Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Notes > Physical Chemistry > Homonuclear diatomic molecules & their Electronic Configuration
Homonuclear diatomic molecules & their Electronic Configuration | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
What are Diatomic molecules?
Molecules formed upon the bonding of two same elements are known as homonuclear diatomic molecules. For example dihydrogen (H2), dinitrogen (N2), etc. In this article, we will study the formation of these diatomic molecules, their stability, and other characteristics.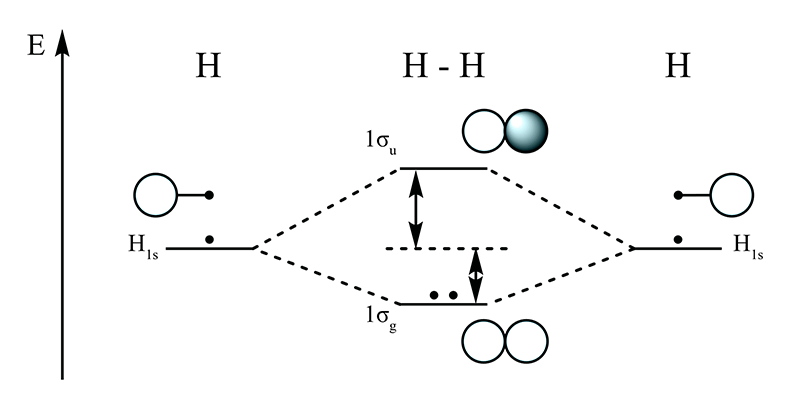
Some common diatomic molecules
- Hydrogen molecule (H2): Dihydrogen molecule belongs to the family of diatomic molecules, which consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to each other by a covalent bond. According to the atomic number of hydrogen, it has only one electron in its 1s orbital. The electronic configuration of H2 molecule is given as:
H2: (σ1s)2
Bond order = = = 1
Due to the absence of unpaired electrons in the hydrogen molecule, it is diamagnetic in nature. - Lithium molecule (Li2): Lithium molecule belongs to the family of diatomic molecules, which consists of two lithium atoms, bonded to each other by a covalent bond. The electronic configuration of Li2 molecule is given as:
Li2: (σ1s)2 (σ*1s)2 (σ2s)2
Bond order == 1
Thus the Li2 molecule is stable and is diamagnetic in nature due to the absence of unpaired electrons. - Carbon molecule (C2): Carbon molecule belongs to the family of diatomic molecules, which consists of two carbon atoms, bonded to each other by a covalent bond. The electronic configuration of the Carbon molecule is given as,
C2 :(σ1s)2 (σ*1s)2(σ2s)2 (σ *2s)2 (π2p2x= π 2p2y)
Bond order = = 2
Due to the absence of unpaired electrons, C2 is diamagnetic in nature. Furthermore, due to the presence of four electrons in pi bonding orbitals, the double bond in C2 consists of both pi bonds. - Oxygen molecule (O2): Oxygen molecule belongs to the family of diatomic molecules, which consists of two oxygen atoms, bonded to each other by a covalent bond. The electronic configuration of the Oxygen molecule is given as,
O2: (σ1s)2 (σ*1s)2 (σ2s)2 (σ *2s)2 (σ2pz) 2 (π2p2x= π 2p2y) (π*2p1x= π*2p1y)
Bond order = = 2.
Due to the presence of one unpaired electron, O2molecule should be paramagnetic. - Helium molecule (He2): According to the atomic number of helium, it has two electrons in 1s.The electronic configuration of the helium molecule according to molecular orbital theory is given as:
He2: (σ1s)2 (σ*1s)2
Bond order == 0.
Thus, He2 molecule is unstable and does not exist.
The document Homonuclear diatomic molecules & their Electronic Configuration | Physical Chemistry is a part of the Chemistry Course Physical Chemistry.
All you need of Chemistry at this link: Chemistry
|
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Homonuclear diatomic molecules & their Electronic Configuration - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What are diatomic molecules? |  |
Ans. Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of two atoms of the same element bonded together. Examples of diatomic molecules include oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and hydrogen (H2).
| 2. What are homonuclear diatomic molecules? |  |
Ans. Homonuclear diatomic molecules are a specific type of diatomic molecule where both atoms in the molecule are the same element. For example, oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2) are homonuclear diatomic molecules.
| 3. What is the electronic configuration of diatomic molecules? |  |
Ans. The electronic configuration of diatomic molecules depends on the elements involved. Each atom in the molecule contributes its own electron configuration. For example, the electronic configuration of oxygen (O2) is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4.
| 4. Can diatomic molecules have different electronic configurations for each atom? |  |
Ans. No, diatomic molecules consist of the same element bonded together, so both atoms in the molecule will have the same electronic configuration. The electrons are shared between the atoms.
| 5. How are diatomic molecules formed? |  |
Ans. Diatomic molecules are formed through a process called covalent bonding, where atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The shared electrons create a strong bond between the two atoms, forming a diatomic molecule.
Related Searches
















