Oscillators - 2 | Analog Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Oscillators with LC Feedback Circuits
- Although the RC feedback oscillators, particularly the Wien bridge, are generally suitable for frequencies up to about 1 MHz, LC feedback elements are normally used in oscillators that require higher frequencies of oscillation.
- Also, because of the frequency limitation (lower unity-gain frequency) of most op-amps, transistors (BJT or FET) are often used as the gain element in LC oscillators.
- This section introduces several types of resonant LC feedback oscillators like the Colpitts, Clapp, Hartley & crystal-controlled oscillators.
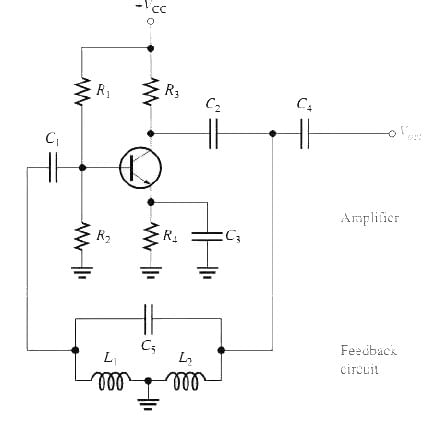
The Hartley Oscillator
- The Hartley oscillator is similar to the Colpitts except that the feedback circuit consists of two series inductors and a parallel capacitor
- In this circuit, the frequency of oscillation for Q > 10, is
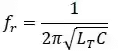
- where LT = L1 + L2.
- The inductors act in a role similar to C1 and C2 in the Colpitts to determine the attenuation, B, of the feedback circuit.
B = L1/L2 - To assure start-up of oscillation, Av must be greater than 1/B.
Av = L2/L1 - Loading of the tank circuit has the same effect in the Hartley as in the Colpitts; that is, the Q is decreased and thus Fr decreases.
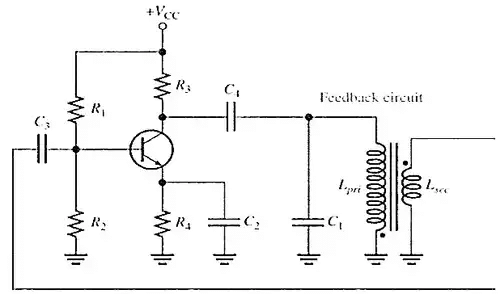
The Armstrong Oscillator
- This type of LC feedback oscillator uses transformer coupling to feed back a portion of the signal voltage.
- The transformer secondary coil provides the feedback to keep the oscillation going.
- The Armstrong is less common than the Colpitts, Clapp, and Hartley, mainly because of the disadvantage of transformer size and cost.
- The frequency of oscillation is set by the inductance of the primary winding Lpri in parallel with C1.
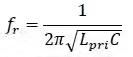
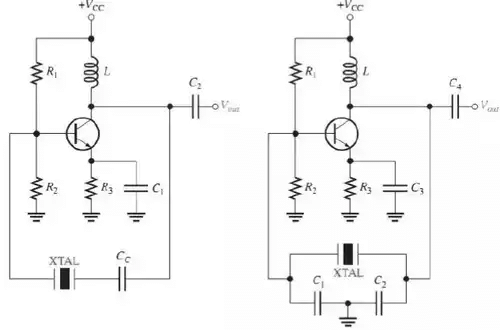
Crystal-Controlled Oscillators
- The most stable and accurate type of feedback oscillator uses a piezoelectric crystal in the feedback loop to control the frequency.
The Piezoelectric Effect
- Quartz is one type of crystalline substance found in nature that exhibits a property called the piezoelectric effect.
- When a changing mechanical stress is applied across the crystal to cause it to vibrate, a voltage develops at the frequency of mechanical vibration.
- Conversely, when an AC voltage is applied across the crystal, it vibrates at the frequency of the applied voltage.
- The greatest vibration occurs at the crystal’s natural resonant frequency, which is determined by the physical dimensions and by the way the crystal is cut.
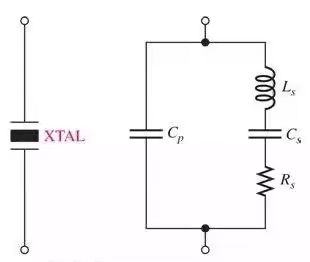
- As you can see, the crystal’s equivalent circuit is a series-parallel circuit and can operate in either series resonance or parallel resonance.
- The impedance of the crystal is minimum at the series resonant frequency, thus providing maximum feedback.
- The crystal tuning capacitor, Cc is used to “fine tune” the oscillator frequency.
- The impedance of the crystal is maximum at parallel resonance, thus developing the maximum voltage across the capacitors.
- The voltage across C1 is fed back to the input.
Relaxation Oscillators
- The second major category of oscillators is the relaxation oscillator.
- Relaxation oscillators use an RC timing circuit and a device that changes states to generate a periodic waveform.
