MOSFET Biasing & Amplifiers | Analog Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction
In this article, you will find the Circuits Analysis and Applications of Diodes, BJT, FET and MOSFET which will cover the topics such as Basics of MOSFET, Drain Current equation for Triode and Saturation Region, Operating Condition of MOSFET, MOS Transconductance, Different biasing methods of MOSFET.
Basics of MOSFET
- A Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is a field effect transistor (FET with an insulated gate) where the voltage determines the conductivity of the device. It is used for switching or amplifying signals.
- The ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. MOSFETs are now even more common than BJTs in digital and analog circuits.
 MOSFET Structure
MOSFET Structure
Drain Current Equation
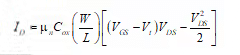
where μn = mobility of electron
Cox = Capacitance of oxide layer
Cox = εox/tox, εr = 3.9 for SiO2- εox = 3.9ε0
= 3.9 x 8.85 x 10-12 F/m
= 3.45 x 10-11 F/m
W/L → aspect ratio
VDS = drain to source voltage
There are three possible regions for the working of the MOSFET:
- Triode Region
- Cut-off Region
- Saturation Region
1. Triode Region
- VDS < VGS – Vt, if VDS (mV)
- ID = μnCax(W/L)(VGS-VT)VDS
- RDS = VDS/ID =
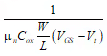
2. Current Saturation
- VDS ≥ VGS – Vt
- (VDS)Sat = VGS – Vt
- ID = 1/2(μnCox(W/L)(VGS-Vt)2
- 1/2nCox(W/L)=kn Transconductance parameter) mA/V2
→ gm should be more, so kn should be more μn → faster, gain → higher.
→ A good MOSFET should have high value of kn - ID = kn(VGS-Vt)2
∴gm = ∂ID/∂Vas = 2kn(VGS-Vt)
Operating Condition for MOSFET
Table: Operating Condition for N channel Enhancement type MOSFET.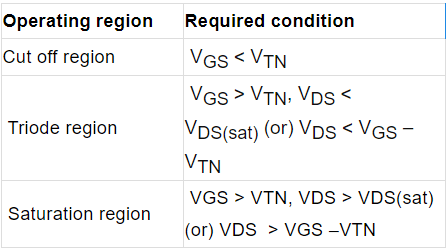
Table: Operating Condition for P channel Enhancement type MOSFET.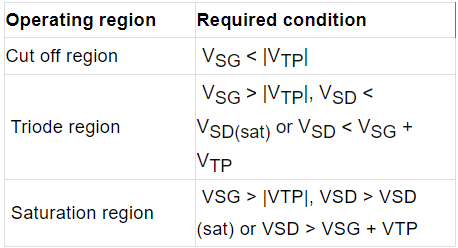
Table: Operating Condition for N channel depletion type MOSFET.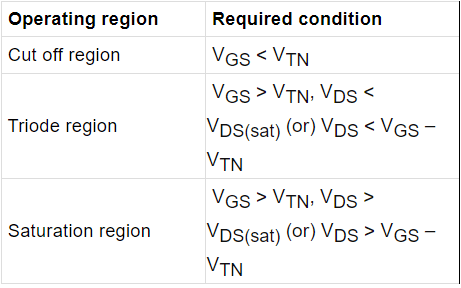
Table: Operating Condition for P channel depletion type MOSFET.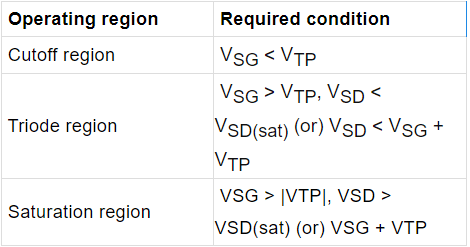
MOS Transconductance
- As a voltage-controlled source, a MOS transistor can be characterized by its transconductance
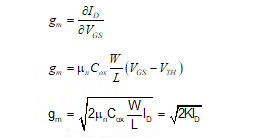
- Various dependencies of gm:
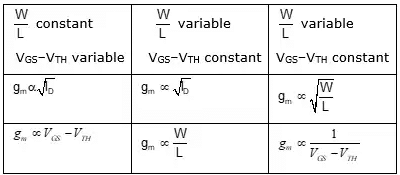
Different biasing methods of MOSFET
There are four biasing methods for MOSFET:
- Drain to gate bias
- Voltage divider bias
- Fixed bias
- Self-bias
1. Drain to Gate Bias Configuration
Drain to gate bias Configuration is shown below: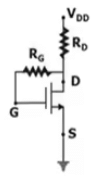
DC Equivalent of above circuit: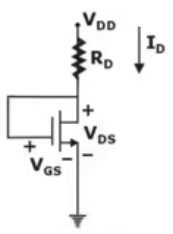
DC Analysis:
- Gate current, IG =0
- So, we have voltage drop across resistance RG = VRG = 0
- Therefore, we get a direct connection between drain and source i.e. VD = VG
VDS = VGS - Note: Drain to gate bias always enables MOSFET in saturation region
For output circuit, we have VDS = VDD – IDRD
2. Voltage Divider Bias Configuration
Voltage Divider Configuration is show below: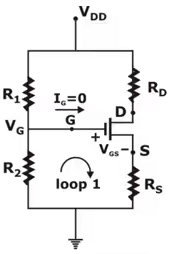
DC Equivalent: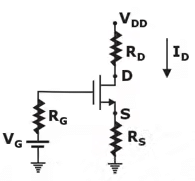
DC – ANALYSIS:
- Using voltage divider, gate voltage is obtained by:
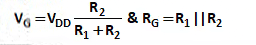
- Applying KVL is loop 1, we get
VG – VGS – IDRS = 0
VGS = VG – IDRS …. (1) - Assume that MOSFET is in saturation, so we have ID = Kn (VGS – VTN)2
- By solving the quadratic equation, determine the value of VGS or ID, then apply KVL in source to drain loop
VDD – IDRD – VDS – ISRS = 0
VDS = VDD – ID (RS + RD) - If VDS > VGS – VTN, then the transistor is indeed biased in saturation region, as we have assumed.
- However, if VDS < VDS (sat), then transistor is biased in the non saturation region
Therefore from equation (1)
VGS = VG – IDRS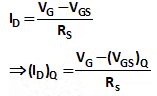
3. Fixed bias Configuration
Fixed bias Configuration is shown below: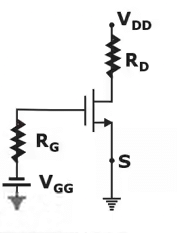
DC Equivalent: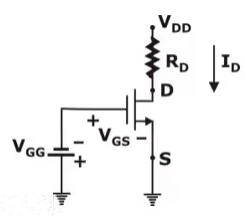
(In DC model, RG is short and input impedance is very high i.e. (IG ≃ 0))
Drawback of fixed bias: It is a dual battery design which makes it expensive and more space occupied bias Configuration.
4. Self-bias Configuration
Self Bias Configuration is shown below: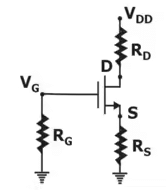
DC Equivalent: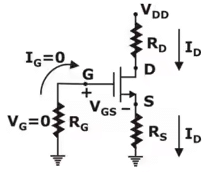
DC ANALYSIS:
0 = VGS + IDRS
VGS = – IDRS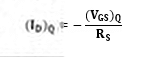
|
3 videos|75 docs|64 tests
|
















