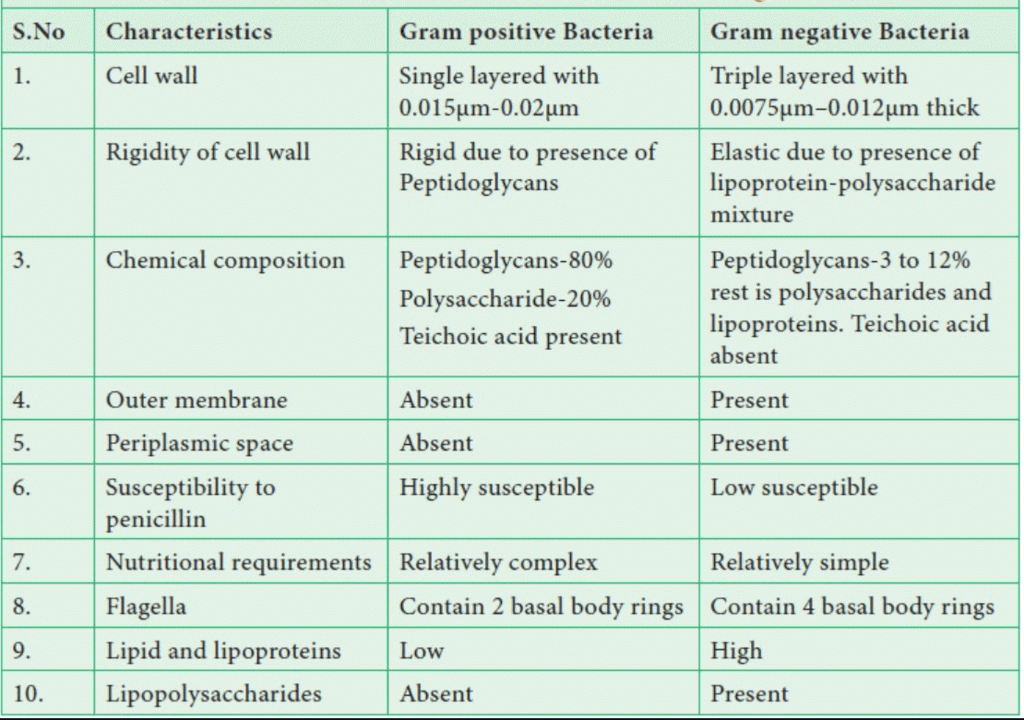 Differences between Gram Positive and Gram Negative bacteria
Differences between Gram Positive and Gram Negative bacteria
Mycobacteria
The cell envelope of mycobacteria is different from that of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.- It lacks an outer cell membrane but has a cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, arabinogalactan and mycolic acid.
Composition of Cell Envelope
- The cell envelope is composed of the cell wall, cell membrane and outer membrane.
- The cell envelope of gram-positive bacteria comprises the cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane and capsule.
- The cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria comprises the cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, outer membrane, periplasmic space and capsule.

Functions of Cell Envelope
Following are the important functions of the cell envelope:
- The bacterial cell wall not only maintains the cell shape and prevents it from bursting or collapsing but, as observed in the case of motile bacteria, it forms filamentous extensions called flagella.
- The cell membrane also regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.
- A special structure known as a mesosome is formed by an extension of the plasma membrane into the cell wall.
- These extensions are usually in the form of vesicles, tubules, and lamellae.
- They help the cell for various functions like a synthesis of a cell wall, DNA replication, and distribution of daughter cells, respiration, secretions, etc.
Components of Bacterial Cell
A bacterial cell consists of a cell envelope, cytoplasm, nucleoid, plasmids, inclusion bodies, flagella, pili and fimbriae.
1. Cell Envelope. It is the outer covering of the protoplasm of the bacterial cell. Cell envelope consists of 3 components- glycocalyx, cell wall and cell membrane.
(i) Glycocalyx
- It lies outside the cell wall.
- Glycocalyx consists of two parts, inner S-layer and outer mucilage.
- S-layer is mostly made of polypeptides rich in acidic amino acids.
