NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Fibre to Fabric | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 5 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Paheli wants to present her friend a gift made of plant-fibre. Which out of the following will she select?
(a) Jute bag
(b) Woollen shawl
(c) Silk saree
(d) Nylon scarf
Ans: a
Solution: Jute is a natural plant fibre which is long, soft, shiny that can be spun into coarse strong threads. It is obtained from the stems of jute plants (Corchorus).
Wool is obtained from the fur of animals like sheep, yak etc.
Silk is obtained from silkworms.
Nylon is a man-made fibre which is synthesized using chemicals at factories.
 Jute YarnQ.2. Which statement out of the following is incorrect?
Jute YarnQ.2. Which statement out of the following is incorrect?
(a) Use of charkha was popularized by Mahatma Gandhi as a part of the Independence Movement.
(b) In India, jute is mainly grown in Kerala and Punjab.
(c) To make fabric, the fibres are first converted into yarns.
(d) Sufi saint Kabir was a weaver.
Ans: b
Solution: The correct answer is: In India, jute is mainly grown in Bihar, West Bengal, Assam and Andhra Pradesh.
Q.3. Which of the following materials did people use in ancient times for making clothes
(i) Leaves of trees
(ii) Newspaper
(iii) Metal foils
(iv) Animal skins and furs
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: d
Solution: In ancient times people used to bark and leaves of trees, skin and fur of animals to cover their bodies.
In those times newspapers and metal foils were not available.
Q.4. Which of the following is not a natural fibre?
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Nylon
(d) Flax
Ans: c
Solution: Nylon is a synthetic fibre manufactured using chemicals at factories.
Whereas cotton, jute and flax are natural fibres obtained from plants.
Q.5. Which set of substances is not used for making fibres?
(a) Silk, chemicals
(b) Yak hair, camel hair
(c) Husk, bones
(d) Flax, wool
Ans: c
Q.6. Boojho went to a cloth shop. There he found a fabric which was smooth to touch, had vibrant colour and shine. The fabric could be
(a) cotton
(b) wool
(c) silk
(d) jute.
Ans: c
Solution: Silk is obtained from the cocoon of the silkworm. Silk fabric is very smooth to touch and has a vibrant colour and shine.
Q.7. Which part of the jute plant is used for getting jute fibre?
(a) Flower
(b) Stem
(c) Fruit
(d) Leaf
Ans: b
Solution: Jute is a natural plant fibre which is long, soft, shiny that can be spun into coarse strong threads. It is obtained from the stems of jute plants (Corchorus).
Q.8. Yarn is woven to get fabric using
(a) charkha
(b) spinning machines
(c) looms
(d) knitting needles.
Ans: c
Solution: The weaving of yarn is done on looms. Looms are either hand operated or power operated.
Q.9. Beera is a farmer. His field has black soil and the climate is warm. Which fibre yielding plant should he grow in his field?
(a) Jute
(b) Cotton
(c) Coconut
(d) Wool
Ans: b
Solution: Places having black soil and the warm climatic condition is good to yield cotton plants.
Q.10. The correct sequence to get cloth is
(a) fibre → fabric → yarn
(b) fibre → yarn → fabric
(c) fabric → yarn → fibre
(d) yarn → fibre → fabric.
Ans: b
Solution: Three processes such as spinning and weaving or knitting are involved to convert fibre into the fabric.
Spinning is the method of making yarn from fibres.
Weaving and knitting are the two methods to convert yarn into fabric.
Weaving is the process of arranging two sets of yarn together to make a fabric.
Whereas in knitting, a single yarn is used to make a fabric.
Q.11. Boojho wants to make yarn from fibre at home. Which of the following will he use to carry out the task?
(a) Powerloom
(b) Handloom
(c) Charkha
(d) Knitting needles
Ans: c
Solution: Spinning is the method of making yarn from fibres. Charkha is a simple hand-operated device used for spinning.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.12. Yarn, fabric and fibres are related to each other. Show the relationship by filling the blanks in the following sentence.
The fabric of cotton saree is made by weaving cotton_______ which in turn is made by spinning thin cotton ______.
Ans: yarn, fibres
Q.13. Some terms related to fabrics are jumbled up and given below. Write them in their correct form.
(a) onttoc
(b) sinnping
(c) vingwea
(d) bisref
Ans: (a) Cotton
(b) Spinning
(c) Weaving
(d) Fibres
Q.14. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, correct them.
(a) Silk is a plant fibre.
(b) Jute is obtained from the leaves of a plant.
(c) Weaving is a process of arranging two sets of yarn together.
(d) Cotton yarn on burning gives an odour similar to that of a burning paper.
Ans: (a) False. Since silk is an animal fibre obtained from silkworms.
(b) False. Since jute is obtained from the stem of a plant.
(c) True
(d) True
Q.15. The following is an answer given by Boojho to a question asked by his teacher- “Cotton, wool, silk and jute are classified as natural fibres whereas nylon and polyester are classified as synthetic fibres”. Can you tell what question the teacher has asked?
