Nature of Roots | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Download
Quadratic equations are the equations where polynomial has the degree two. Quadratic equations are the equations of type ax2 + bx + c = 0 where x is unknown and a, b, c are known real numbers and a should not be zero. If a=0 then the equation will not remain quadratic, it will be then linear as a = 0 will eliminate x2 term. As the quadratic equation has the highest degree two, so this equation has two roots, or we can say that we will find two values of x for a quadratic equation.
How to find roots?
Method 1: The roots of the quadratic equations can be found by the Shridharacharaya formula.
x = [-b±√(b2 – 4ac)]/2a
Example: The length of sides of a rectangle is given by x – 3 and x – 5 and the area of the rectangle is 3 unit2. Find the sides of the rectangle.
Solution:
Area of rectangle = length*breadth = (x – 3)(x – 5) = 3
Area = x2 – 8x + 15 = 3
= x2 – 8x + 12 = 0
Discriminant = b2 – 4ac = 64 – (4(1)(12)) = 64 – 48 = 16
x = [-b ± √(b2-4ac)]/2a = [-(-8) ± √16]/2 = (8±4)/2
x = 12/2 or 4/2
x = 2 or 6
When x is 2, sides are x – 3 = 2 – 3 = -1 and x – 5 = 2 – 5 = -3.
Since length of sides cannot be equal therefore x = 2 is not a valid ans.
When x is 6, sides are x – 3 = 6 – 3 = 3 and x – 5= 6 – 5 =1.
Therefore, x = 6 is the valid answer and the sides are 3 and 1.
Method 2. The other way is the factorizing method. A quadratic equation can be considered a factor of two terms. Like ax2 + bx + c = 0 can be written as (x – x1)(x – x2) = 0 where x1 and x2 are roots of quadratic equation.
Steps:
- Find two numbers such that there product = ac and there sum = b.
- Then write x coefficient as sum of these two numbers and split them such that you get two terms for x.
- factor the first two as a group and last two terms as a group.
- Take common factors from these and on equating the two expression with zero after taking common factors and rearranging the equation we get the roots.
Example: Let be the quadratic equation x2 + 3x = 18
x2 + 3x – 18 = 0
Step:
1. 6 and -3 are the numbers whose sum is equal to b and product is equal ac.
2. x2 + (6-3)x – 18 = x2 + 6x -3x – 18 =0
3. x(x + 6) – x(x + 6) = 0
4. taking (x + 6) as common.
(x + 6)(x – 3) = 0
x = -6 or x = 3
In a factorizing method it is not necessary that you will always find these two numbers easily(especially in the case when roots are imaginary or irrational) so it is better to use the quadratic formula.
Nature of roots
The nature of roots depends on the discriminant of the quadratic equation. The discriminant of a quadratic equation is given by b2 – 4ac. It is so because in quadratic formula square root of discriminant is there.
Root 1: If b2 – 4ac > 0 roots are real and different. As the discriminant is >0 then the square root of it will not be imaginary. It has two cases.
- If b2 – 4ac is a perfect square then roots are rational. As the discriminant is a perfect square, so we will have an integer as a square root of the discriminant. Hence, the roots are rational numbers.
Example: Let the quadratic equation be x2-5x+6=0.
Then the discriminant of the given equation is b2 – 4ac=(-5)2 – 4*1*6 = 25-24 = 1
According to Shridharacharaya formula
x = [-b±√(b2-4ac)]/2a = x = [-(-5) ± √1]/2
x1 = [-(-5) + √1]/2 = 6/2 = 3
x2 = [-(-5) – √1]/2 = 4/2 = 2
Therefore, the roots are 3,2. Both are rational and different.
- If b2 – 4ac is not a perfect square then the square root of discriminant is irrational hence roots are irrational and occurs in pair.
Example: Let the quadratic equation be x2-7x+8 = 0.
Then the discriminant of the given equation is
b2 – 4ac=(-7)2 – 4*1*8 = 49-32 = 17
According to Shridharacharaya formula
x = [-b±√(b2-4ac)]/2a = x = [-(-7) ± √17]/2
x1 = [-(-7) + √17]/2 = [7 + √17]/2
x2 = [-(-7) – √17]/2 = [7 – √17]/2
Therefore, the roots are [7 + √17]/2,[7 – √17]/2. Both are irrational and in pairs.
Root 2: If b2 – 4ac = 0 roots are real and equal.
Example: Let the quadratic equation be 3x2-6x+3=0.
Then the discriminant of the given equation is
b2 – 4ac=(-6)2 – 4*3*3 = 36 – 36 = 0
According to Shridharacharaya formula
x = [-b±√(b2-4ac)]/2a = x = [-(-6) ± √0]/[(2)(3)]
x1 = [-(-6) + √0]/2 = 6/6 = 1
x2 = [-(-6) – √0]/2 = 6/6 = 1
Therefore, the roots are 1,1. Both are real and equal.
Root 3: If b2 – 4ac < 0 roots are imaginary, or you can say complex roots. It is imaginary because the term under the square root is negative. These complex roots will always occur in pairs i.e, both the roots are conjugate of each other.
Example: Let the quadratic equation be x2+6x+11=0.
Then the discriminant of the given equation is
b2 – 4ac=(6)2 – 4*1*11 = 36-44 = -8
According to Shridharacharaya formula
x = [-b±√(b2-4ac)]/2a = x = [-(6) ± √(-8)]/2
x1 = [-(6) + √(-8)]/2 = [-6 + √8i]/2 = 2[-3 + √2i]/2 = -3 + √2i
x2 = [-(6) – √(-8)]/2 = [-6 – √8i]/2 = 2[-3 – √2i]/2 = -3 – √2i
Therefore, the roots are 3,2. Both are imaginary and conjugate of each other(in pair).