- It protects the bacteria cell wall dissolving lysozyme and other harmful chemicals.
- Mucilage is carbohydrate-rich which when thick is called a capsule.
- Glycocalyx gives a sticky character to the cell.
- It is not absolutely essential for the survival of bacteria.
- However, it has several secondary functions.
(a) Prevention of desiccation.
(b) Protection from phagocytes.
(c) Protection from toxic chemicals and drugs.
(d) Protection from viruses.
(e) Attachment.
(f) Immunogenicity
(g) Virulence. - A variety of bacteria, including Azotobacter and Salmonella, produce extracellular cellulose.
(ii) The cell wall
- It is a rigid solid covering that gives the cell shape and structural support.
- The cell wall is located between the plasma membrane and the glycocalyx.
- The periplasmic space exists between the plasma membrane and the cell wall.
- Bacterial cells are protected from bursting in hypotonic solution by their cell wall.
- Gram-positive bacteria have walls that are 20-80 nm thick.
- It has a single layer and is smooth.
- The wall of Gram-negative bacteria is 8-12 nm thick, complex, wavy, and two-layered.
- The outer layer is also known as the outer membrane.
- It is made up of lipopolysaccharides, lipids, and proteins.
- The outer membrane contains hydrophilic channels made up of 16-stranded B-barrel proteins known as porins.
- Gram-positive bacteria have a single-layered cell wall, while Gram-negative bacteria have an inner wall layer made up of peptidoglycan, proteins, non-cellulosic carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, and other substances.
- The structural network of the cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan.
- Murein and mucopeptide are other names for it.
- Peptidoglycan is made up of long glycan strands made up of repeating N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) units (NAM).
- They are linked together by small peptide chains. In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan accounts for 70-80% of the wall.
- The lipid content is low.
- In Gram-negative bacteria, peptidoglycan accounts for 10-20% of the wall.
- The lipid content ranges between 20 and 30%.
- Diaminopimelic acid or lysine is an amino acid found in the wall.
- Teichoic acids in Gram-positive bacteria's walls form receptor sites and surface antigens.
- The wall of Mycobacterium and Nocardia contains long-chain fatty acids known as mycolic acids.
 Bacterial Cell Structure
Bacterial Cell Structure
(iii) Plasma Membrane
- The innermost component of the cell envelope is a selectively permeable cytoplasmic covering.
- The structure of the bacterial plasma membrane, also known as plasmalemma, is similar to that of a typical membrane.
- It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and various types of proteins (extrinsic, integral, transmembrane).
- It contains receptor molecules that detect and respond to various chemicals in the environment.
- The bacterial membrane is metabolically active because it participates in respiration, lipid synthesis, and cell wall component synthesis.
2. Cytoplasm
- The protoplasm, with the exception of its nucleoid, is formed by a crystallo-colloidal complex.
- The presence of a large number of ribosomes causes the cytoplasm to be granular.
- Membrane-bound cell organelles, such as those found in eukaryotes, are not present.
- Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, contain all biochemical pathways.
- There is no cytoplasmic streaming.
- Sap vacuoles are not present. Instead, there are gas vacuoles.
The following are some of the structures found in the cytoplasm:
(i) Mesosome (Fitz James 1960)
- It is a bacterial cell membrane with a characteristic circular to the villiform specialization that develops as an ingrowth from the plasma membrane.
- It is made up of vesicles, tubules, and lamellae.
- Mesosome is classified into two types: septal and lateral.
- The septal mesosome connects the nucleoid to the plasma membrane.
- It aids in nucleoid replication by providing points of attachment to the red ones.
- The septal mesosome is also thought to aid in septum formation.
- During time division, the plasma membrane grows in the region where the septal mesosoma is present, presumably providing membranes for rapid elongation.
- The nucleoid is not connected to the lateral mesosoma. It contains respiratory enzymes and is thus often referred to as chondroid.
- It is thought to be equivalent to the mitochondrion of eukaryotes.
- However, respiratory enzymes can be found on the plasma membrane.
(ii) Ribosomes
- They are small membraneless submicroscopic ribonucleoprotein entities measuring 20 nm x 14-15 nm.