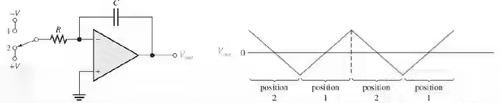
- A Triangular-Wave Oscillator:
- The op-amp integrator can be used as the basis for a triangular-wave oscillator.
- When the switch is in position 1, the negative voltage is applied, and the output is a positive-going ramp.
- When the switch is thrown into position 2, a negative-going ramp is produced.
- If the switch is thrown back and forth at fixed intervals, the output is a triangular wave consisting of alternating positive-going and negative-going ramps.
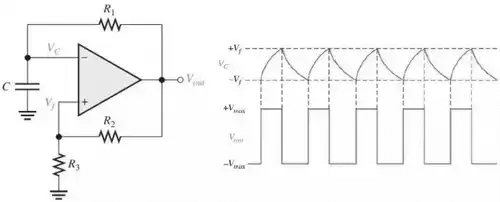
- A Square-Wave Oscillator:
- The basic square-wave oscillator is a type of relaxation oscillator because its operation is based on the charging and discharging of a capacitor.
- Notice that the op-amp’s inverting input is the capacitor voltage and the non inverting input is a portion of the output fed back through resistors R2 and R3 to provide hysteresis.
- When the circuit is first turned on, the capacitor is uncharged, and thus the inverting input is at 0 V.
- This makes the output a positive maximum, and the capacitor begins to charge toward Vout through R1.
- When the capacitor voltage Vc reaches a value equal to the feedback voltage Vf on the non-inverting input, the op-amp switches to the maximum negative state.
- At this point, the capacitor begins to discharge from +Vf toward –Vf.
- When the capacitor voltage reaches –Vf the op-amp switches back to the maximum positive state.
- This action continues to repeat and a square-wave output voltage is obtained.
Linear wave shaping Circuits
- The process of where by the form of a non-sinusoidal signal is altered by transmission through a linear network is called “LINEAR WAVE SHAPING"
- RC Low Pass Circuit
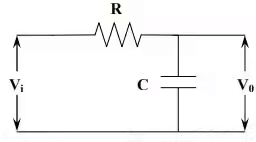 The circuit passes low frequencies readily but attenuates high frequencies because the reactance of the capacitor decreases with increasing frequency. At very high frequencies the capacitor acts as a virtual short circuit and the output falls to zero. This circuit also works as integrating circuit. A circuit in which the output voltage is proportional to the integral of the input voltage is known as integrating circuit. The condition for integrating circuit is RC value must be much greater than the time period of the input wave (RC>>T).
The circuit passes low frequencies readily but attenuates high frequencies because the reactance of the capacitor decreases with increasing frequency. At very high frequencies the capacitor acts as a virtual short circuit and the output falls to zero. This circuit also works as integrating circuit. A circuit in which the output voltage is proportional to the integral of the input voltage is known as integrating circuit. The condition for integrating circuit is RC value must be much greater than the time period of the input wave (RC>>T).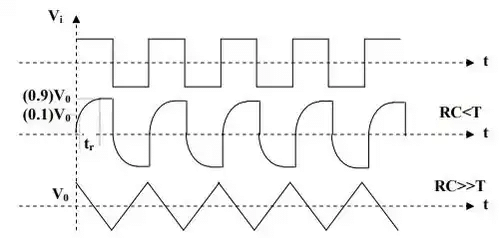
- RC High Pass Circuit
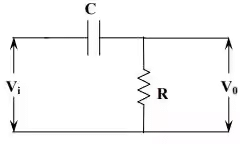 The higher frequency components in the input signal appears at the output with less attenuation than the lower frequency components because the reactance of the capacitor decreases with increase in frequency. This circuit works as a differential circuit. A circuit in which the output voltage is proportional to the derivative of the input voltage is known as differential circuit. The condition for differential circuit is RC value must be much smaller then the time period of the input wave (RC<<T).
The higher frequency components in the input signal appears at the output with less attenuation than the lower frequency components because the reactance of the capacitor decreases with increase in frequency. This circuit works as a differential circuit. A circuit in which the output voltage is proportional to the derivative of the input voltage is known as differential circuit. The condition for differential circuit is RC value must be much smaller then the time period of the input wave (RC<<T).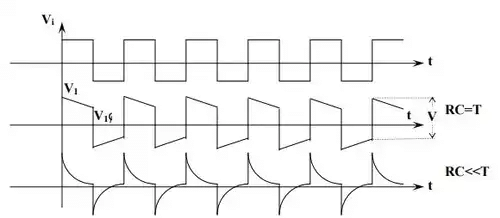
The document Oscillators - 2 | Analog Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) is a part of the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Course Analog Circuits.
All you need of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) at this link: Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
|
3 videos|75 docs|64 tests
|
Related Searches





















