Photosynthesis: Early Experiments & Factors affecting | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What Do We Know? |

|
| Early Experiments |

|
| Factors Affecting Photosynthesis |

|
Introduction
- All animals, including humans, rely on plants for food. But where do plants get their food from?
- Green plants actually make or synthesize their own food through a process called photosynthesis. This is why they are called autotrophs. Autotrophic nutrition is found only in plants, while all other organisms that depend on green plants for food are known as heterotrophs.
- Photosynthesis is a process where green plants use light energy to create organic compounds. This process is crucial because it provides the primary source of food for all living beings on Earth and is also responsible for releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
- Without oxygen, life as we know it would be impossible. We will explore the structure of the photosynthetic machinery and the various reactions that convert light energy into chemical energy.
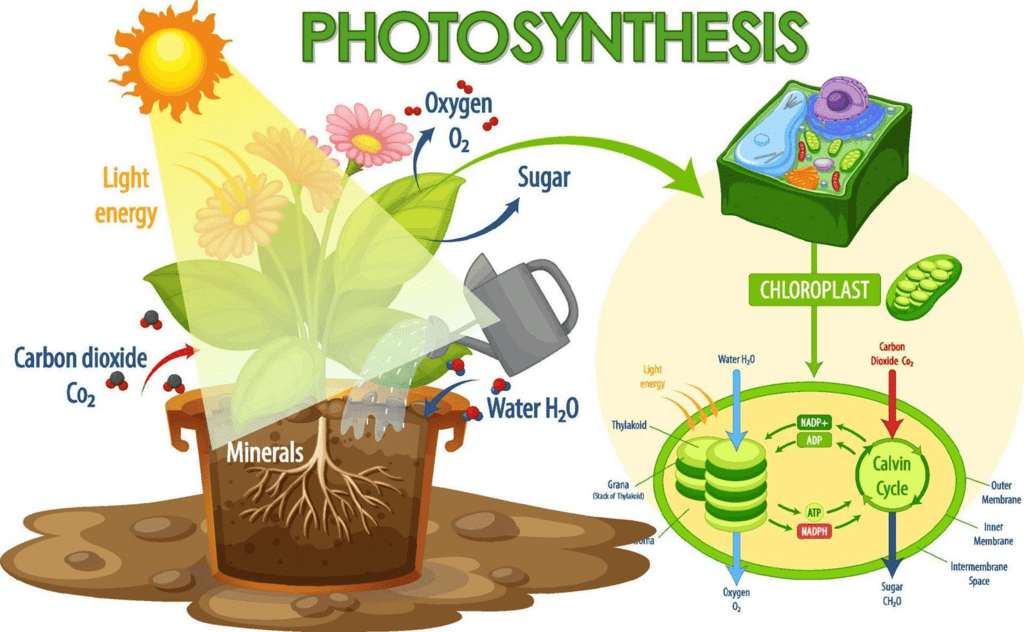
What Do We Know?
Photosynthesis is a process that needs certain things to happen, like chlorophyll(the green pigment in leaves),light, and carbon dioxide (CO2). Let's look at some simple experiments that show what we know about photosynthesis.