- Ribosomes are classified into two types: fixed and free.
- Ribosomes that have been fixed to the plasma membrane.
- In the cytoplasmic matrix, free ribosomes exist.
- Ribosomes are naturally 70S. (In this case, S stands for sedimentation coefficient or Svedberg number.)
- Each ribosome is made up of two subunits, the larger 50S and the smaller 30S.
- Ribosomes are typically found in helical groups known as polyribosomes or polysomes.
- 4-8 ribosomes are attached to a single strand of messenger or mRNA in each polysome.
- It is a mechanism for producing multiple copies of the same protein.
(iii) Chromatophores
- They are photosynthetic forms' internal membrane systems that contain photosynthetic pigments.
- Purple bacteria have typical membranes, whereas green bacteria have non-unit, nonlipid, and proteinaceous membranes.
- Chlorosomes are the chlorophores of green bacteria. Bacteriochlorophyll, bacterio-pheophytin (bacterio-viridin), and carotenoids are photosynthetic pigments.
3. Nucleoid
- It represents prokaryotic genetic material.
- Nucleoid has been given several other names, including genophore, prochromosome, incipient nucleus, and chromoneme.
- A nucleoid is made up of a single circular strand of duplex DNA that has been supercoiled with the help of RNA and polyamine to form a nearly oval or spherical complex.
- The folding is done between 250 and 700 times.
- Polyamines and id proteins are not the same as histone proteins.
- Prokaryotic DNA is considered naked due to its lack of association with histone proteins and the absence of a nuclear envelope around it.
- The nucleoid in E.coli has an 1100 um long DNA duplex with 4.6 x 106 base pairs.
- The nucleoid is freely embedded in the cytoplasm.
- A cell can contain two or more nucleoids, but they are all duplicated copies of the same nucleoid.
- Because a nucleoid is made up of a single double strand of DNA, it is equivalent to a single chromosome in eukaryotes.
- The nucleoid can be attached to the plasma membrane directly.
4. Plasmids
- They are extrachromosomal segments of double-stranded, circular, naked DNA that self-replicate.
- Plasmids give bacteria distinct phenotypic characteristics.
- They are not dependent on the main nucleoid.
- Some of them contain critical genes such as the fertility factor, nif genes, resistance factors, and colicinogenic factors.
5. Inclusion Bodies
- They are non-living structures present in the cytoplasm.
- The inclusion bodies may occur freely inside the cytoplasm (e.g., cyanophycean granules, volutin or phosphate granules, glycogen granules) or covered by 2-4 nm thick non-lipid, non-unit protein membrane (e.g., gas vacuoles, carboxysomes, sulphur granules, PHB granules).
- On the basis of their nature, the inclusion bodies are of 3 types - gas vacuoles, inorgánic inclusions and food reserve.
(i) Gas Vacuoles
- They are gas storing vacuoles found in cyanobacteria, purple and green bacteria and a few other planktonic forms.
- A gas vacuole is without any covering of its own.
- It consists of a variable number of hexagonal, hollow and cylindrical gas vesicles.
- Each gas vesicle is surrounded by a single non-unit, non-lipid protein-membrane having ribs or folds.
- The membrane is impermeable to water but is permeable to atmospheric gases.
- Gas vacuoles protect the bacteria from harmful radiations.
(ii) Inorganic Inclusions
- Several types of inorganic granules occur in bacteria.
- They include volutin granules, sulphur granules, iron granules, magnetite granules, etc.
- Because of the ability to pick up different colours with basic dyes, they are called metachromatic granules.
(iii) Food Reserve
- Blue-green algae have cyanophycean starch or a-granules, B granules or lipid globules and cyanophycin or protein granules.
- In bacteria, starch is replaced by glycogen.
- Neutral fats are absent.
- Instead, poly-beta-hydroxy-butyrate or PBH granules are present.
- Biodegradable plastic can be prepared from PBH.
- Protein granules are present.
- Carboxysomes occur in photosynthetic forms.
6. Flagella
- Bacterial flagella are uni-stranded, resembling a single microtubular fibre.
