Synthesis, Reactivity and Properties of Furan | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
Furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly volatile liquid with a boiling point close to room temperature. It is soluble in common organic solvents, including alcohol, ether, and acetone, and is slightly soluble in water. Its odor is "strong, ethereal; chloroform-like".It is toxic and may be carcinogenic in humans. Furan is used as a starting point for other speciality chemicals.
Synthesis
Industrially, furan is manufactured by the palladium-catalyzed decarbonylation of furfural, or by the copper-catalyzed oxidation of 1,3-butadiene: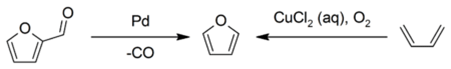
In the laboratory, furan can be obtained from furfural by oxidation to 2-furoic acid, followed by decarboxylation.It can also be prepared directly by thermal decomposition of pentose-containing materials, and cellulosic solids, especially pine wood.
One of the simplest synthesis methods for furans is the reaction of 1,4-diketones with phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) in the Paal–Knorr synthesis.
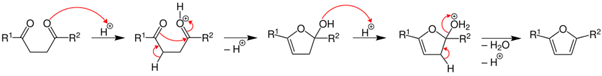
Paal- Knorr Synthesis
The acid catalyzed furan synthesis proceeds by protonation of one carbonyl which is attacked by the forming enol of the other carbonyl. Dehydration of the hemiacetal gives the resultant furan
Reactions & Properties of Furan
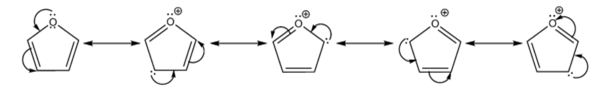
Furan is aromatic because one of the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom is delocalized into the ring, creating a 4n + 2 aromatic system (see Hückel's rule) similar to benzene. Because of the aromaticity, the molecule is flat and lacks discrete double bonds. The other lone pair of electrons of the oxygen atom extends in the plane of the flat ring system. The sp2 hybridization is to allow one of the lone pairs of oxygen to reside in a p orbital and thus allow it to interact within the π system.
Due to its aromaticity, furan's behavior is quite dissimilar to that of the more typical heterocyclic ethers such as tetrahydrofuran.
- It is considerably more reactive than benzene in electrophilic substitution reactions, due to the electron-donating effects of the oxygen heteroatom. Examination of the resonance contributors shows the increased electron density of the ring, leading to increased rates of electrophilic substitution.
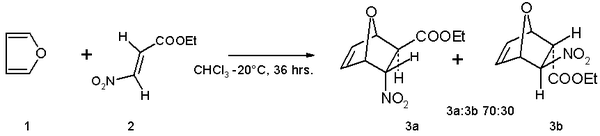
- Furan serves as a diene in Diels–Alder reactions with electron-deficient dienophiles such as ethyl (E)-3-nitroacrylate.The reaction product is a mixture of isomers with preference for the endo isomer:
Diels-Alder reaction of furan with arynes provides corresponding derivatives of dihydronaphthalenes, which are useful intermediates in synthesis of other polycyclic aromatic compounds.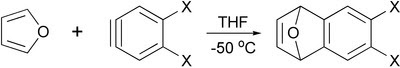
- Hydrogenation of furans sequentially affords dihydrofurans and tetrahydrofurans.
- In the Achmatowicz reaction, furans are converted to dihydropyran compounds.
- Pyrrole can be prepared industrially by reacting furan and ammonia in the presence of solid acid catalysts, such as SiO2 and Al2O3.
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Synthesis, Reactivity and Properties of Furan - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What is the synthesis of furan? |  |
| 2. What is the reactivity of furan? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of furan? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of furan? |  |
| 5. Is furan toxic? |  |