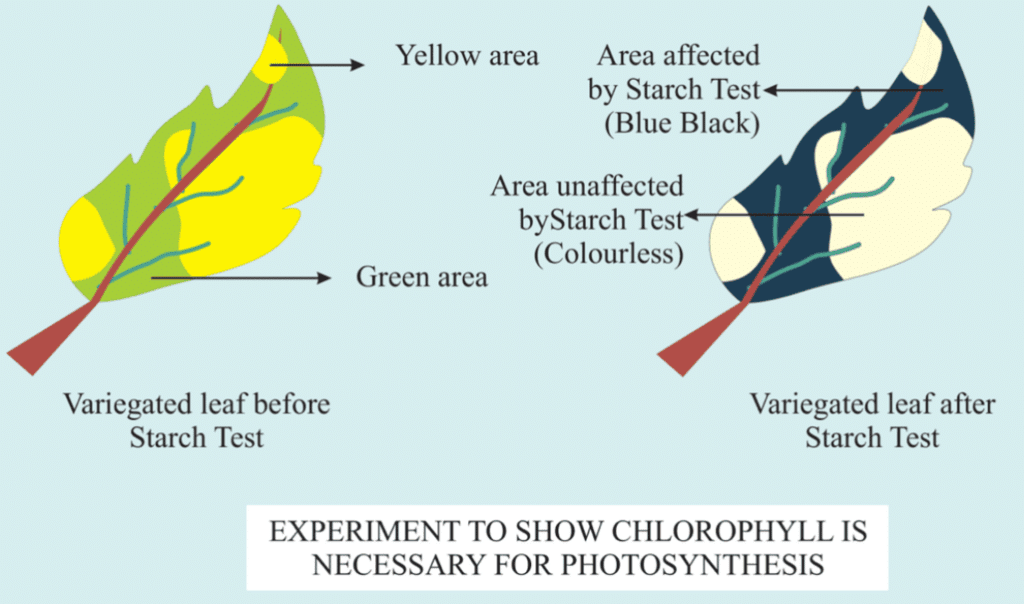
Starch Formation in Leaves: A few of you might have done an experiment where you checked for starch in two leaves: one that was partly green and one that was covered with black paper. When these leaves were tested for starch after being in the light, it became clear that photosynthesis only happened in the green parts of the leaves when there was light.
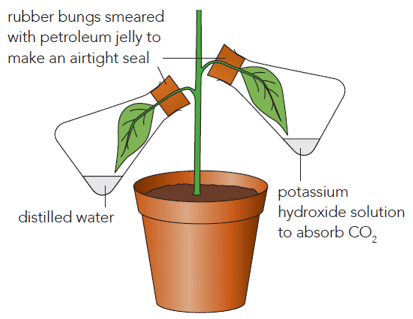
Testing for Carbon Dioxide: Another experiment involved taking a leaf and putting part of it in a test tube with potassium hydroxide (KOH) soaked cotton, which absorbs CO2. The other part of the leaf was left open to the air. When this setup was placed in the light for a while and then tested for starch, the exposed part of the leaf had starch while the part in the tube did not. This showed that carbon dioxide (CO2) is necessary for photosynthesis.
Early Experiments
Early experiments in the 18th century helped scientists understand the role of air and light in photosynthesis.
- In 1770, Joseph Priestley conducted experiments showing that plants release something important into the air.
- Jan Ingenhousz later discovered that sunlight is essential for this process.
Priestley’s Experiment
Priestley conducted an experiment using a bell jar, a candle, a mouse, and a mint plant.
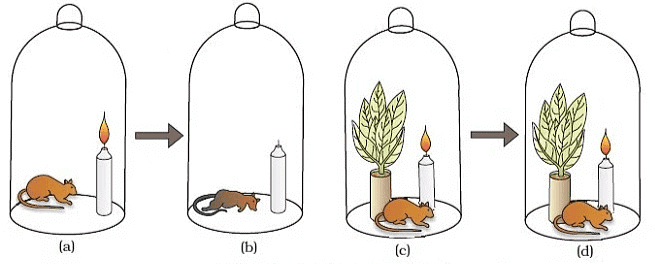 Priestly's Experiment
Priestly's Experiment
Steps of the Experiment:
- A candle was placed inside a bell jar and lit.
- As the candle burned, it consumed oxygen and produced carbon dioxide, causing the air inside the jar to become unfit for breathing.
- A mouse was then placed inside the jar. Without enough oxygen, the mouse would suffocate.
- However, when a mint plant was added to the jar, the plant restored the air quality.
- The candle continued to burn, and the mouse survived because the plant released oxygen.
Priestley’s Conclusion:
- Priestley concluded that plants restore the air by releasing oxygen, which is essential for the survival of animals and for combustion.
- He proposed that plants play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere.
Ingenhousz’s Experiment
Jan Ingenhousz built on Priestley’s work and conducted experiments with aquatic plants to demonstrate the importance of sunlight in photosynthesis.
