Logical (Virtual) Vs Physical Address Space | Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Memory Allocation Techniques
To store the data and to manage the processes, we need a large-sized memory, and, at the same time, we need to access the data as fast as possible. But if we increase the size of memory, the access time will also increase, and, as we know, the CPU always generates addresses for secondary memory, i.e., logical addresses. But we want to access the main memory, so we need Address translation of logical address into a physical address.
The main memory interacts with both the user processes and the operating system. So we need to use the main memory efficiently. Main memory is divided into non-overlapping memory regions called partitions.
The main memory can be broadly allocated in two ways
- Contiguous memory allocation
- Non-Contiguous memory allocation
1. Contiguous memory allocation can be categorized into two ways:
- Fixed partition scheme
- Variable partition scheme.
(i) Different Partition Allocation methods are used in Contiguous memory allocations
- First Fit
- Best Fit
- Worst Fit
- Next Fit
2. Non-Contiguous memory allocation can be categorized into many ways:
- Paging
- Multilevel paging
- Inverted paging
- Segmentation
- Segmented paging
MMU(Memory Management Unit): The run-time mapping between the Virtual address and Physical Address is done by a hardware device known as MMU.
In memory management, the Operating System will handle the processes and move the processes between disk and memory for execution. It keeps track of available and used memory.
MMU scheme:
CPU------- MMU------Memory

- CPU will generate a logical address, for eg: 346
- MMU will generate a relocation register (base register), for eg: 14000
- In memory, the physical address is located e.g.:(346+14000= 14346)
The value in the relocation register is added to every address generated by a user process at the time the address is sent to memory. The user program never sees the real physical addresses. The program can create a pointer to location 346, store it in memory, manipulate it, and compare it with other addresses—all like the number 346.
The user program generates only logical addresses. However, these logical addresses must be mapped to physical addresses before they are used.
Address binding: Address binding is the process of mapping from one address space to another address space. A logical address is an address generated by the CPU during execution, whereas a Physical Address refers to the location in the memory unit(the one that is loaded into memory). The logical address undergoes translation by the MMU or addresses the translation unit in particular. The output of this process is the appropriate physical address or the location of code/data in RAM.
An address binding can be done in three different ways:
- Compile Time: If you know that during compile time, where the process will reside in memory, then an absolute address is generated. i.e., The physical address is embedded in the executable of the program during compilation. Loading the executable as a process in memory is very fast. But if the generated address space is preoccupied with other processes, then the program crashes and it becomes necessary to recompile the program to change the address space.
- Load time: If it is not known at the compile time where the process will reside, then a relocatable address will be generated. The loader translates the relocatable address to an absolute address. The base address of the process in the main memory is added to all logical addresses by the loader to generate an absolute address. In this, if the base address of the process changes, then we need to reload the process again.
- Execution time: The instructions are in memory and are being processed by the CPU. Additional memory may be allocated and/or deallocated at this time. This is used if a process can be moved from one memory to another during execution(dynamic linking-Linking that is done during load or run time). Example: Compaction.

Mapping Virtual Addresses to Physical Addresses
In Contiguous memory allocation, mapping from virtual addresses to physical addresses is not a difficult task because if we take a process from secondary memory and copy it to the main memory, the addresses will be stored in a contiguous manner, so if we know the base address of the process, we can find out the next addresses.
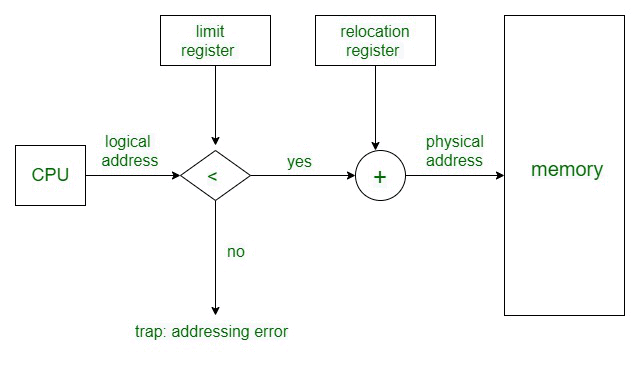
The Memory Management Unit is a combination of 2 registers
- Base Register (Relocation Register)
- Limit Register.
- Base Register: contains the starting physical address of the process.
- Limit Register: mentions the limit relative to the base address on the region occupied by the process.
The logical address generated by the CPU is first checked by the limit register, If the value of the logical address generated is less than the value of the limit register, the base address stored in the relocation register is added to the logical address to get the physical address of the memory location.
If the logical address value is greater than the limit register, then the CPU traps the OS, and the OS terminates the program by giving fatal error.
In Non-Contiguous Memory allocation, processes can be allocated anywhere in available space. The address translation in non-contiguous memory allocation is difficult.
There are several techniques used for address translation in noncontiguous memory allocation like Paging, Multilevel paging, Inverted paging, Segmentation, and Segmented paging. Different data structures and hardware support, like TLB, are required in these techniques.
Logical and Physical Address in Operating System
A logical address is generated by the CPU while a program is running. The logical address is a virtual address as it does not exist physically. Therefore, it is also known as a Virtual Address. This address is used as a reference to access the physical memory location by CPU. The term Logical Address Space is used for the set of all logical addresses generated by a program’s perspective.
The hardware device called Memory-Management Unit is used for logical mapping address to its corresponding physical address.
Physical Address identifies a physical location of required data in memory. The user never directly deals with the physical address but can access its corresponding logical address. The user program generates the logical address and thinks that the program is running in this logical address but the program needs physical memory for its execution; therefore, the logical address must be mapped to the physical address by MMU before they are used. The term Physical Address Space is used for all physical addresses corresponding to the logical addresses in a Logical address space.
 |
Download the notes
Logical (Virtual) Vs Physical Address Space
|
Download as PDF |
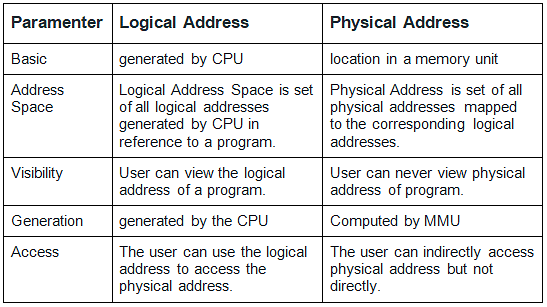
Differences Between Logical and Physical Addresses in Operating System
- The fundamental difference between a physical address and the logical address is that a logical address is generated by the CPU while the program is running, whereas the physical address is a location in memory.
- The logical address is generated by the CPU, whereas the physical address is computed by the MMU.
- The logical address does not exist physically in the memory hence it is sometimes known as a virtual address, whereas the physical address is a location in the memory unit.
- The logical address is used as a reference to access the physical address. The physical address cannot be accessed directly.
- Users can view the logical address of a program. But, they cannot view the physical address of a program.
- The set of all the logical addresses generated in reference to a program by the CPU is called Logical Address Space, whereas the set of all the physical addresses mapped to the logical address is called Physical Address Space.
Comparison Chart:
|
10 videos|99 docs|33 tests
|