Oxidation & Reduction | Science Class 10 PDF Download
What is Oxidation?
We get to hear the terms like oxidation and reduction a lot in CBSE class 12th Chemistry and to be precise, oxidation means gaining oxygen in a chemical reaction We will be looking at oxidation and reduction from two different points of view.
- Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Oxygen transfer
- Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Electron transfer

What is Reduction?
In Chemistry, it is referred to as the loss of oxygen when it is with respect to the oxygen transfer. It is the job of the reducing agent to remove the oxygen from another substance.
Similarly, in the case of hydrogen transfer, it is the gain of hydrogen. That means it is reducing agent’s work to remove oxygen from one substance and hydrogen to it.
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Oxygen transfer
- In early chemistry, oxidation and reduction were terms associated with oxygen.
- Oxidation meant gaining oxygen and Reduction meant losing oxygen.
- The term ‘reduction’ comes from Latin and means ‘-to lead back’.
- Therefore, anything that leads back to the free metal state is referred to as a reduction reaction.
Magnesium undergoes both oxidation and reduction in reactions with different reactants.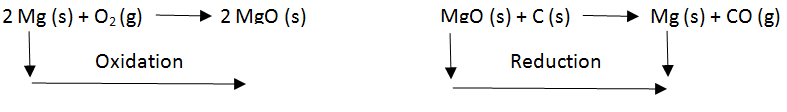
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Electron Transfer
- This is the most commonly used definition of oxidation and reduction and most widely applicable.
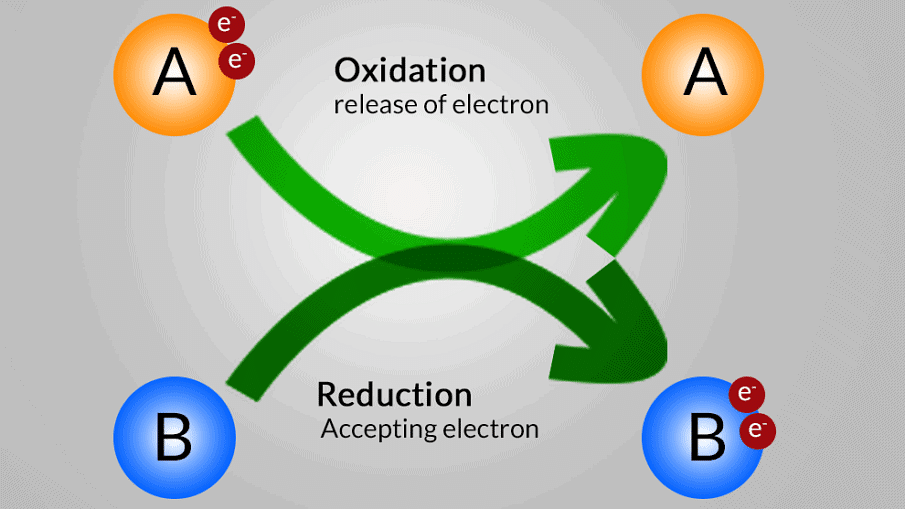
- In this case, Oxidation is the loss of electrons and Reduction is the gain of electrons.
- A very clever mnemonic to remember this concept is oil rig.
OIL RIG
Oxidation is loss Reduction is gain
Oxidation and Reduction reactions are always interlinked. Because electrons are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, oxidation and reduction always occur in pairs, it is impossible to have one without the other. In the below reaction Magnesium gets oxidized by losing two electrons to oxygen which gets reduced by accepting two electrons from magnesium.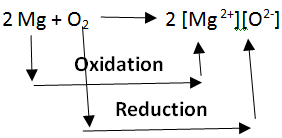
Since oxidation and reduction cannot occur individually, they as a whole are called ‘Redox Reactions’. The reactant that oxidizes the other reactants is called as the Oxidizing agent and reactant that reduces is called Reducing agent. There is quite some confusion about the aspect of whether oxidizing agents accept or give away electrons.
The following steps can help you figure it out.
- An oxidizing agent oxidizes the other reactants
- This must mean that the oxidizing agent is getting reduced
- Oxidation is the loss of electrons (OIL RIG)
- So an oxidizing agent must gain electrons
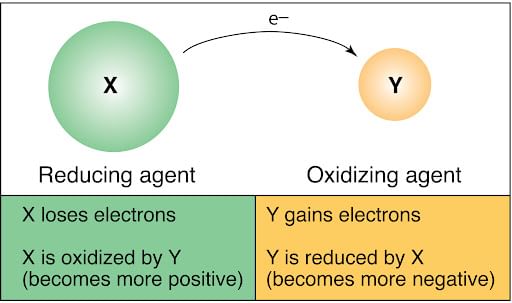 Reducing and Oxidizing agent
Reducing and Oxidizing agent
Common Redox Reactions
The three common redox reactions are discussed below:
1. Combustion reaction – It is a type of redox reaction which occurs between molecular oxygen and compound to form oxygen-containing products.
2C8H18+25O2 → 16CO2(g)+18H2O
2. Disproportionation reaction – It is a type of redox reaction where a single reactant is reduced and oxidized. It is also known as an auto-oxidation reaction.
3ClO−(aq) → ClO3−(aq)+2Cl−(aq)
3. Single replacement reaction – It is a type of redox reaction that involves two elements switching places within a compound. It is also known as a single displacement reaction.
Zn(s)+2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g)
How to Balance Redox Reaction?
- Assign the elements with oxidation numbers.
- Write half-reactions for reduction and oxidation.
- Multiplication of half-reaction number to equalize.
A chemical reaction in which one of the reactants is decreased and the other is oxidized is a reduction / oxidation (redox) reaction. Reduction and oxidation apply to the transition between elements or compounds of electrons which is characterized by the state of oxidation.
As their amount of oxidation increases, an atom is oxidized and reduced when the amount of oxidations reduces. The essential functions of life, such as photosynthesis and breathing, include redox reactions.[3] There are a few more steps involved in balancing a redox reaction than balancing a normal chemical equation. The most critical step is to determine if there is still a redox reaction.
Summary
Originally, the term oxidation was used to describe reactions where an element combines with oxygen. For example, the oxidation of magnesium involves the chemical reaction between magnesium metal and oxygen to form magnesium oxide. The word reduction comes from the “to lead back” sense of the Latin stem. Thus, everything that leads back to magnesium metal in the previously mentioned chemical reaction implies reduction. An example of the reduction of magnesium oxide to magnesium metal is a reaction between magnesium oxide and carbon at 2000 degrees Celsius to form magnesium metal and carbon monoxide.
Due to the changes in oxidation states that occur without the independent transfer of electrons, many reactions in organic chemistry can be classified as redox reactions. For instance, the oxidation state of carbon atoms in the wood increases during the combustion of wood with molecular oxygen, and that of oxygen atoms decreases as carbon dioxide and water are produced. The oxygen atoms are reduced, formally receiving electrons, while the carbon atoms are oxidised, losing electrons. Therefore, oxygen is the oxidising agent and the reducing agent in this reaction is carbon.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Oxidation & Reduction - Science Class 10
| 1. What is oxidation? |  |
| 2. What is reduction? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of oxidation reactions? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of reduction reactions? |  |
| 5. How does oxidation and reduction occur in a redox reaction? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|