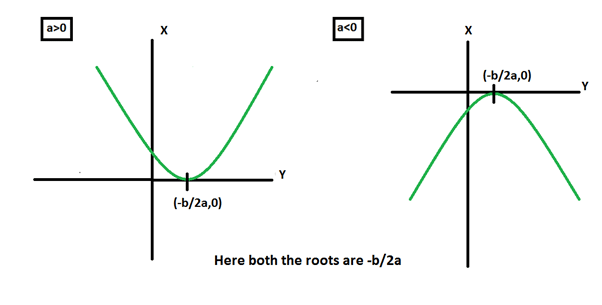
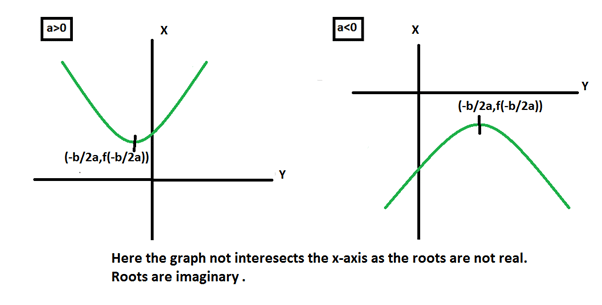
Graphs for Roots
The maximum/minimum value of quadratic function is found at x = -b/2a
Proof:
We get maxima or minima when d(f(x))/dx = 0.
On differentiating quadratic function f(x) = ax2 + bx + c.
We get,
2ax + b = 0
x = -b/2a
This x is either maxima(a<0) or minima(a>0).
1. When b2– 4ac > 0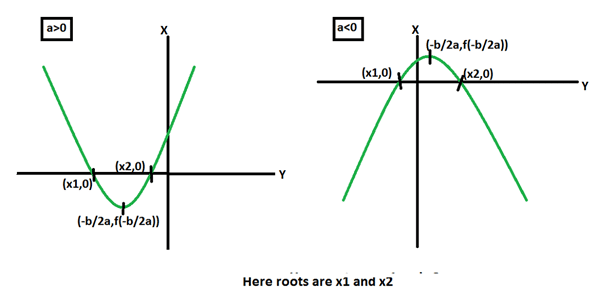
2. When b2– 4ac = 0
3. When b2– 4ac < 0
Quadratic Equations word problems
Question 1. The height of a triangle is less than 4 cm than the base. The area of triangle is 30 cm2. Find the height and base of triangle.
Solution:
Let the base of triangle be x cm then height is x-4 cm
Area of triangle = 1/2*height*base = 1/2*(x)(x – 4)=30
Area = x2 – 4x = 30*2
= x2 – 4x = 60
= x2 – 4x – 60 = 0
Discriminant = (-4)2 – 4(1)(-60) = 16+240 = 256
x = [-b±√(b2 – 4ac)]/2a = [-(-4)±√256]/2 = (4±16)/2
x = 20/2 or -12/2
x = 10 or -6
As side cannot be negative, therefore -6 is not correct.
So, when x is 10, base =10 cm and height =x – 4 = 10 – 4 = 6 cm
Therefore, x = 10 is the valid answer and the base and height of the triangle are 10 and 6 respectively.
Question 2. The volume of a box is 600 inch2. The length of box is 2 inches less than the width. The height of box is 5 inches. Find the dimensions of box.
Solution:
Let the width of box be x inches then length = x – 2 inches.
Volume of box =Length* Width *Height = (x-2)(x)5= 600
x2 – 2x = 120 => x2 – 2x -120 = 0
x2 + 10x – 12x – 120 = 0
x(x + 10) – 12(x + 10)=0
(x – 12)(x + 10)=0
x = 12 or x = -10
As width can not be negative, therefore, -10 is not correct.
When x = 12, width = 12 inches, length = x – 2 = 12 – 2 = 10 inches, height = 5 inches
Question 3. A ball is thrown from the top of a building . its height in meters above the ground as a function of time is given by h(t) = -4t2 + 24t + 3. a) How much time it take to reach the maximum height and what is the maximum height. b) Find also the time at which ball hits the ground.
Solution:
a) Since a<0, therefore the time to reach maximum height is = -b/2a. (refer graph part)
t = -24/(2(-4)) = -24/-8
t = 3 sec.
Height = h(t) = -4(3)2 +24(3)+3 = 39 meters.
b) When the ball hits the ground h(t)=0.
-4t2 + 24t + 3 = 0
The discriminant of the given equation is
b2 – 4ac=(24)2 – 4*(-4)*3 = 576 + 48 = 624
According to Shridharacharaya formula
x = [-b±√(b2-4ac)]/2a = x = [-(24) ± √624]/[(2)(-4)]
x1 = [-24 + √624]/-8= 4 [-6 + √39]/-8 = [-6 + √39]/-2 = [6 – √39]/2 = -0.122499 = -0.1225(approx)
x2 = [-24 – √624]/-8= 4 [-6 – √39]/-8 = [-6 – √39]/-2 = [6 + √39]/2 = 6.122499 = 6.1225(approx)
As time can not be negative, therefore, [6 – √39]/2 sec is not correct.
Therefore, the ball hits the ground at [6 + √39]/2 = 6.122499 = 6.1225 sec
|
127 videos|550 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Nature of Roots - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10
| 1. What is the nature of roots in a quadratic equation? |  |
| 2. How can I determine the nature of roots using the discriminant? |  |
| 3. What does it mean if the roots of a quadratic equation are complex? |  |
| 4. Can the nature of roots be visualized graphically? |  |
| 5. What role does the coefficient of x² play in determining the nature of roots? |  |






