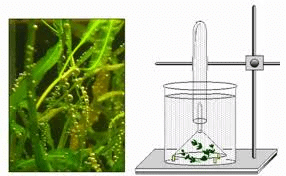 Ingenhousz's Experiment Setup
Ingenhousz's Experiment Setup
Steps of Ingenhousz’s Experiment:
- He placed an aquatic plant in water and exposed it to bright sunlight.
- He observed that tiny bubbles formed around the green parts of the plant when it was in the light.
- When the plant was kept in the dark, no bubbles formed.
Ingenhousz’s Conclusion:
- Ingenhousz concluded that the bubbles were oxygen gas, released by the green parts of the plant.
- This showed that only the green parts of plants, when exposed to sunlight, can produce and release oxygen.
Significance of the Experiments
- Priestley’s and Ingenhousz’s experiments were crucial in understanding that plants play a vital role in producing oxygen and purifying the air.
- They laid the foundation for the discovery of photosynthesis, where plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
Priestley and Ingenhousz’s experiments were foundational in understanding the role of plants in producing oxygen and purifying the air, leading to the discovery of photosynthesis where plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
The process of photosynthesis in plants was not fully understood until the contributions of scientists like Julius von Sachs and Cornelius van Niel in the 19th century.
Julius von Sachs and the Discovery of Photosynthesis
In 1854, Julius von Sachs conducted experiments that demonstrated plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. He found that this glucose is typically stored as starch.- Sachs also discovered that the green pigment in plants, known as chlorophyll, is found in special structures within plant cells called chloroplasts.
- He concluded that photosynthesis mainly occurs in the green parts of plants, where glucose is produced and stored as starch.
Experiments by T.W. Engelmann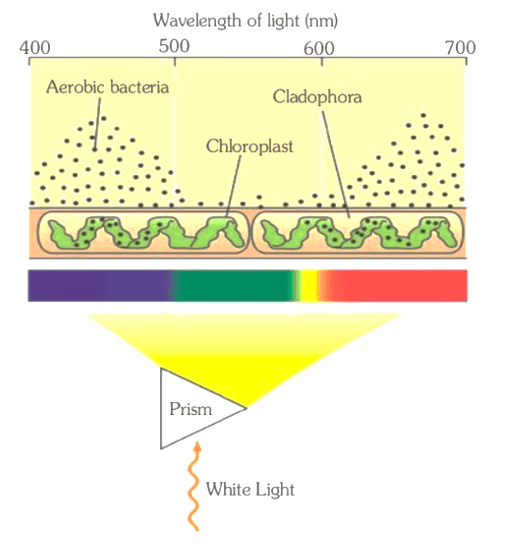
- T.W. Engelmann conducted experiments using a prism to split light into its different colors and then illuminated a green alga called Cladophora.
- He placed the alga in a suspension of aerobic bacteria to observe where oxygen (O2) was being produced during photosynthesis.
- Engelmann noticed that the bacteria gathered mainly in the blue and red light regions, indicating these colors were most effective for photosynthesis.
- This experiment helped establish the first action spectrum of photosynthesis, showing which light wavelengths are most effective for the process.
Understanding Photosynthesis
- By the mid-1800s, it was clear that plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into carbohydrates like glucose.
- The overall process of photosynthesis in oxygen-evolving organisms was represented by the equation:
- CO2 + H2O + Light → [CH2O] + O2
- Where [CH2O] represents a carbohydrate, such as glucose.
Cornelius van Niel's Contribution
- Cornelius van Niel, a microbiologist, significantly advanced the understanding of photosynthesis by studying purple and green bacteria.
- He proposed that photosynthesis is a light-dependent reaction where hydrogen from an oxidizable compound reduces carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
- This process can be simplified as:
- H2A + CO2 + Light → CH2O + H2A + O2
- In green plants, water (H2O) is the hydrogen donor and is oxidized to oxygen (O2).
