Double Circulation & Disorders of Circulatory System | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Double Circulation |

|
| Regulation of Cardiac Activity |

|
| Disorders of Circulatory System |

|
Introduction
The circulatory system is responsible for the transportation of nutrients and gases like oxygen, for the body and metabolic waste products away from the body. The heart and the lungs play an important role in circulating and purification of blood throughout the body. But is the heart the only organ that helps in purification? Let’s have a brief study on double circulation and the relevant organs involved.
Double Circulation
- The blood flows strictly by a fixed route through Blood Vessels—the arteries and veins.
- Arteries are the main blood vessels that carry and transport oxygenated blood or oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
- Veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins,
- Basically, each artery and vein consists of three layers: an inner lining of squamous endothelium, the tunica intima, a middle layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres, the tunica media, and an external layer of fibrous connective tissue with collagen fibres, the tunica externa. The tunica media is comparatively thin in the veins.
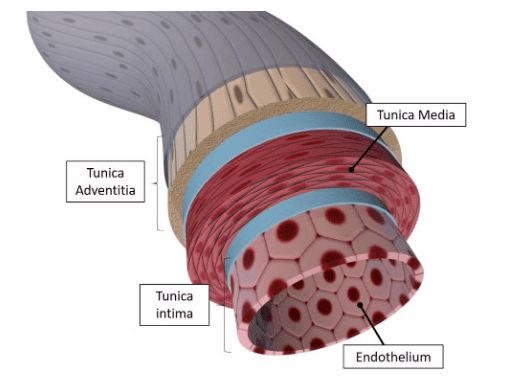 Layers of Arteries and Veins
Layers of Arteries and Veins
- The heart is the key organ for blood circulation and the double circulation is an efficient way of circulation as it provides an effective way of circulation. The main difference is that the blood follows two routes – one for oxygenated blood and the other for deoxygenated blood. Hence, the name “double circulation.” The majority of mammals, including humans utilize a double circulatory system.
The human heart is divided into four chambers:
- Left Atria
- Right Atria
- Left Ventricles
- Right Ventricles
Further, the heart is connected to the lungs through the pulmonary artery and vein. In double circulation, there are two pathways in which the blood flows. They are:
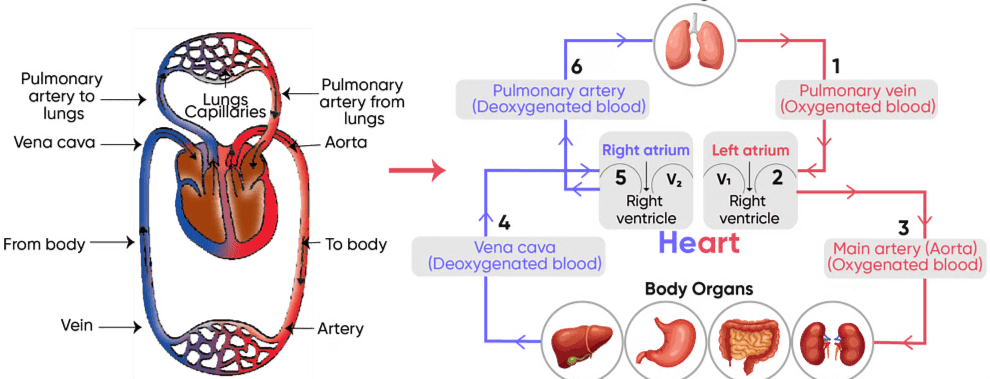
A. Systemic Circulation
Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricles to the tissue capillaries.
- The oxygen-rich blood is transferred to the aorta for circulating into various parts of the body.
- Later, the veins and venules collect the deoxygenated blood – which is rich in carbon dioxide from various parts of the body.
- The deoxygenated blood is pumped back into the superior vena cava and then to the right atrium.
- Once, after receiving the deoxygenated blood, the right atrium carries blood to the right ventricle for pulmonary circulation.
B. Pulmonary Circulation
In the pulmonary circulation, the blood circulation starts from the right atrium to the left atrium. In this pathway:
- The pulmonary artery collects the blood from the right ventricle and carries to lungs for oxygenation.
- Once, after the purification process, the oxygenated blood is pumped back to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein which is carried to the left ventricles.
- The left ventricles pump the oxygenated blood to the aorta for systemic circulation.