Ans: A teacher must have asked the students to classify the following fibres into natural and synthetic fibres.
Jute, Silk, Nylon, Cotton, Wool, Polyester.
Q.16. Once, Paheli visited a tailor shop and brought home some cuttings of fabric to study their properties. She took two pieces and found that one of the pieces were shrinking when it was burnt with a candle. However the other did not shrink on burning. Can you help her to find out which of the two was a cotton fabric and which a silk fabric?
Ans: On burning, silk fabric shrinks due to the presence of protein whereas cotton fabric does not shrink.
Q.17. One way of making fabric from yarn is weaving, what is the other
Ans: Another way of making fabric from yarn is Knitting.
Short Answer Questions:
Q.18. Boojho with perfect eyesight was finding it difficult to pass a thread through the eye of a needle. What can be the possible reason for this?
Ans: May be due to the fault in the thread, the end of the thread was separated into a few thin strands or the thread was quite thick. Hence Boojho found it difficult to pass a thread through the eye of a needle.
Q.19. In ancient times stitching was not known. People used to simply drape the fabrics around different parts of their body. Even today a number of unstitched fabrics are used by both men and women. Can you give four such examples of clothes?
Ans: Saree, dupatta, dhoti, lungi, turban, etc. are unstitched fabrics used by both men and women.
Q.20. Match the articles given in column I with the articles of column II.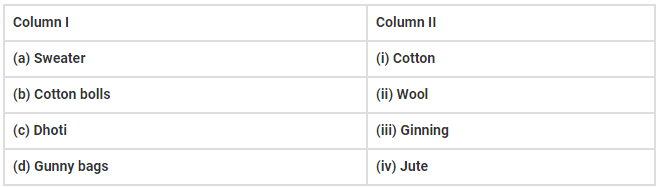
Ans: The correct match is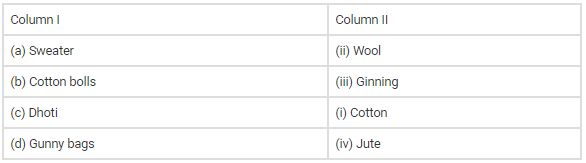
Q.21. Fill in the blanks to complete the life story of cotton fibre.
My parents, cotton plants were grown in ______ soil and ______ climate. The plants bore fruits called ______. I, the cotton fibre was separated from seeds in the cotton bolls by the process of______. Other cotton fibres and myself were made into yarn by the process of ______. The yarn was ______ to give beautiful colours and then to get cotton fabric.
Ans: (i) black
(ii) warm
(iii) cotton bolls
(iv) ginning
(v) spinning
(vi) dyed
(vii) woven
Q.22. Match the terms given in column I with the statements given in column II.
Ans: The correct match is
Q.23. Fill in the names of useful items made from jute fibres in Fig. 3.1. One such example is given.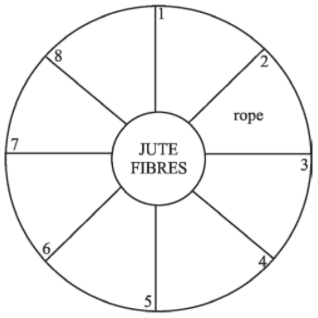
Ans: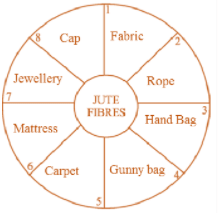
Long Answer Questions
Q.24. A cotton shirt, before it reaches you, completes a long journey. Elaborate on this journey starting from cotton bolls.
Ans: The journey of a cotton shirt starting from cotton bolls is as follows:
- Picking: The seeds covered with cotton fibres are handpicked from the cotton bolls.
- Ginning: Seeds are separated from fibres by combing is called ginning. Now a day’s ginning is done with the help of machines.
- Spinning: Here, fibres are drawn out from cotton wool and twisted. This brings the fibres together to make a strong yarn. With the help of hand-operated devices spinning is done.
- Weaving and knitting: The two methods of converting cotton yarn into the cotton fabric is by weaving and knitting. A cotton shirt is usually made by weaving so in weaving, two sets of yarns are arranged together to make a fabric.
- Stitching: The cotton fabric is then stitched into the cotton shirt.
Q.25. Describe the two main processes of making fabric from yarn.
Ans: Two main processes of making fabric from yarn are weaving and knitting.
- Weaving: Weaving is the process of arranging two sets of yarns together to make a fabric.
- Knitting: In knitting a single yarn which is used to make a piece of fabric.
|
26 videos|28 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Fibre to Fabric - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 5
| 1. What is fibre to fabric? |  |
| 2. How are natural fibres obtained for fabric production? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between natural and synthetic fibres? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of spinning in the fibre to fabric process? |  |
| 5. How are fabrics made from yarns? |  |
