- Some organisms, like purple and green sulfur bacteria, do not release oxygen during photosynthesis. Instead, they use hydrogen sulfide (H2S) as the hydrogen donor, producing sulfur or sulfate instead of oxygen.
- Van Niel's work led to the understanding that the oxygen released by green plants during photosynthesis comes from water, not carbon dioxide. This was later confirmed using radioisotopic techniques.
The Overall Equation of Photosynthesis
- The correct equation representing the overall process of photosynthesis is:
- 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
- Where C6H12O6 represents glucose, and the oxygen released comes from water.
- It is important to note that this equation describes a complex, multistep process known as photosynthesis, not a single reaction.
Why Twelve Molecules of Water are Used
- The use of twelve molecules of water in the overall equation of photosynthesis reflects the fact that water is both a reactant and a product in the process.
- During photosynthesis, six molecules of water are used to produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
- However, in the process of converting water into glucose and oxygen, additional water molecules are produced as byproducts.
- Thus, the net balance of water molecules in the reaction accounts for the water used and produced, leading to the use of twelve water molecules in the equation.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is influenced by various factors, both internal to the plant and external from the environment.
1. Internal Factors:- Number, size, age, and orientation of leaves: These determine how much sunlight the plant can capture.
- Mesophyll cells and chloroplasts: Their quantity and health affect how efficiently photosynthesis occurs.
- Internal CO2 concentration: Higher levels can enhance photosynthesis.
- Amount of chlorophyll: More chlorophyll means better light absorption.
- Sunlight: Essential for providing the energy needed for photosynthesis.
- Temperature: Affects the speed of biochemical reactions involved in photosynthesis.
- CO2 concentration: Availability of carbon dioxide is crucial as it is one of the raw materials.
- Water: Necessary for the photosynthetic process and for maintaining plant health.
All these factors work together to affect the rate of photosynthesis, but usually, one factor is the most limiting at any given time. Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors: This principle states that when multiple factors influence a process, the rate is determined by the factor that is closest to its minimum requirement. For example, even with sufficient light and CO2, if the temperature is too low, photosynthesis will not occur effectively.
1. Light: Quality, Intensity, and Duration
- Photosynthesis is influenced by light quality, light intensity, and the duration of light exposure.
- At low light intensities, there is a linear relationship between incident light and CO2 fixation rates.
- As light intensity increases, there comes a point where the rate of photosynthesis does not increase further because other factors become limiting.
- Interestingly, light saturation occurs at only 10 per cent of full sunlight. This means that, except for plants in shady areas or dense forests, light is rarely a limiting factor for photosynthesis in nature.
- However, if incident light increases beyond a certain point, it can lead to the breakdown of chlorophyll and a decrease in photosynthesis.
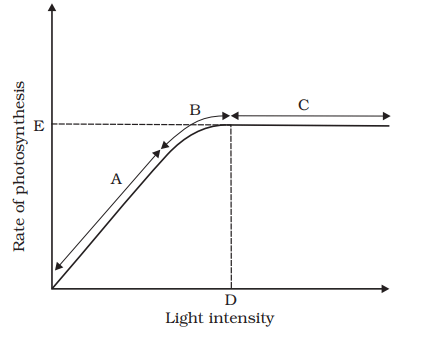 Graph of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
Graph of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
2. Carbon Dioxide
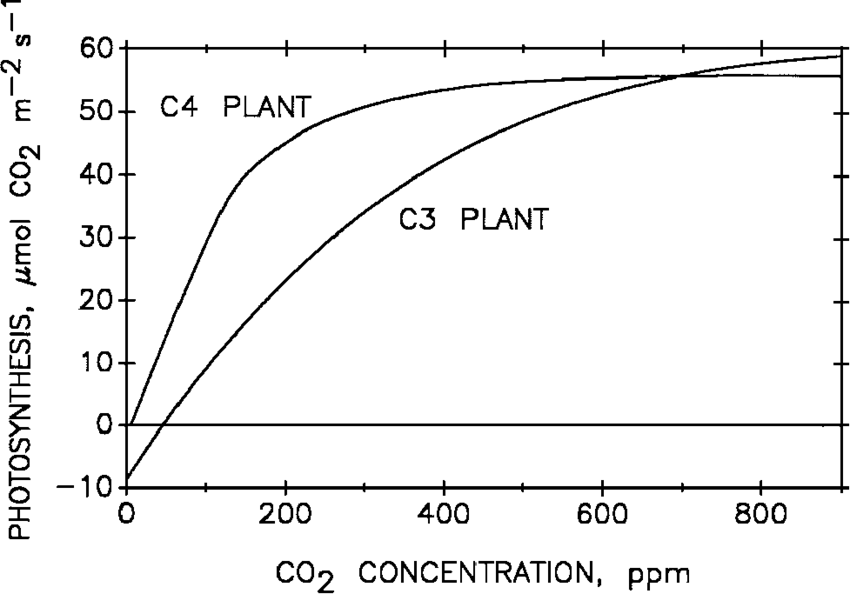
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a crucial factor for photosynthesis, but its concentration in the atmosphere is very low, ranging from 0.03 to 0.04 percent.