Double circulation supports a strict separation of both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Therefore, this circulation ensures that the body always has a dedicated supply of oxygen and also, it improves body efficiency. This is also one of the reasons why mammals can maintain their body temperatures. Apart from the double circulation, a third portal system also exists to improve circulation efficiency.
Regulation of Cardiac Activity
Intrinsic Regulation: The heart's normal activities are regulated intrinsically by specialized muscle tissue known as nodal tissue. This is why the heart is called myogenic.
Role of Neural Centre: A special neural center in the medulla oblongata can moderate cardiac function through the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Sympathetic Nervous System: Neural signals from the sympathetic part of the ANS can increase:
- Heart rate
- Strength of ventricular contraction
- Cardiac output
Parasympathetic Nervous System: Neural signals from the parasympathetic part of the ANS can decrease:
- Heart rate
- Speed of conduction of action potentials
- Cardiac output
Adrenal Medullary Hormones: Hormones from the adrenal medulla can also increase cardiac output.
Disorders of Circulatory System
(i) Hypertension
Hypertension refers to blood pressure that is higher than normal, specifically above 120/80 mm Hg. In this measurement:120 mm Hg represents the systolic (pumping) pressure, while 80 mm Hg indicates the diastolic (resting) pressure.
If an individual's blood pressure consistently measures 140/90 mm Hg or higher, it indicates hypertension. High blood pressure is a serious condition that can lead to heart diseases and adversely affect vital organs such as the brain and kidneys.
(ii) Atherosclerosis/ Coronary Artery Disease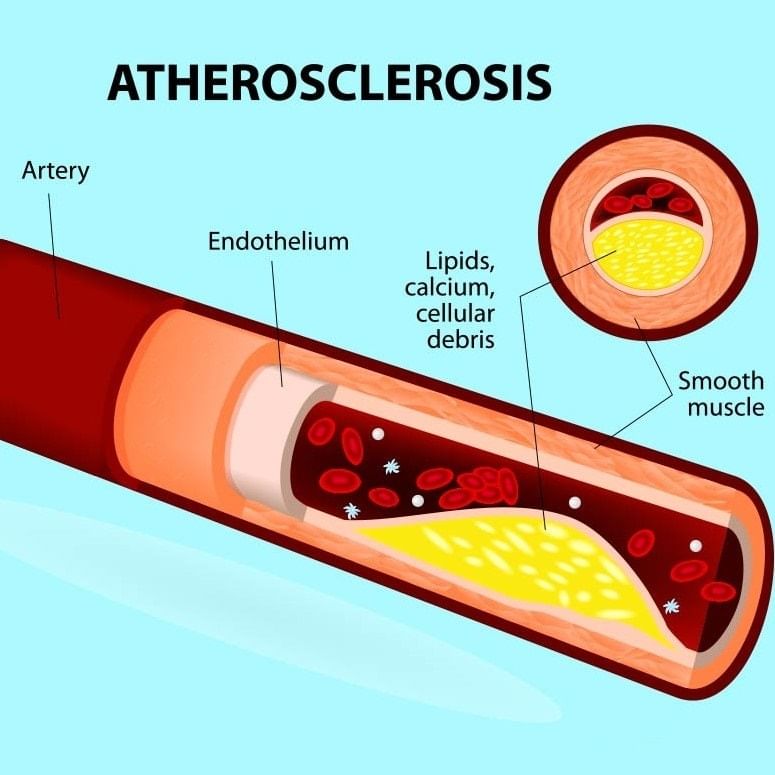
- Coronary Artery Disease, commonly known as atherosclerosis, impacts the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
- This condition is triggered by the buildup of calcium, fat, cholesterol, and fibrous tissues in the arteries, leading to a narrowing of their lumen (the inner open space of the artery).
(iii) Angina
- Angina, also referred to as angina pectoris, is characterized by acute chest pain resulting from insufficient oxygen reaching the heart muscle.
- While angina can affect individuals of any age, it is more prevalent among middle-aged and elderly individuals.
- This condition arises due to factors that impair blood flow to the heart.
(iv) Heart Failure
- Heart failure describes a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body's needs.
- It is sometimes called congestive heart failure because one of the primary symptoms is lung congestion.
- It is important to note that heart failure is not the same as cardiac arrest(when the heart stops beating) or a heart attack(when the heart muscle is suddenly damaged due to inadequate blood supply).
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Double Circulation & Disorders of Circulatory System - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the difference between single and double circulation in the circulatory system? |  |
| 2. How does the heart regulate cardiac activity? |  |
| 3. What are common disorders of the circulatory system? |  |
| 4. How can double circulation benefit mammals and birds compared to single circulation? |  |
| 5. What lifestyle changes can help prevent disorders of the circulatory system? |  |















