Blood Groups, Lymph & Circulatory pathway | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Blood Groups |

|
| Blood Coagulation |

|
| Lymph |

|
| Circulatory Pathways |

|
Blood Groups
Two blood groupings are present:
1) ABO Blood Grouping
2) Rh Blood Grouping
1. ABO Grouping
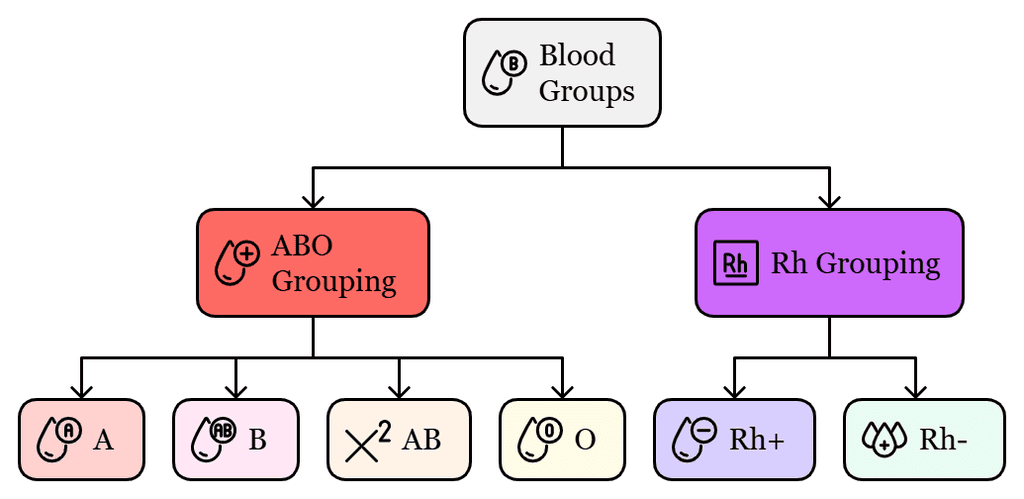
- ABO grouping is based on the presence or absence of two surface antigens on the RBCs, namely A and B.
- The plasma of different individuals contains two natural antibodies.
- The distribution of antigens and antibodies in the four groups of blood, A, B, AB and O.
- The blood of a donor has to be carefully matched with the blood of a recipient before any blood transfusion to avoid severe problems of clumping, which leads to the destruction of RBCs.
- Group ‘O’ blood can be donated to persons with any other blood group and hence ‘O’ group individuals are called ‘universal donors’.
- Persons with the ‘AB’ group can accept blood from persons with AB as well as the other groups of blood, and such persons are called ‘universal recipients’.
2. Rh Blood Grouping
- Another type of antigen, known as the Rh antigen, is similar to one found in Rhesus monkeys (which is why it's called Rh). This antigen is found on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs) in about 80 percent of humans.
- People who have this Rh antigen are referred to as Rh positive (Rh+), while those who do not have it are called Rh negative (Rh-).
- If a Rh- person comes into contact with Rh+ blood, their body will create specific antibodies against the Rh antigens.
- Because of this, it is important to match the Rh group before blood transfusions.
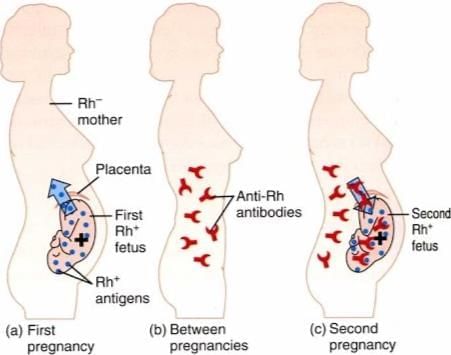
- A special situation called Rh incompatibility can occur during pregnancy when a Rh- mother is carrying a Rh+ baby.
- During the first pregnancy, the blood of the mother and the fetus do not mix because they are separated by the placenta.
- However, during childbirth, there is a chance that the mother's blood may come into contact with a small amount of the Rh+ blood from the fetus.
- When this happens, the mother’s immune system may start to produce antibodies against the Rh antigen.
- In later pregnancies, these Rh antibodies can cross into the fetus’s blood and attack the fetal red blood cells (RBCs).
- This can be very serious for the fetus, leading to conditions like severe anaemia or jaundice, and can even be life-threatening.
- This condition is known as erythroblastosis fetalis.
- To prevent this issue, doctors can give the mother anti-Rh antibodies right after the birth of her first child.
 Erythroblastosis fetalis
Erythroblastosis fetalisBlood Coagulation
- Blood coagulation or clotting is the mechanism to prevent excessive loss of blood from the body.
- Reddish brown scum formed at the site of a cut is due to clot formed mainly of a network of threads called fibrins in which dead and damaged formed elements of blood are trapped.
- Fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive fibrinogens in the plasma by the enzyme thrombin.
- Thrombins are formed from another inactive substance present in the plasma called prothrombin by an enzyme complex known as thrombokinase.
- Calcium ions play a very important role in clotting.
 Blood Clotting
Blood Clotting
Lymph
Blood Capillaries and Interstitial Fluid
