Kosaraju using DFS | Algorithms - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
Given a directed graph, find out whether the graph is strongly connected or not. A directed graph is strongly connected if there is a path between any two pair of vertices. For example, following is a strongly connected graph.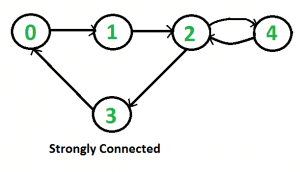
It is easy for undirected graph, we can just do a BFS and DFS starting from any vertex. If BFS or DFS visits all vertices, then the given undirected graph is connected. This approach won’t work for a directed graph. For example, consider the following graph which is not strongly connected. If we start DFS (or BFS) from vertex 0, we can reach all vertices, but if we start from any other vertex, we cannot reach all vertices.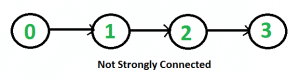
How to do for directed graph?
A simple idea is to use a all pair shortest path algorithm like Floyd Warshall or find Transitive Closure of graph. Time complexity of this method would be O(v3).
We can also do DFS V times starting from every vertex. If any DFS, doesn’t visit all vertices, then graph is not strongly connected. This algorithm takes O(V*(V+E)) time which can be same as transitive closure for a dense graph.
A better idea can be Strongly Connected Components (SCC) algorithm. We can find all SCCs in O(V+E) time. If number of SCCs is one, then graph is strongly connected. The algorithm for SCC does extra work as it finds all SCCs.
Following is Kosaraju’s DFS based simple algorithm that does two DFS traversals of graph:
- Initialize all vertices as not visited.
- Do a DFS traversal of graph starting from any arbitrary vertex v. If DFS traversal doesn’t visit all vertices, then return false.
- Reverse all arcs (or find transpose or reverse of graph)
- Mark all vertices as not-visited in reversed graph.
- Do a DFS traversal of reversed graph starting from same vertex v (Same as step 2). If DFS traversal doesn’t visit all vertices, then return false. Otherwise return true.
The idea is, if every node can be reached from a vertex v, and every node can reach v, then the graph is strongly connected. In step 2, we check if all vertices are reachable from v. In step 4, we check if all vertices can reach v (In reversed graph, if all vertices are reachable from v, then all vertices can reach v in original graph).
Following is the implementation of above algorithm
- C++




- Java



- Python


Output:
Yes
No
Time Complexity: Time complexity of above implementation is sane as Depth First Search which is O(V + E) if the graph is represented using adjacency list representation.
|
81 videos|113 docs|34 tests
|





