Increasing CO2 concentration to about 0.05 percent can enhance CO2 fixation rates. However, levels beyond this can be harmful over time.
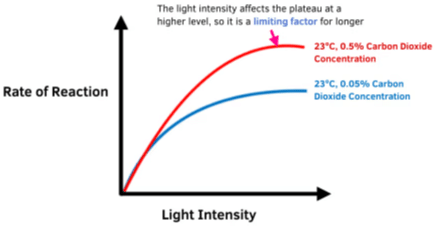
- At low light conditions, neither C3 nor C4 plants benefit from high CO2 levels.
- At high light intensities, both C3 and C4 plants show increased rates of photosynthesis.
C4 plants reach their saturation point at around 360 µL/L of CO2, while C3 plants continue to respond to increased CO2 levels, reaching saturation only above 450 µL/L.
This means that current CO2 levels are limiting for C3 plants.
C3 plants can increase their photosynthesis rates and productivity with higher CO2concentrations. This principle is used in greenhouse cultivation of crops like tomatoes and bell peppers, where they are grown in CO2-enriched environments to boost yields.
3. Temperature
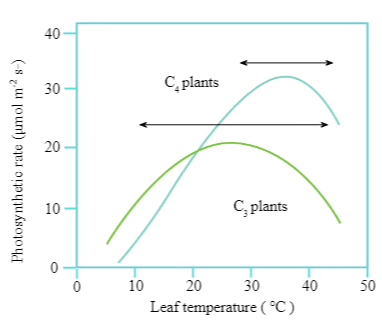
- Dark Reactions: These are enzymatic processes and are controlled by temperature. They are more sensitive to temperature changes compared to light reactions.
- Light Reactions: While also affected by temperature, these reactions are impacted to a lesser extent than dark reactions.
- C3 Plants: These plants have a lower temperature optimum for photosynthesis. They do not respond as well to higher temperatures.
- C4 Plants: These plants thrive at higher temperatures and exhibit a higher rate of photosynthesis in warm conditions.
- Temperature Optimum: The ideal temperature for photosynthesis varies among different plants and is influenced by their habitat. Tropical plants, for example, have a higher temperature optimum compared to plants adapted to temperate climates.
4. Water
- Water is a reactant in the light reaction of photosynthesis, but its impact is more about how it affects the plant rather than directly influencing the process.
- When plants experience water stress, the stomata (tiny openings on leaves) close. This closure reduces the availability of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is essential for photosynthesis.
- Additionally, water stress causes leaves to wilt, decreasing their surface area and metabolic activity. This further hampers the plant's ability to carry out photosynthesis effectively.
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Photosynthesis: Early Experiments & Factors affecting - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis? |  |
| 2. What were some key early experiments that contributed to our understanding of photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. How do light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis? |  |
| 4. What role does chlorophyll play in photosynthesis? |  |
| 5. Why is photosynthesis important for life on Earth? |  |
