- It has a diameter of about 20 nm (0.02 m) and a length of 1-7m.
- The bacterial flagellum is composed of three parts: the basal body, the hook, and the filament.
- The basal body is shaped like a rod and is inserted into the cell envelope.
- The basal body has ring-like swellings in the plasma membranous membrane and cell wall.
- Gram-negative bacteria have two pairs of rings (L and P rings in the cell wall and S and M rings embedded in the cell membrane) and Gram-positive bacteria have only one pair of rings (S and M rings embedded in the cell membrane).
- The hook is a curved tubular structure that joins the filament to the basal body.
- It is the thickest section of the flagellum.
- The filament is a long tubular structure that creates turbulence in the liquid medium.
- It is composed of a protein known as flagellin.
 Schematic Representation of Flagella (Bacterial)
Schematic Representation of Flagella (Bacterial)
7. Pili and Fimbriae
- Both terms have been used interchangeably for bacterial appendages that do not participate in locomotion.
- Actually, pili (plural-pilus) are longer, fewer, and thicker tubular outgrowths that develop in Gram-negative bacteria in response to P* or a fertility factor.
- They are composed of the protein pilin.
- A donor bacterial cell containing a fertility factor produces 1-4 pili.
- They are useful in attaching to recipient cells and forming conjugation tubes due to their length (18-20 m).
- Fimbriae are small bristle-like protein fibres that sprout in large numbers from the cell surface.
- Each cell has 300-400 of them.
- The diameter is 3-10 nm, and the length is 0.5-1.5 m.
- Fimbriae play a role in the attachment of bacteria to solid surfaces (e.g., rock in a body of water) or host tissues (e.g., urinary tract in Neisseria gonorrhoeae).
- Some fimbriae cause RBC agglutination. They also aid in the mutual clinging of bacteria.
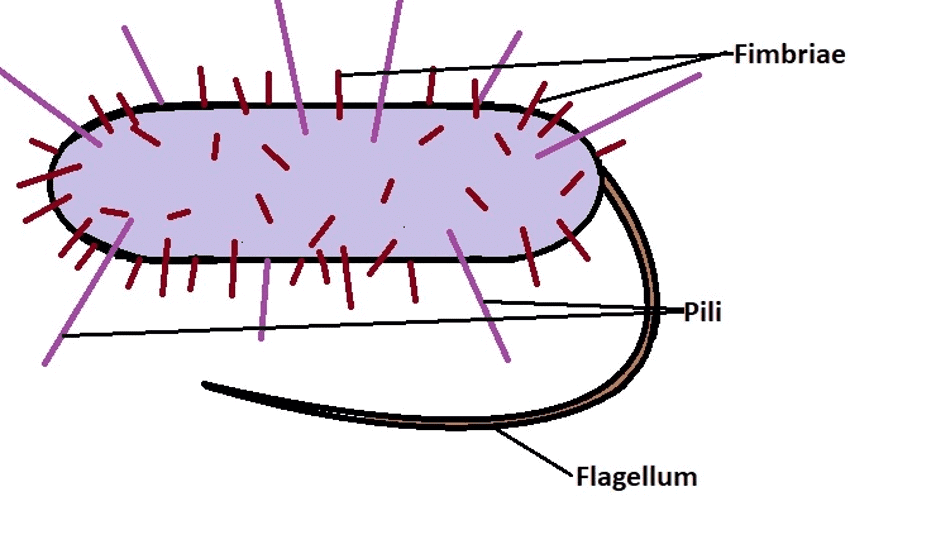
 Differences between Pilli and Fimbriae
Differences between Pilli and Fimbriae
|
208 videos|226 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Envelope & Components of Bacterial Cell - Biology for ACT
| 1. What is the cell envelope in prokaryotic cells? |  |
| 2. What are the components of the bacterial cell envelope? |  |
| 3. What is the function of the cell envelope in prokaryotic cells? |  |
| 4. How does the cell envelope differ in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria? |  |
| 5. Can the cell envelope of bacteria be targeted for antibiotic treatment? |  |
















