Electric Motor & Electric Generator | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
An electric motor is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Let’s go through an instance: What does the mixer in your house do for you? The rotating blades mash and mix things for you. And if someone were to ask you how that works, what would you say? You would probably say that it works on electricity. Well, that’s not incorrect. Motors convert electric energy to mechanical work. The opposite is done by generators that convert mechanical work to electrical energy.
Different Parts of an Electric Motor and Their Function
A simple motor has the following parts:
- A power supply – mostly DC for a simple motor
- Field Magnet – could be a permanent magnet or an electromagnet
- An Armature or rotor
- Commutator
- Brushes
- Axle
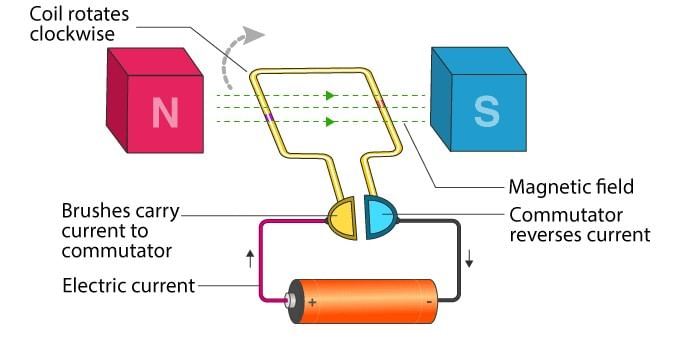
- Power Source: A simple motor usually has a DC power source. It supplies power to the motor armature or field coils.
- Commutator: It is the rotating interface of the armature coil with a stationary circuit.
- Field Magnet: The magnetic field helps to produce a torque on the rotating armature coil by virtue of Fleming’s left-hand rule.
- Armature Core: Holds the armature coil in place and provides mechanical support.
- Armature Coil: It helps the motor to run.
- Brushes: It is a device that conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly the rotating shaft.
What Is The Working Principle of An Electric Motor?
The working of an electric motor is based on the fact that a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. To better understand, imagine the following situation.
Take two bar magnets and keep the poles facing each other with a small space in between. Now, take a small length of a conducting wire and make a loop. Keep this loop in between the space between the magnets such that it is still within the sphere of influence of the magnets. Now for the last bit. Connect the ends of the loop to battery terminals.
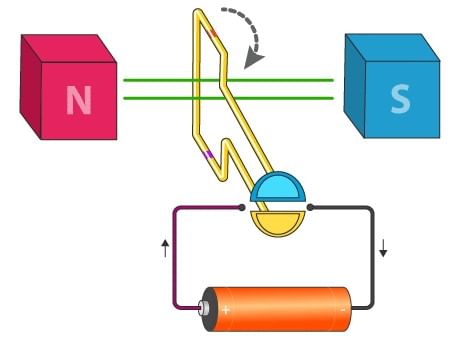
Once electricity flows through your simple circuit, you will notice that your loop “moves”. So why does this happen? The magnetic field of the magnets interferes with that produced due to electric current flowing in the conductor. Since the loop has become a magnet, one side of it will be attracted to the north pole of the magnet and the other to the south pole. This causes the loop to continuously rotate. This is the principle of working of electric motor.
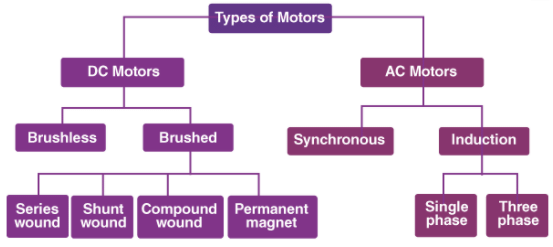
Types of Electric Motor
The primary classification of electric motor is as follows:
Uses of an Electric Motor
Electric motors are used in a variety of applications. Some of them are listed below.
- Drills
- Water Pumps
- Hard Disc Drives
- Washing Machines
- Industrial Equipment
You can expect the efficiency of a functioning motor to be around 70 – 85% as the remaining energy is wasted in heat production and sounds emitted.
Electric Generator (Not included in CBSE Curriculum
2021-22 )
What is an Electric Generator?
Electric generators, also known as dynamos is an electric machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The electric generator’s mechanical energy is usually provided by steam turbines, gas turbines, and wind turbines. Electrical generators provide nearly all the power that is required for electric power grids.

The reverse conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy is done by an electric motor. Both motors and generators have many similarities. But in this, the article let us focus mainly on electric generators and how they convert mechanical energy to electrical energy.
History of Electric Generators
Electrostatic generators were used before the relationship between electricity and magnetism was discovered. These generators operated on electrostatic principles. Electrostatic generators were never used for generation of commercially significant quantities of electric power due to the following reasons:
- Due to the difficulty in insulating machines that produced high voltages
- Due to the low power rating
Due to this inefficiency of electrostatic generators, the first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday.
How do Generators create Electricity?
Generators do not create electricity instead it uses the mechanical energy supplied to it to force the movement of electric charges present in the wire of its windings through an external electric circuit. This flow of electrons constitutes the output electric current supplied by the generator.
The modern-day generators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday. He realized that the above flow of current can be created by moving an electrical conductor in a magnetic field. This movement creates a voltage difference between the two ends of the conductor which causes the electric charges to flow, hence generating electric current.
Components of an Electric Generator
The main components of an electric generator are given below
- The Frame – the structure
- An Engine – the source of mechanical energy
- The Alternator – produces an electrical output from the mechanical input
- A Fuel System – to keep the generator operational
- A Voltage Regulator – to regulate the voltage output
- A Cooling System – to regulate heat levels that build up in the system
- A Lubrication System– for durable and smooth operations over a span
- An Exhaust System – to dispose of the waste exhaust gases produced in the process
- A Charger – to keep the battery of the generator charged
- Main Control – the control panel controlling generator interface
Types of Electric Generators
The classification of electric generators depends on the type of electrical energy that is produced, which is either direct current or alternating current.
- AC generators: AC generators are known as single-phase generators and are limited to 25 kW.
- DC generators: These generators are divided into three categories, and they are shunt, series, and compound-wound. Shunt generators are used in battery chargers. Series generators are used in street lights. While most of the DC generators are compound-wound.
Uses of an Electric Generator
- They provide the power for most power networks across cities
- Small scale generators provide a good backup for household power needs or small businesses
- At construction sites, before the power is set up, they extensively make use of electric generators
- Energy-efficient as fuel consumption is reduced drastically
- Since they give a range of voltage output, they are used in labs
- They are used to drive motors
- They are used in transportation
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q. Can a generator be used as a motor?
Ans: In principle, any electrical generator can also serve as an electric motor or vice versa.
Q. What kind of power does a generator produce?
Ans: Generators produce both AC and DC depending on its construction and the requirement.
Q. What is an AC generator?
Ans: An AC generator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternative emf or alternating current.
Q. What is a DC generator?
Ans: A DC generator is an electrical machine that converts mechanical energy into DC (direct current) electricity.
Q. How does the water stored in dams generate electricity?
Ans: The water stored in dams contains huge amounts of potential energy stored in it. When the dam gates are opened, the stored potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. This kinetic energy rotates the shaft of the generators and produces electricity.
|
122 videos|149 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Electric Motor & Electric Generator - Physics for Grade 10
| 1. What is an electric generator? |  |
| 2. How does an electric generator work? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of an electric generator? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between an electric motor and an electric generator? |  |
| 5. What are the factors to consider when selecting an electric generator? |  |





















