Basics of Radar | Electromagnetics - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Radar |

|
| PRT Determination Formula |

|
| Key Points |

|
| Doppler Frequency (fd) |

|
Radar
In basic communications, there are two types of communication one is analog and another is digital. But in advanced communication, we will discuss the communication through radar, satellite etc. Mostly they are developed for of military purpose or security purpose.
A radar consists of a transmitter and receiver, each connected to a directional antenna. The transmitter radiates or transmits electromagnetic radiations generated by a magnetron oscillator. The receiver antenna, collects the returned echo signal and delivers it to the receiver where it is processed to detect the presence of the target and to extract its relative velocity with respect to radar station if the target is moving.
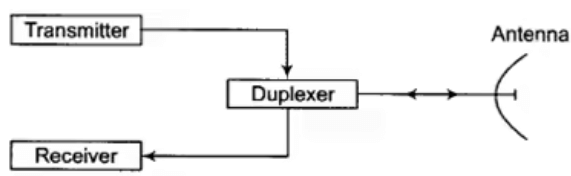 Block diagram of RADAR
Block diagram of RADAR
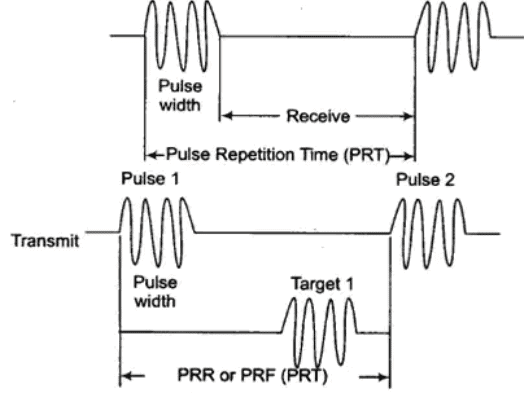 waveform of RADAR
waveform of RADAR
Pulse Reception Frequency (PRF) or Pulse Repetition rate (PRR) is number of pulses per unit time. These pulses are transmitted by a highly directional parabolic antenna at the target, which can reflect (echo) some of the energy back to the same antenna. The reflected energy is received and time measurements are made, to determine the distance of the target.
After the radar pulse has been transmitted, a sufficient rest time must be allowed for echo to return so as not to interfere with next transmit pulse. Time difference between two successive pulses is called as Pulse Repetition Time (PRT).
PRT Determination Formula
Pulse repetition time determines the maximum distance to the target to be measured, that is rangeRange = Δt/12.36 miles
where Δt is the time from transmitter to receiver in microseconds.
For higher accuracy and shorter ranges
Range = 328Δt/2 = 164Δt yards
The range beyond which objects appear as second return echoes is called the Maximum Unambiguous Range (MUR).
MUR = PRT/12.2 miles
where, PRT is in μs.
- In timing diagram distance between pulse 1 and pulse 2 is called as maximum range.
- Minimum range = 164 PW yards
where PW is Pulse-Width in μs.
Duty cycle = PW/PRT
- Average power = Peak power × duty cycle
PRF = 1/PRT
Maximum Range (Rmax): Maximum radar range is the distance beyond which the target cannot be detected. It occurs when the received echo signal power pr just equals the minimum detectable signal (Smin).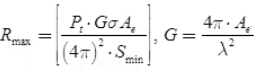
where, λ = Wavelength of radiated energy,
Ae = Capture (or effective) area of receiving antenna
G = Transmitter gain
σ = Radar cross-section of target
Rmax ∝ pt1/4
Note: By increasing Pt by 16 times, Rmax becomes just double.
Effect of Noise on Maximum Range: Noise affects the maximum range in so far, as it determines the minimum power that the receiver can handle.
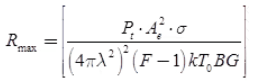
where, k = Boltzmann's constant
T0 = Standard ambient temperature (290 K)
B = Bandwidth of receiver
kT0 B = Noise input power of receiver
F = Noise figure of receiver
Ae = 0.65πD2/4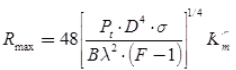
where, D = Antenna diameter in metre
σ = Effective cross-section area in metre2
Key Points
- The single most practical method of improving the radar range is to increase the antenna aperture which is proportional to its gain.
- Bandwidth required for receiver is n/T, where T is the pulse duration and n is number whose ranges from 1 to 10 depending on circumstances.
Blind Speed: If the target has uniform velocity, the successive sweeps will have Doppler phase shifts of exactly 2π and the target appears stationary and gives wrong radar indication. The speed corresponding to this condition is called blind speed.
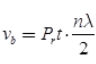
where, vb = Blind speed
λ = Wavelength of transmitted pulse
n = Any integer (1, 2,….)
Doppler Effect: If the observer is moving with respect to source, he observes change in frequency of the wave emitted by source, this is called as Doppler effect or Doppler shift.
Observed frequency f is given by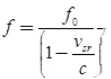
and
doppler shift
|Δf| = vsr/λ
where, vsr = vs – vr is the relative velocity source with respect to receiver.
f0 is frequency of wave radiated by source.
In radar technology, Doppler effect is using for the following tasks
- Speed measuring
- MIT (Moving Target Indication)
- In air or space based radar system for precise determination of lateral distances.
Doppler Frequency (fd)
fd = 2vr/λ Hertz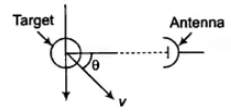 Determination Doppler frequency
Determination Doppler frequency
where, fd = Doppler frequency shift
vr = Relative velocity of target with respect to radar
vr = v cos θ
fd = 2v.cos θ/λ
v = Speed of the target
when θ = 0 (fd)max = 2.v/λ
when θ = 90° (fd)min = 0
|
11 videos|94 docs|89 tests
|