- As blood flows through the capillaries in tissues, some water and small water-soluble substances move out into the spaces between the cells, while larger proteins and most of the formed elements remain in the blood vessels.
- This fluid that is released is called interstitial fluid or tissue fluid. It has a similar mineral distribution to that of plasma.
- The exchange of nutrients, gases, and other substances between the blood and cells occurs through this interstitial fluid.
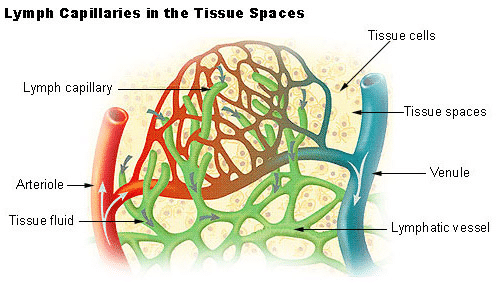
Lymphatic System
- An intricate network of vessels known as the lymphatic system collects this interstitial fluid and drains it back into the major veins.
- The fluid present in the lymphatic system is called lymph. Lymph is a colourless fluid that contains specialised lymphocytes responsible for the body’s immune responses.
- Lymph also plays a crucial role in carrying nutrients, hormones, and other substances.
- Fats are absorbed through the lymph in the lacteals located in the intestinal villi.
Circulatory Pathways
(i) Open Circulatory System: Found in arthropods and molluscs. In this system, blood is pumped by the heart into large vessels that lead to open spaces or body cavities called sinuses.
(ii) Closed Circulatory System: Present in annelids and chordates. Here, blood pumped by the heart is always circulated through a closed network of blood vessels. This system allows for more precise regulation of fluid flow and is considered more advantageous.
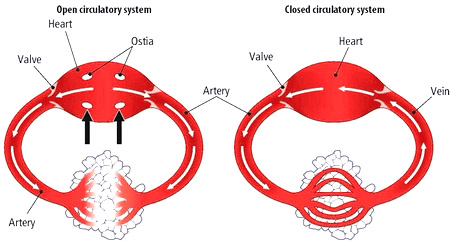 Open and Closed Circulatory System
Open and Closed Circulatory System
Heart Structure in Vertebrates
- All vertebrates have a muscular, chambered heart.
- Fishes have a 2-chambered heart with one atrium and one ventricle.
- Amphibians and reptiles(except for crocodiles) have a 3-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle.
- Crocodiles,birds, and mammals possess a 4-chambered heart with two atria and two ventricles.
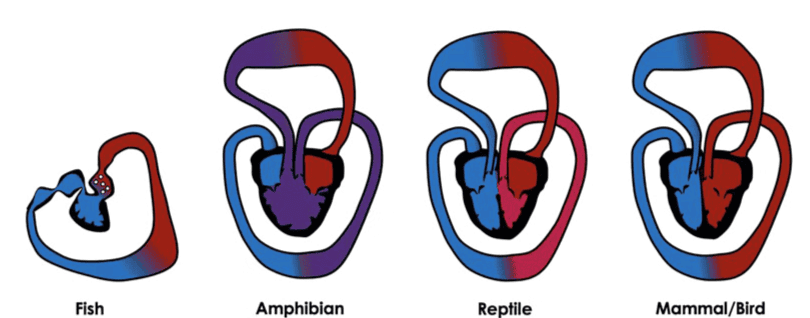 Heart Structure in Vertebrates
Heart Structure in Vertebrates
Circulation in Different Vertebrates
- Fishes: Have a single circulation system where the heart pumps out deoxygenated blood, which is then oxygenated by the gills before being supplied to the body.
- Amphibians and Reptiles: Also have a single circulation system, but the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the gills, lungs, or skin, while the right atrium gets deoxygenated blood from the body. The blood mixes in the single ventricle before being pumped out.
- Birds and Mammals: Have a double circulation system where the left and right atria receive oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, respectively. The ventricles pump the blood out without mixing, creating two separate circulatory pathways.
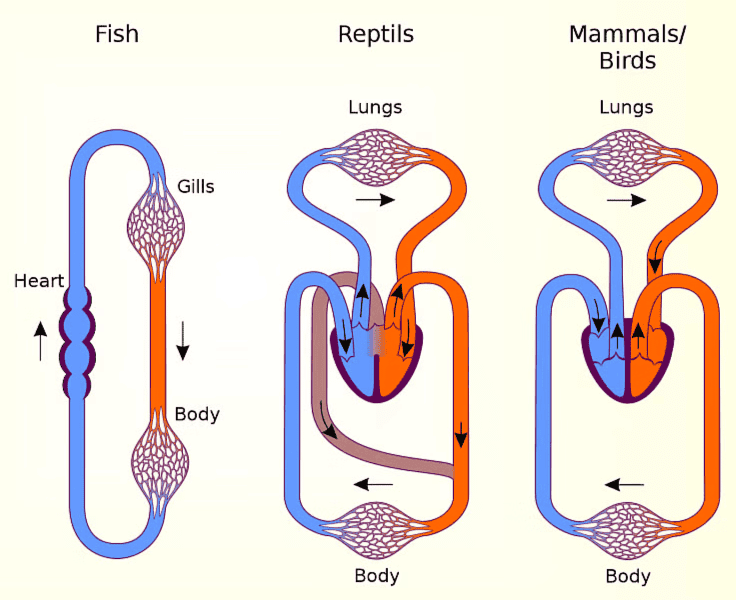 Circulation in Different Vertebrates
Circulation in Different Vertebrates
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Blood Groups, Lymph & Circulatory pathway - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the different blood groups and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. What is the process of blood coagulation? |  |
| 3. What is lymph and what role does it play in the body? |  |
| 4. How does the circulatory pathway function in humans? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to know your blood group? |  |





















